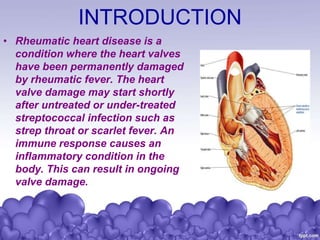
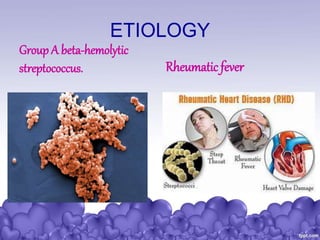
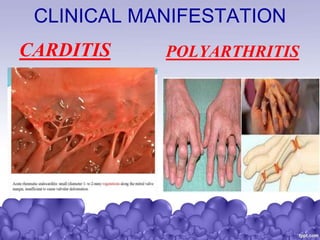
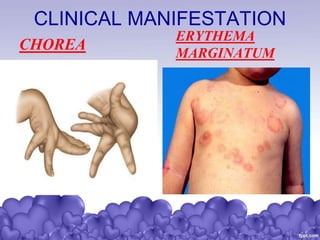
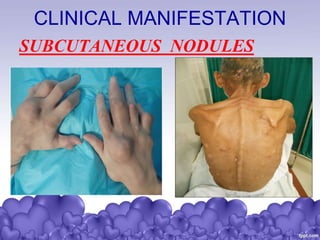
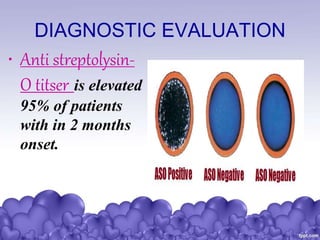
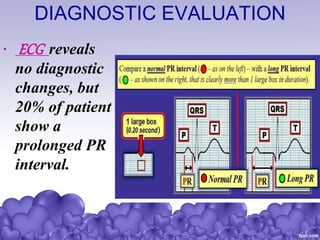
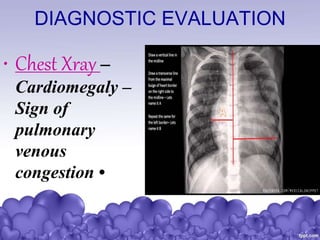
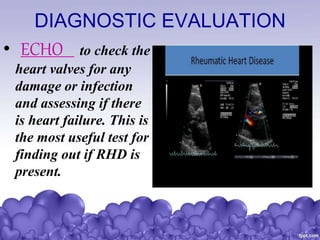
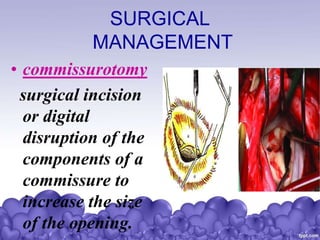
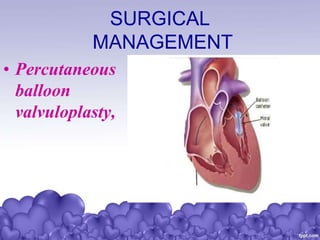
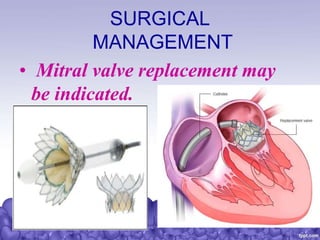
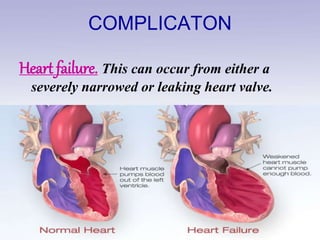
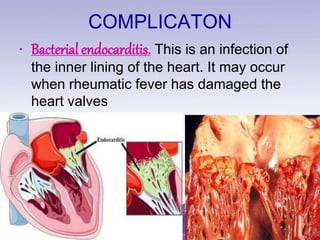
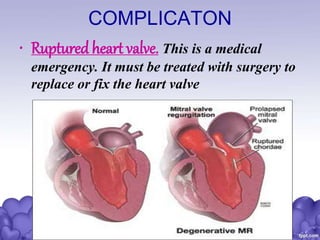
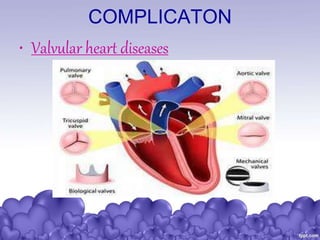
Rheumatic heart disease is a condition where the heart valves are permanently damaged by rheumatic fever, which can result from untreated strep throat infections. It is characterized by inflammation and scarring of the heart valves. Risk factors include poverty, overcrowding, a history of rheumatic fever, and strep throat infections. Symptoms include heart valve problems, joint pain, and heart failure. Treatment involves antibiotics to prevent future strep infections, medications for heart failure, and potentially heart valve surgery. Complications can include heart failure, bacterial endocarditis, and ruptured heart valves.