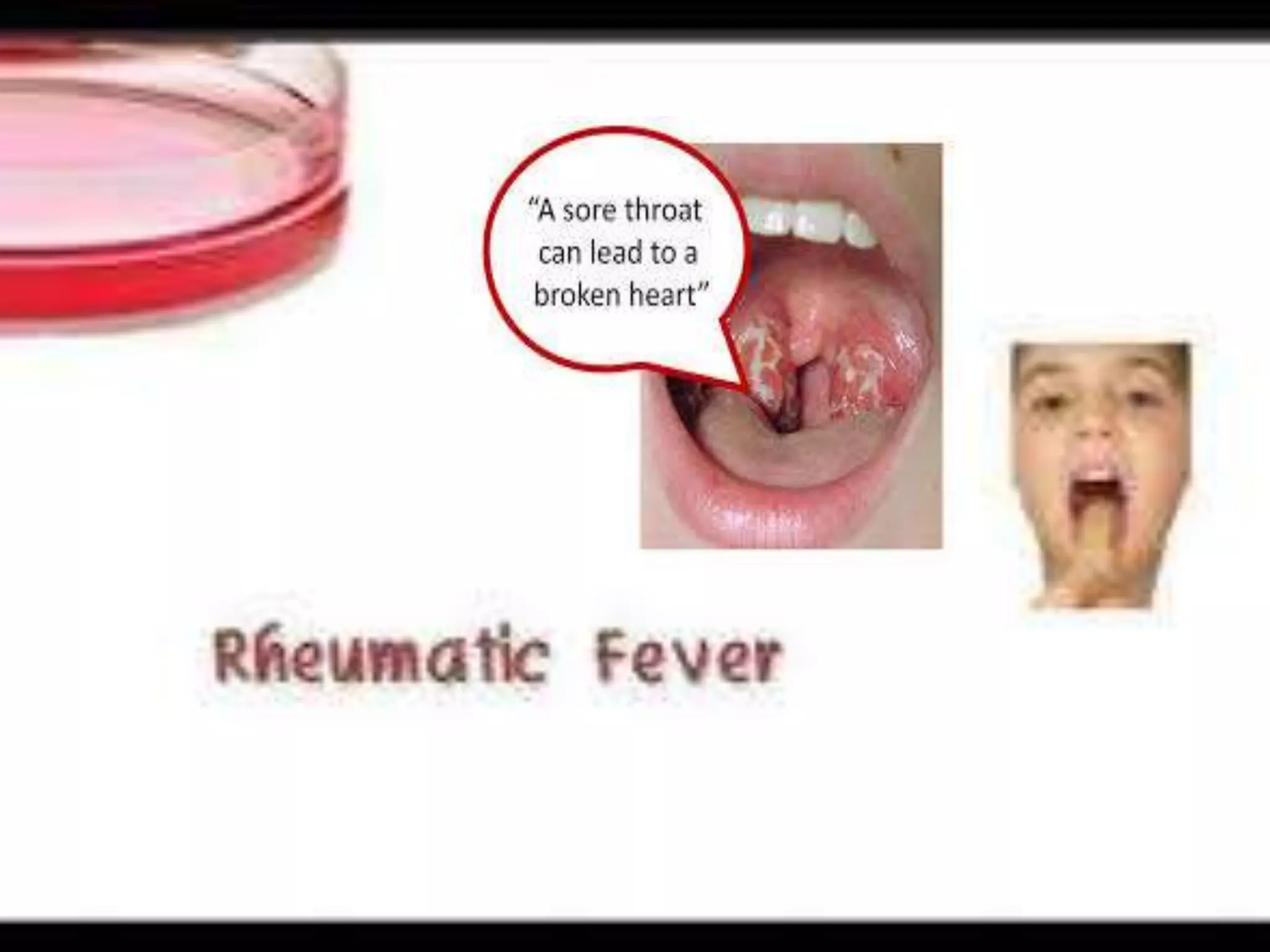
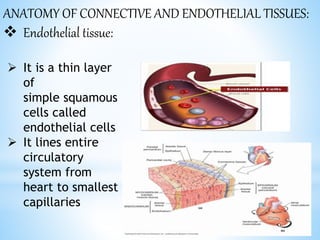
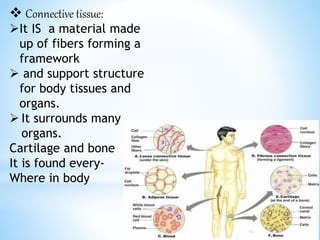
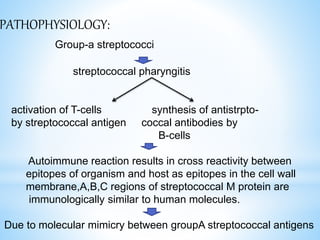
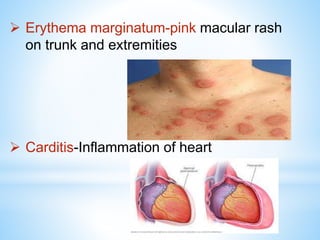
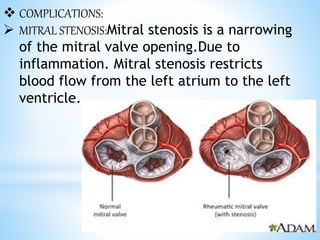
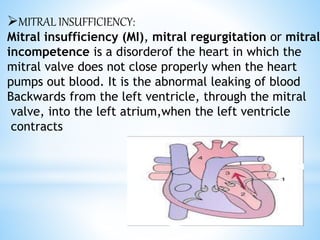
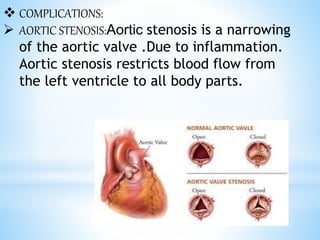
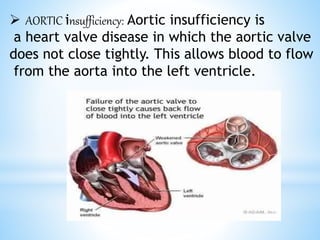
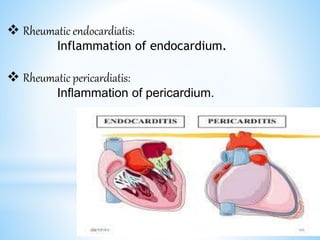
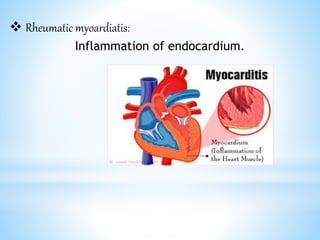
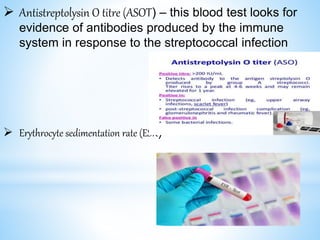
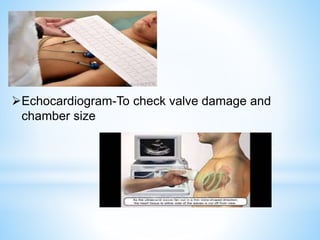
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that can occur as a result of a streptococcal infection. It is caused by an autoimmune response where antibodies created to fight the bacterial infection mistakenly attack healthy tissues in the body, especially the heart valves, joints, skin, and brain. Symptoms include heart valve damage, arthritis, abnormal skin rashes, and involuntary movements. Treatment involves antibiotics to prevent recurrent streptococcal infections, anti-inflammatory drugs, and lifelong prophylaxis to prevent future episodes of rheumatic fever.