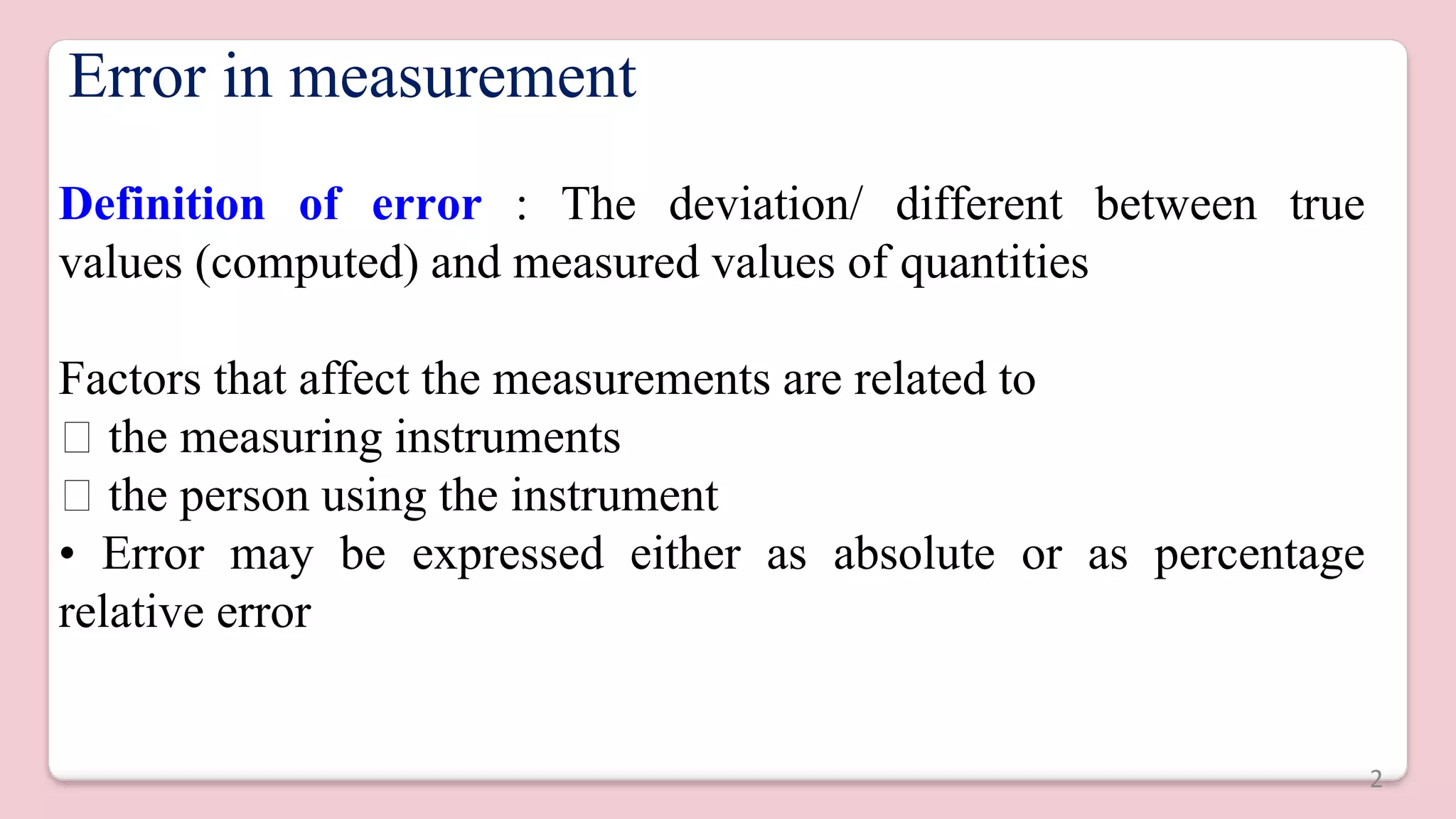
This document discusses different types of errors that can occur in measurement. There are five main types of errors:
1) Gross errors are faults made by the person using the instrument, such as incorrect readings or recordings.
2) Systematic errors are due to problems with the instrument itself, environmental factors, or observational errors made by the observer.
3) Random errors remain after gross and systematic errors have been reduced and are due to unknown causes. Taking multiple readings and analyzing them statistically can help minimize random errors.
4) Absolute error is the difference between the expected and measured values.
5) Relative error expresses the error as a percentage of the real measurement.