Embed presentation





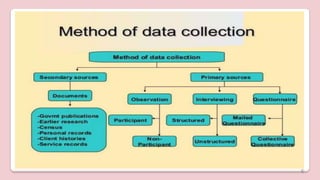



Data collection is the process of gathering information to answer a research question. There are two main categories of data: quantitative data, which deals with measurable numbers, and qualitative data, which involves descriptions and non-numerical data. Data can be either primary, which is originally collected for the research, or secondary, which has already been collected previously. Proper planning is important for data collection, including determining how, when, by whom, and where the data will be collected, as well as ensuring its accuracy.








