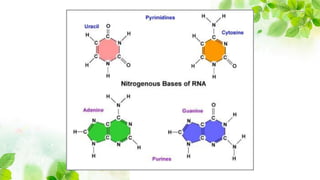
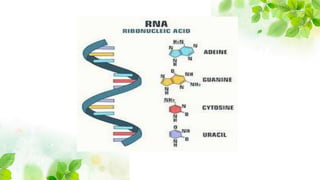
This document discusses different types of RNA, including messenger RNA, transfer RNA, and ribosomal RNA. It describes:
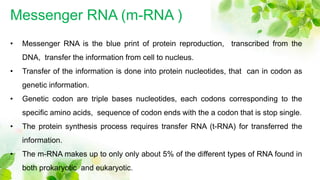
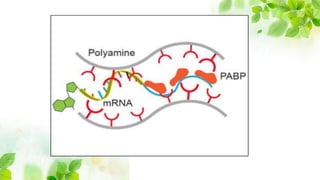
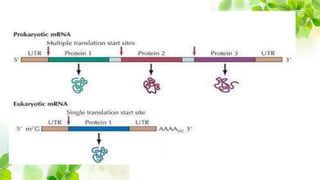
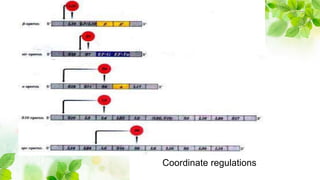
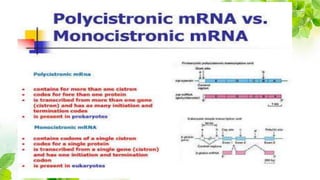
1) Messenger RNA carries genetic information from DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm for protein production. Messenger RNA can be polycistronic, containing information for multiple proteins, or monocistronic, containing information for a single protein.
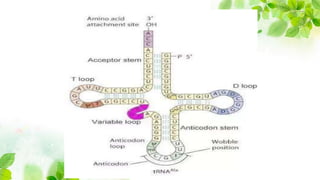
2) Transfer RNA transports amino acids to the ribosome during protein translation based on the messenger RNA code. It has a cloverleaf secondary structure and L-shape tertiary structure.
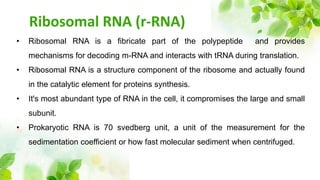
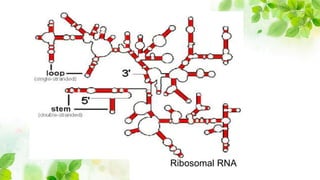
3) Ribosomal RNA is a structural component of ribosomes and facilitates protein synthesis by decoding messenger RNA and interacting with transfer RNA. It comprises the large and