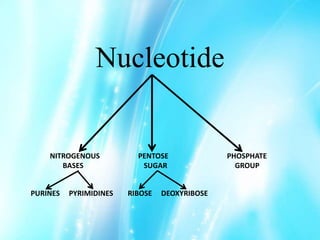
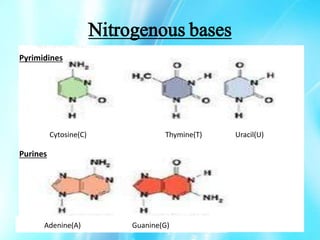
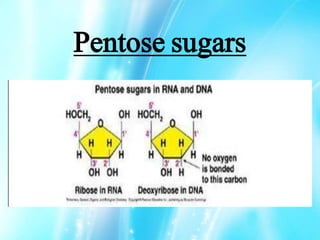
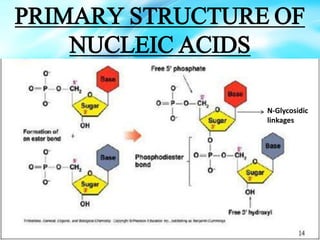
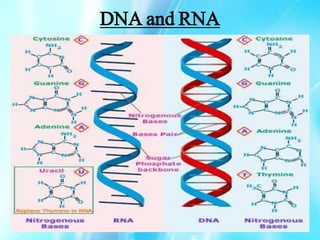
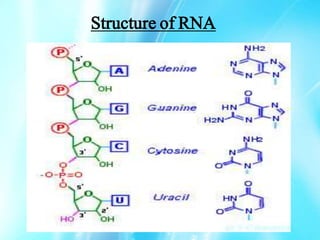
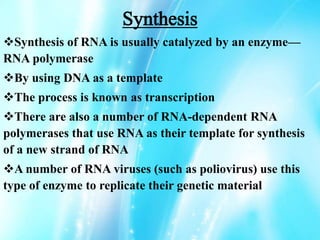
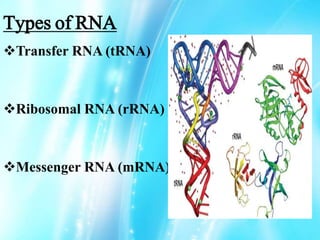
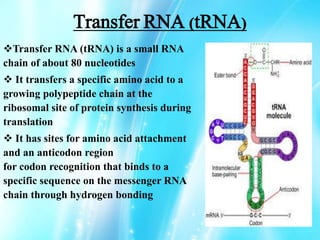
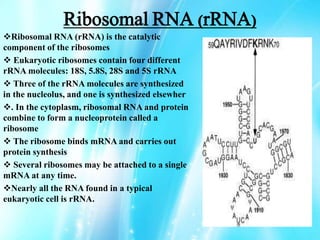
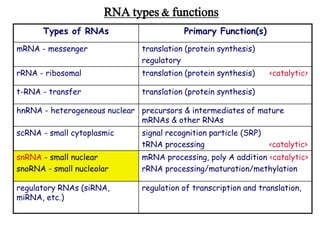
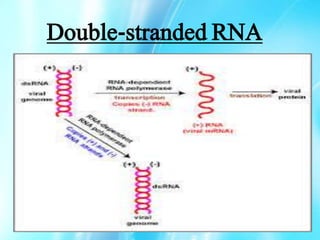
Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides that include DNA and RNA, which are found in living systems. RNA is one of the major biological macromolecules essential for life, along with DNA and proteins. There are different types of RNA including mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA that have primary functions like translation, protein synthesis, and mRNA processing. RNA can also carry genetic information like DNA and some viruses have RNA genomes.