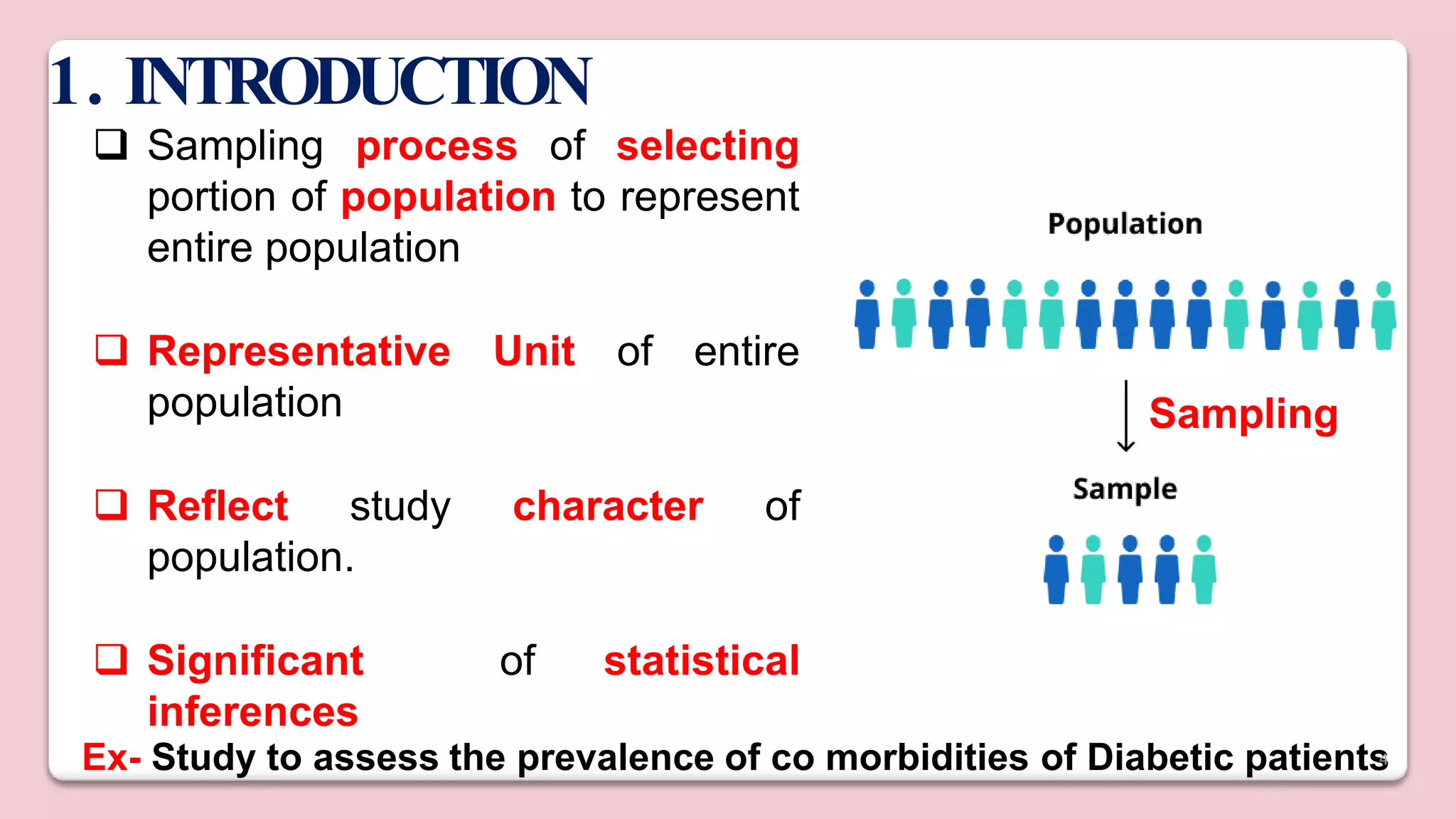
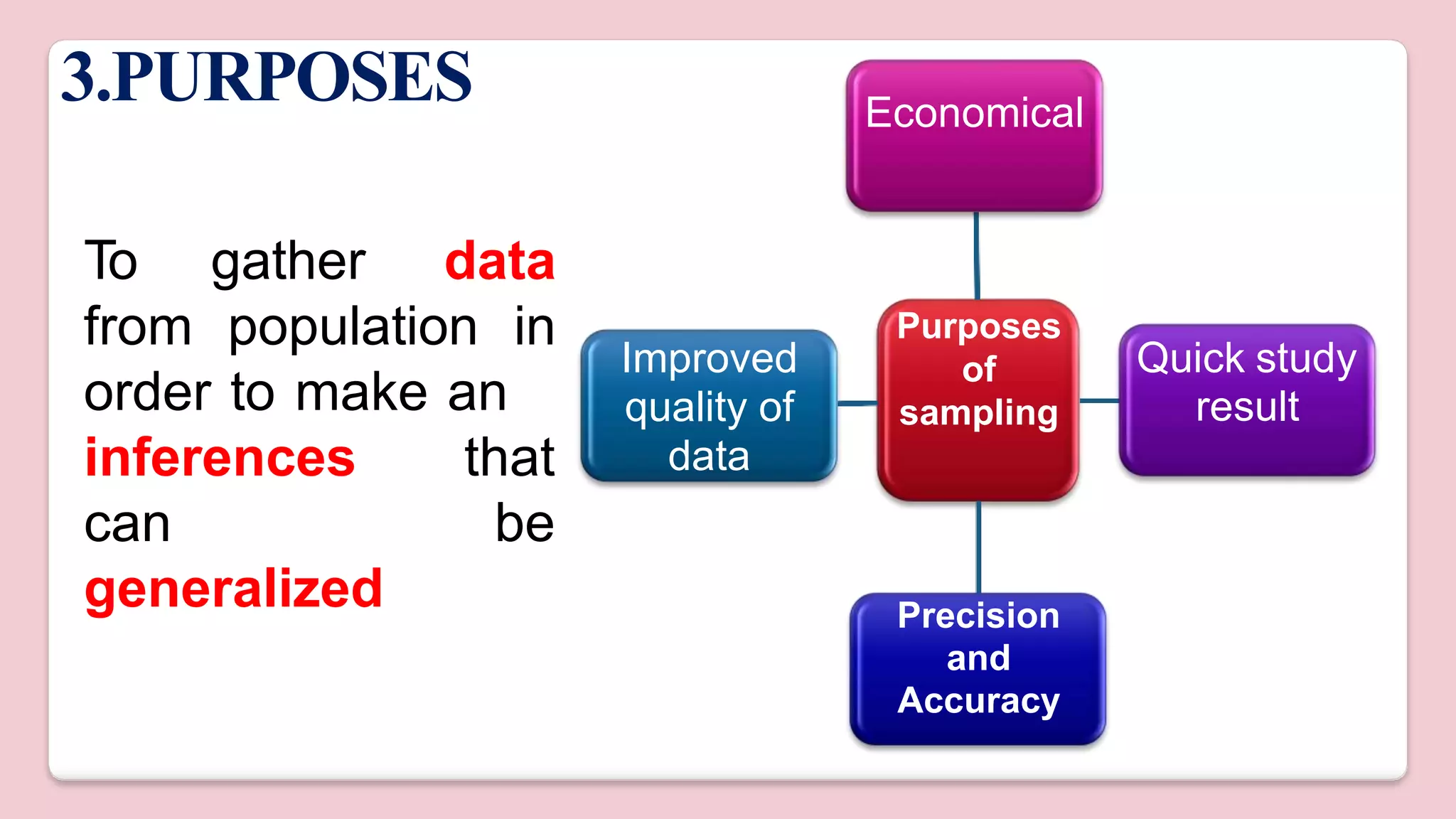
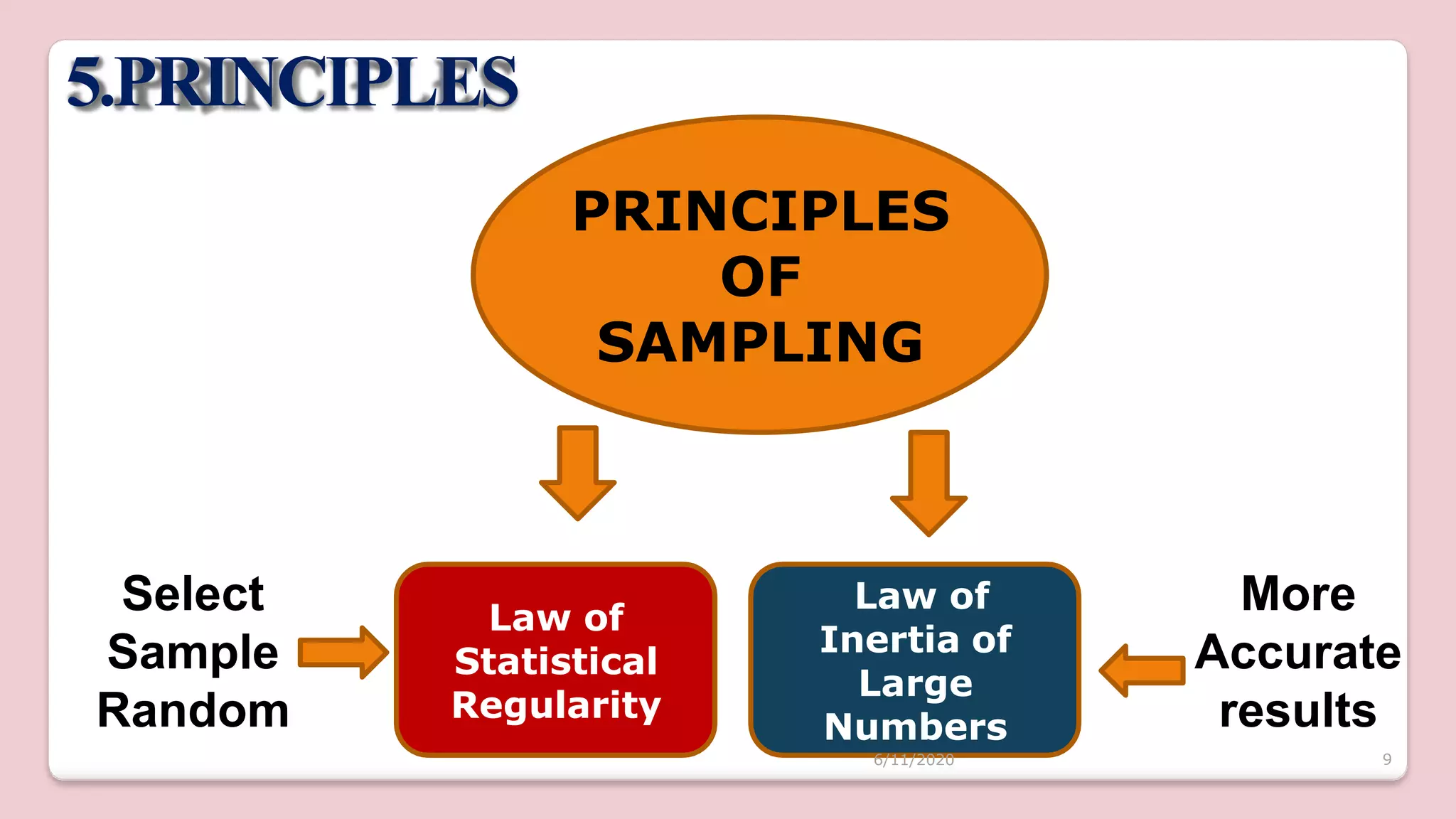
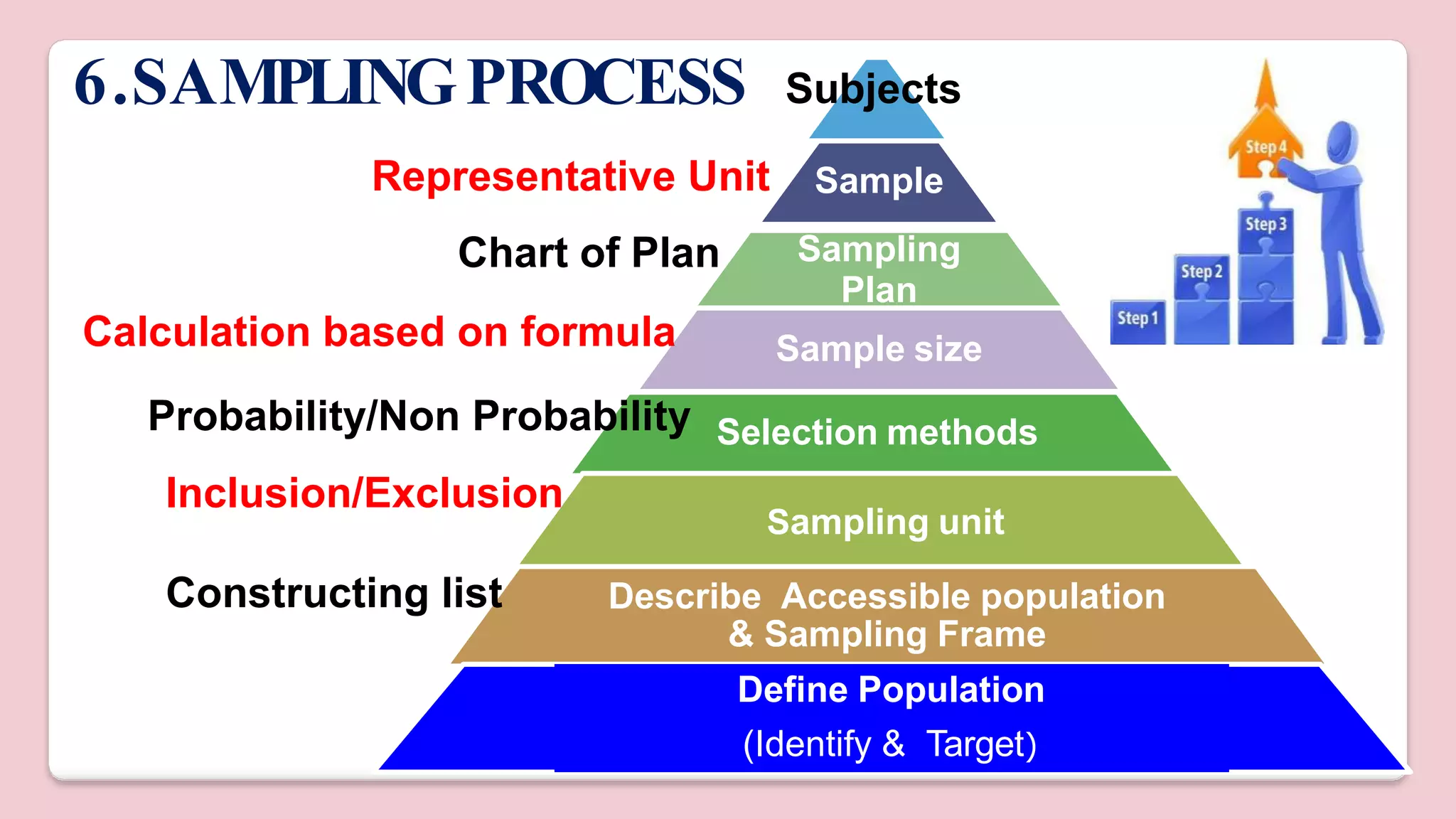
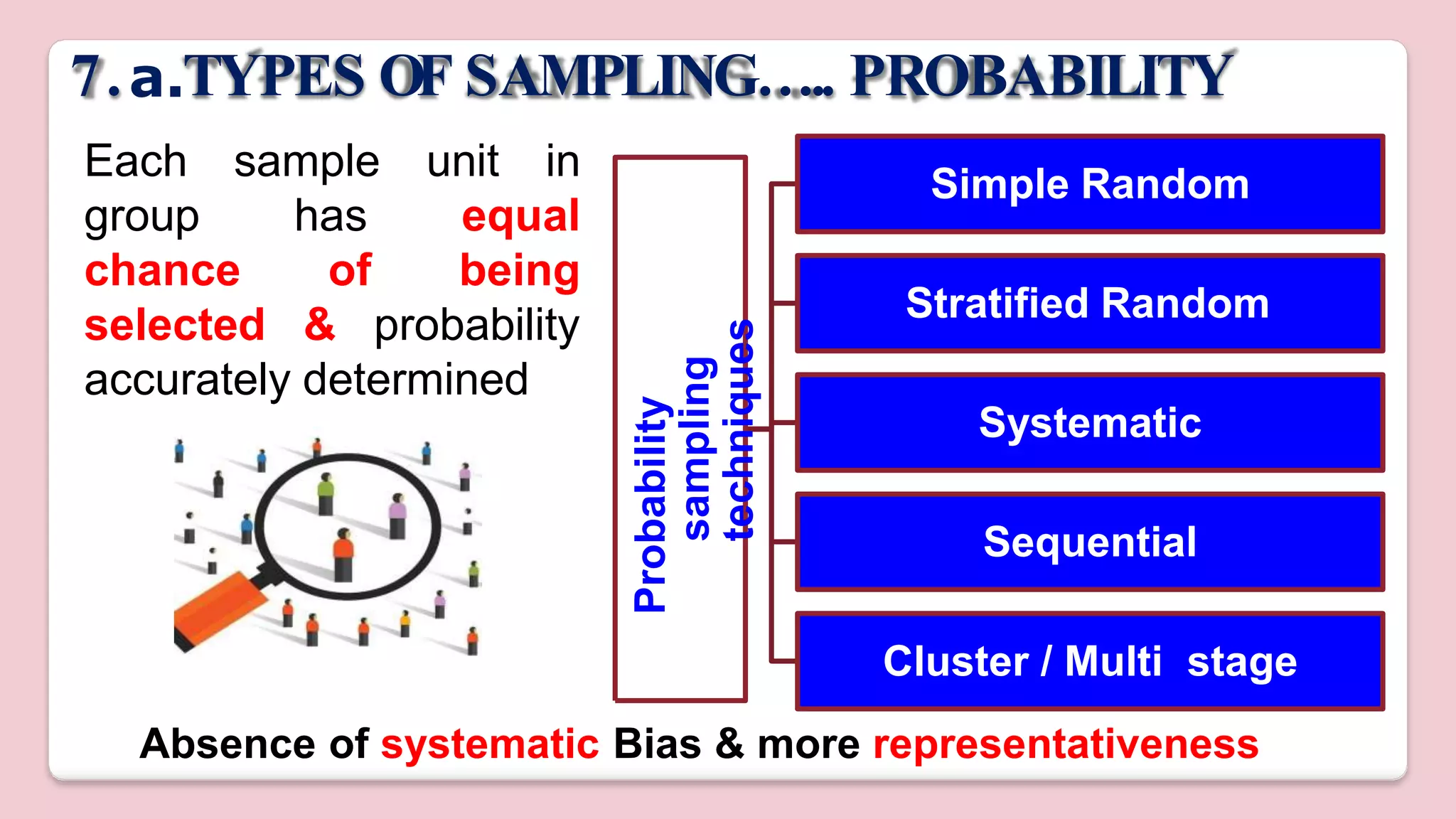
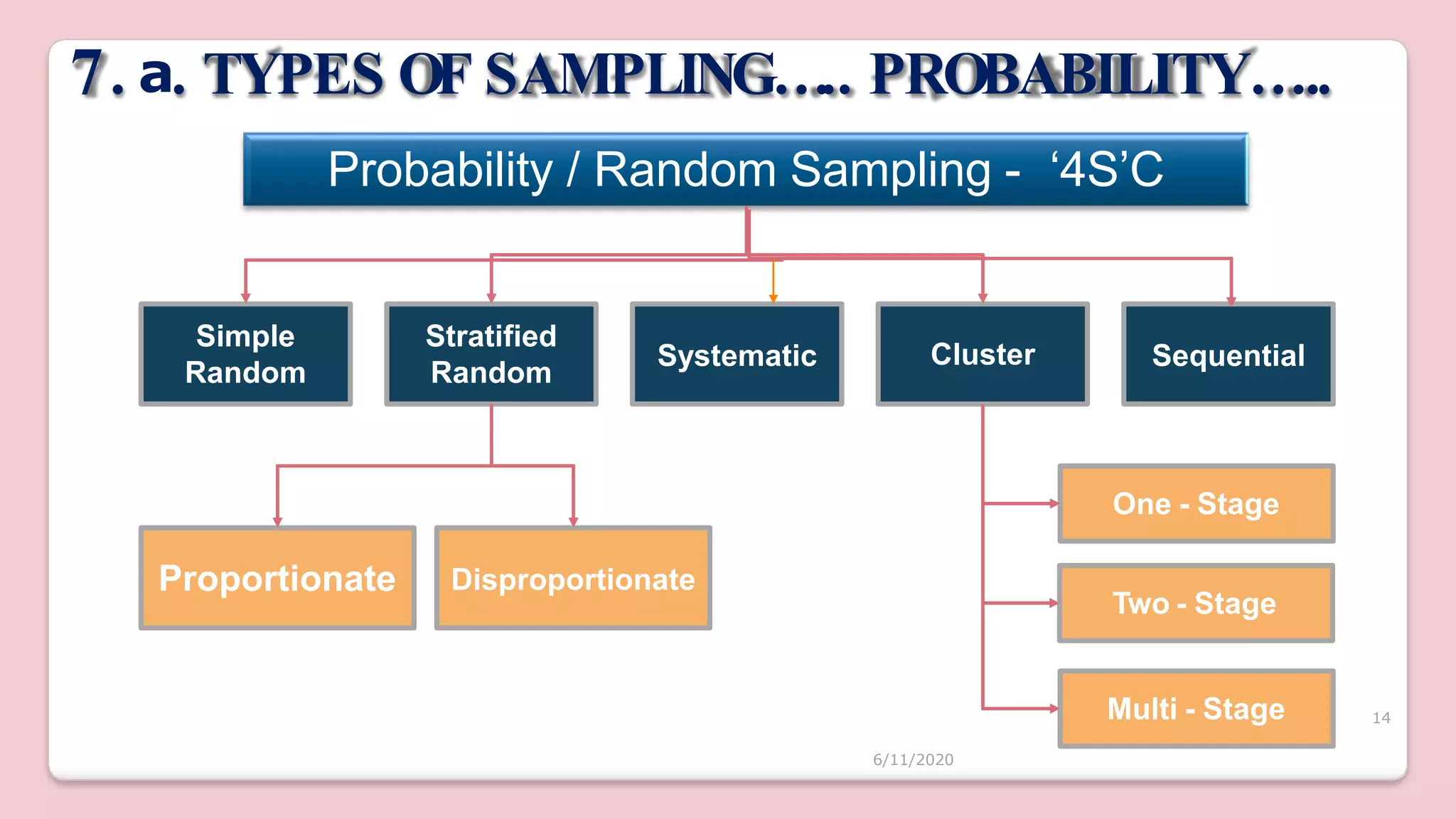
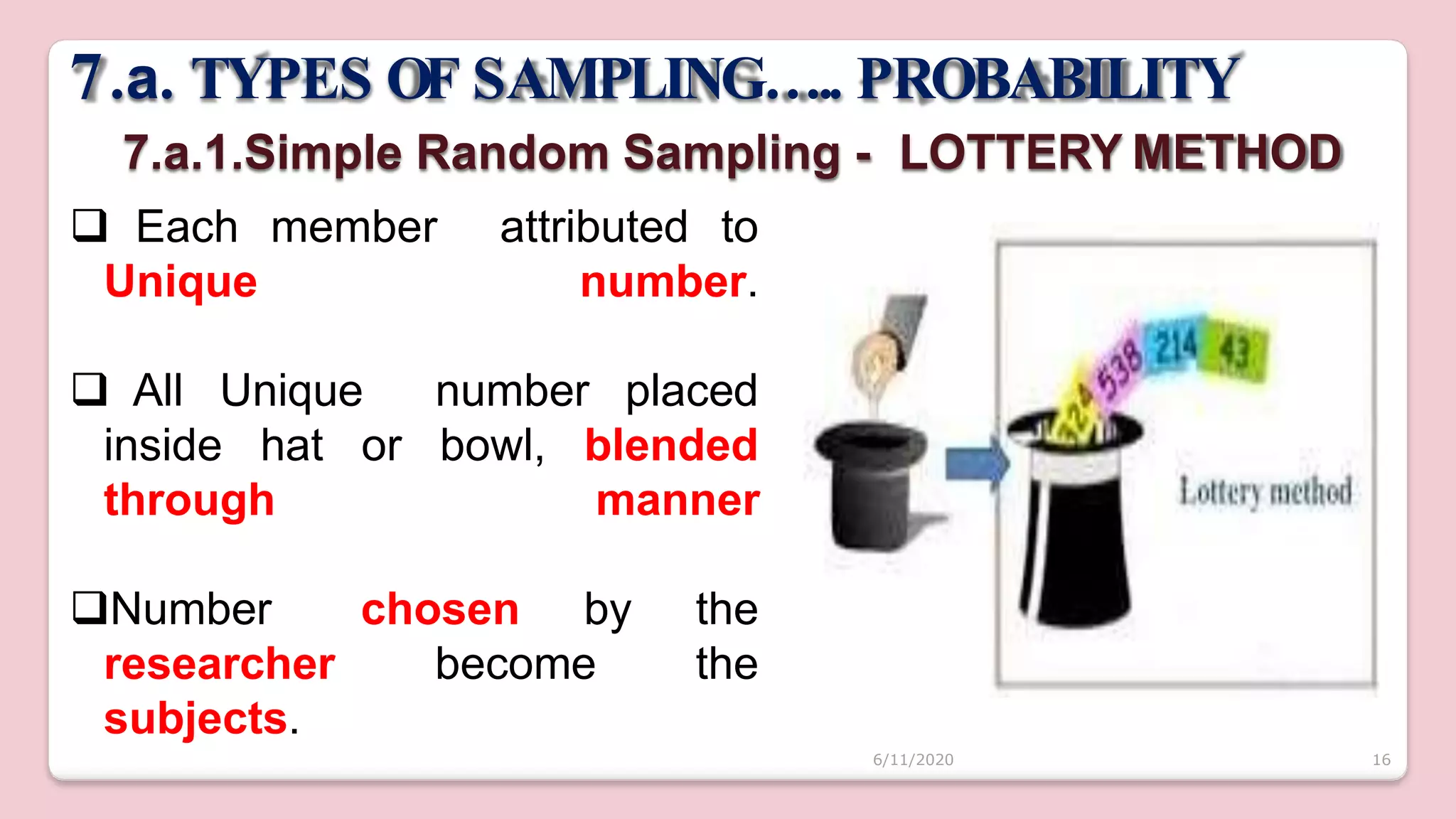
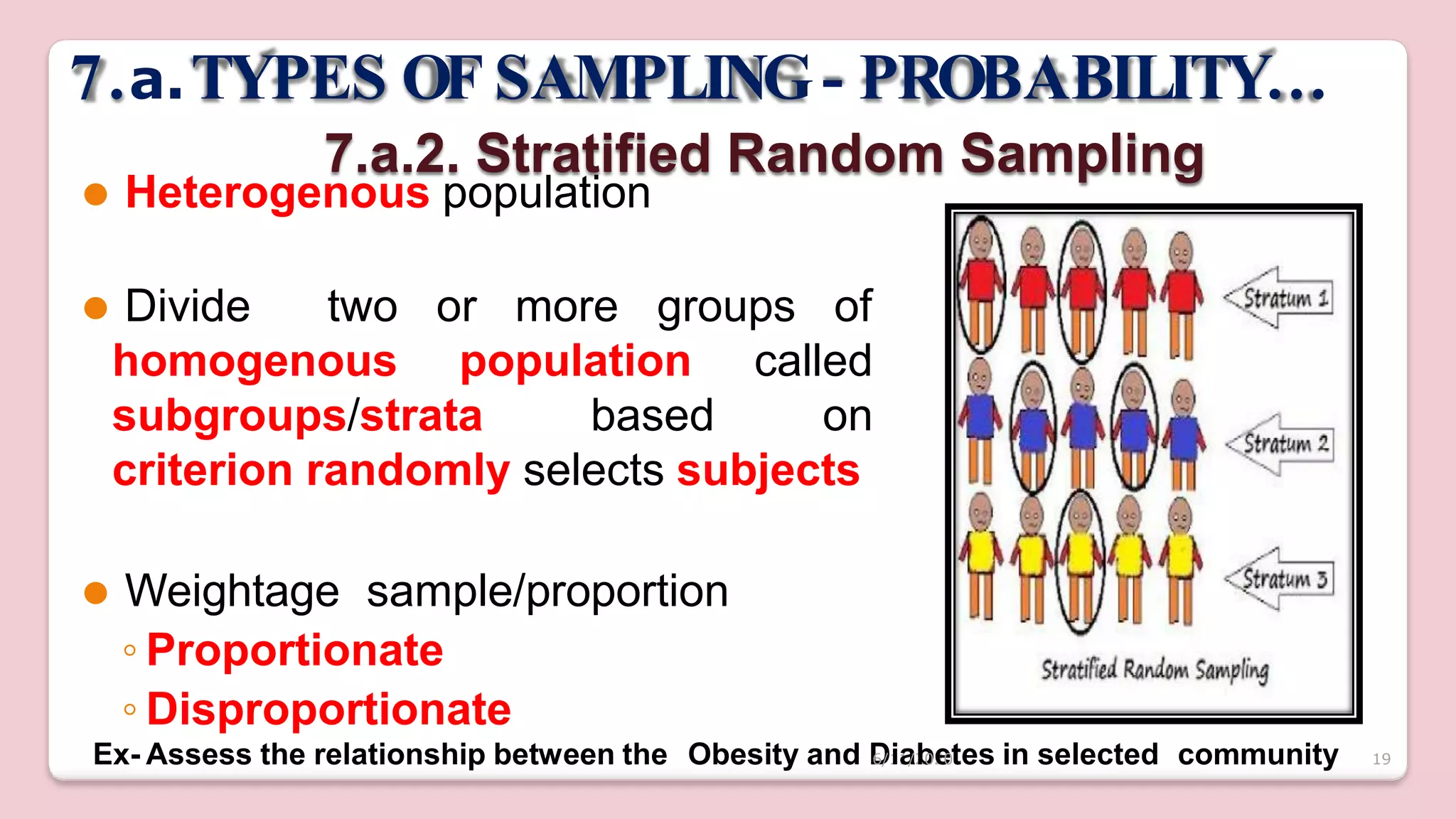
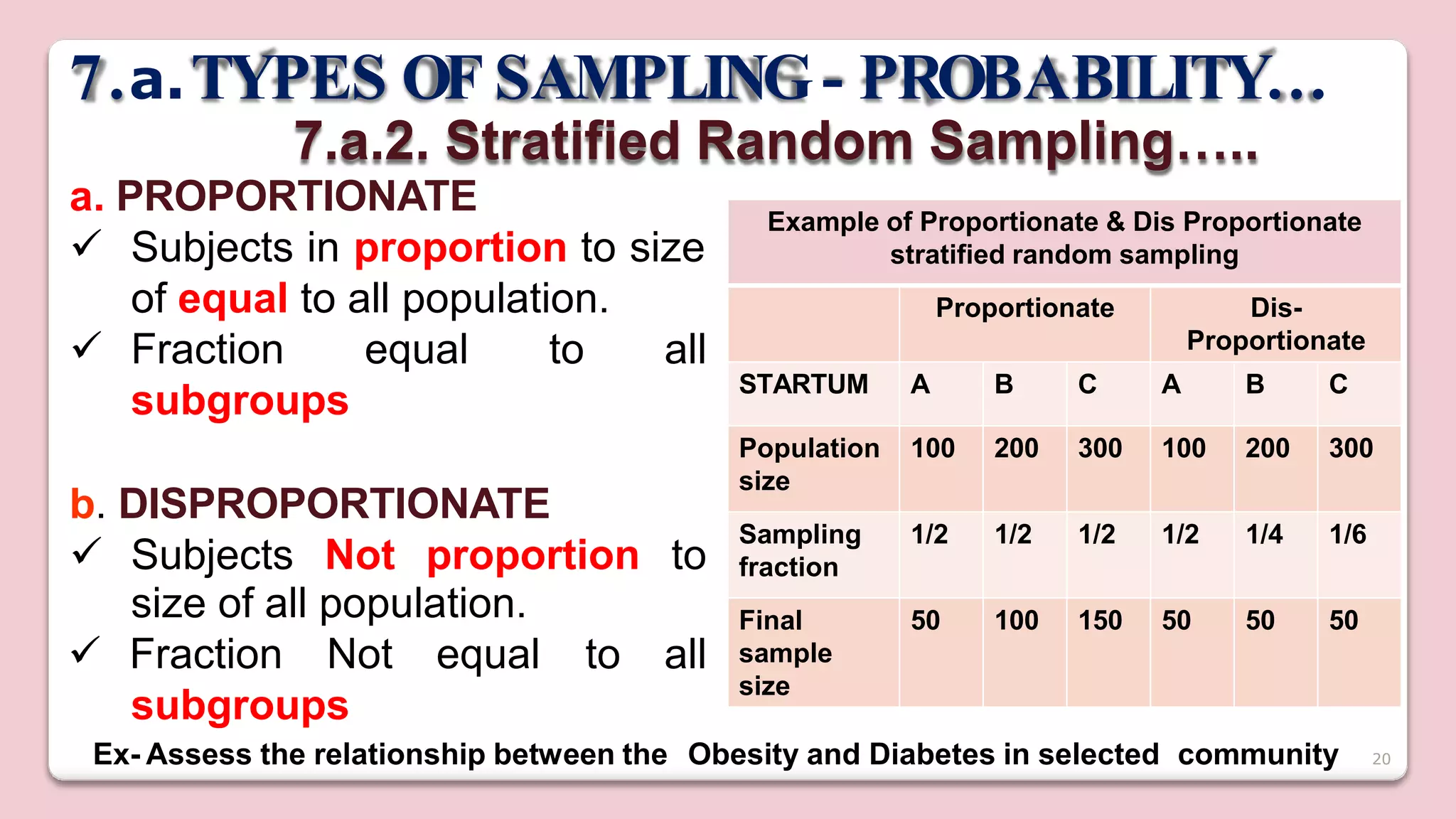
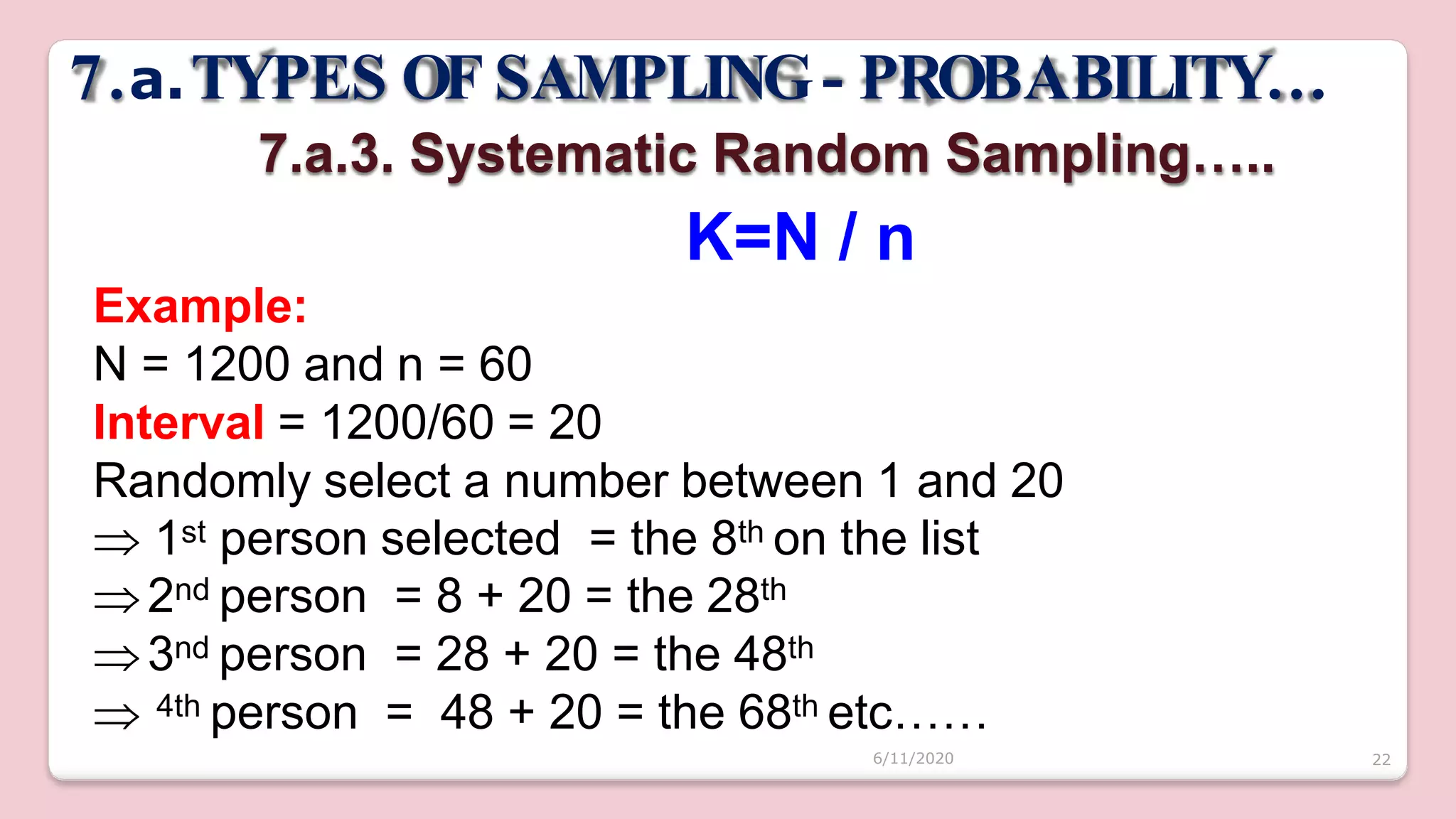
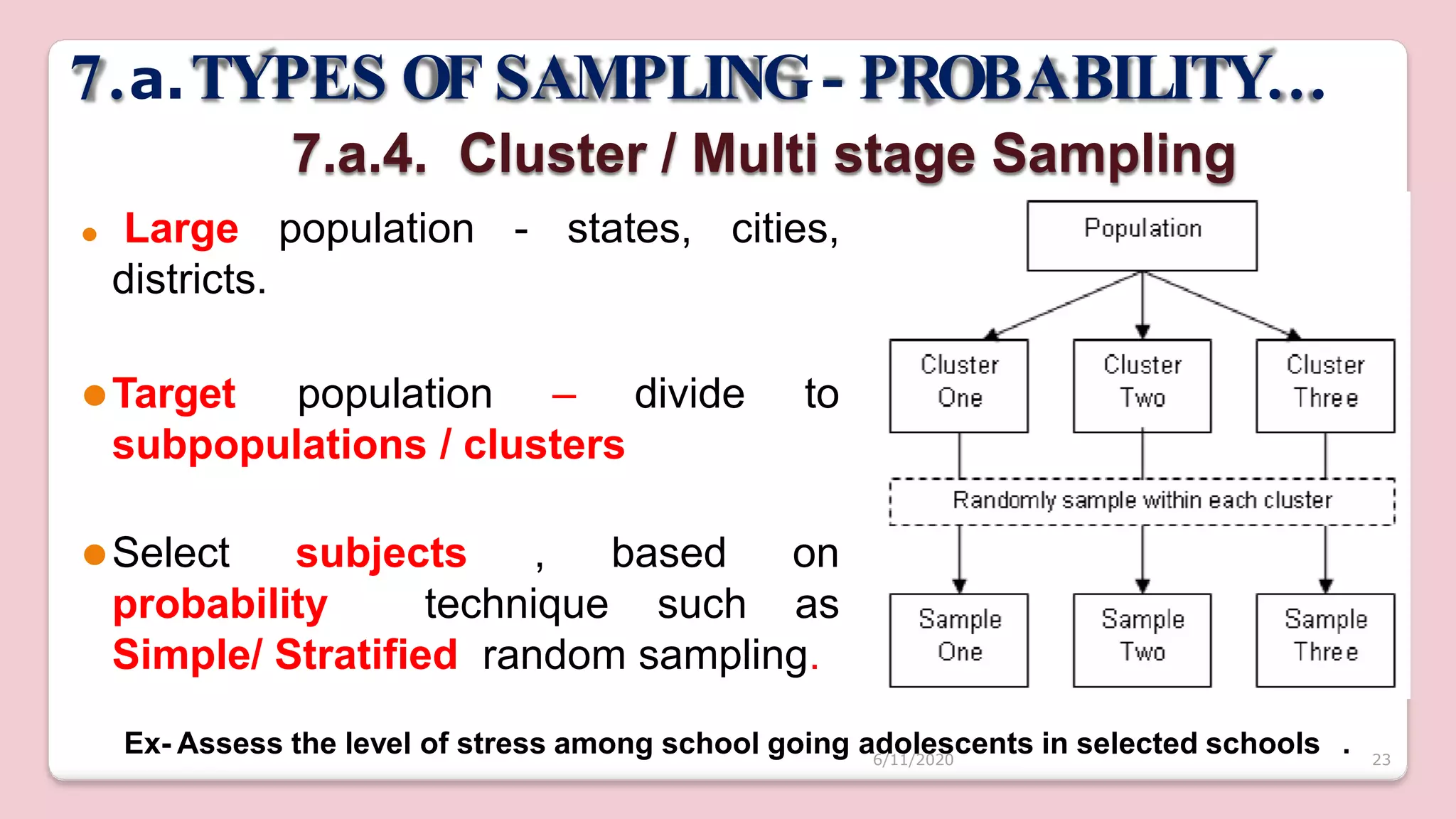
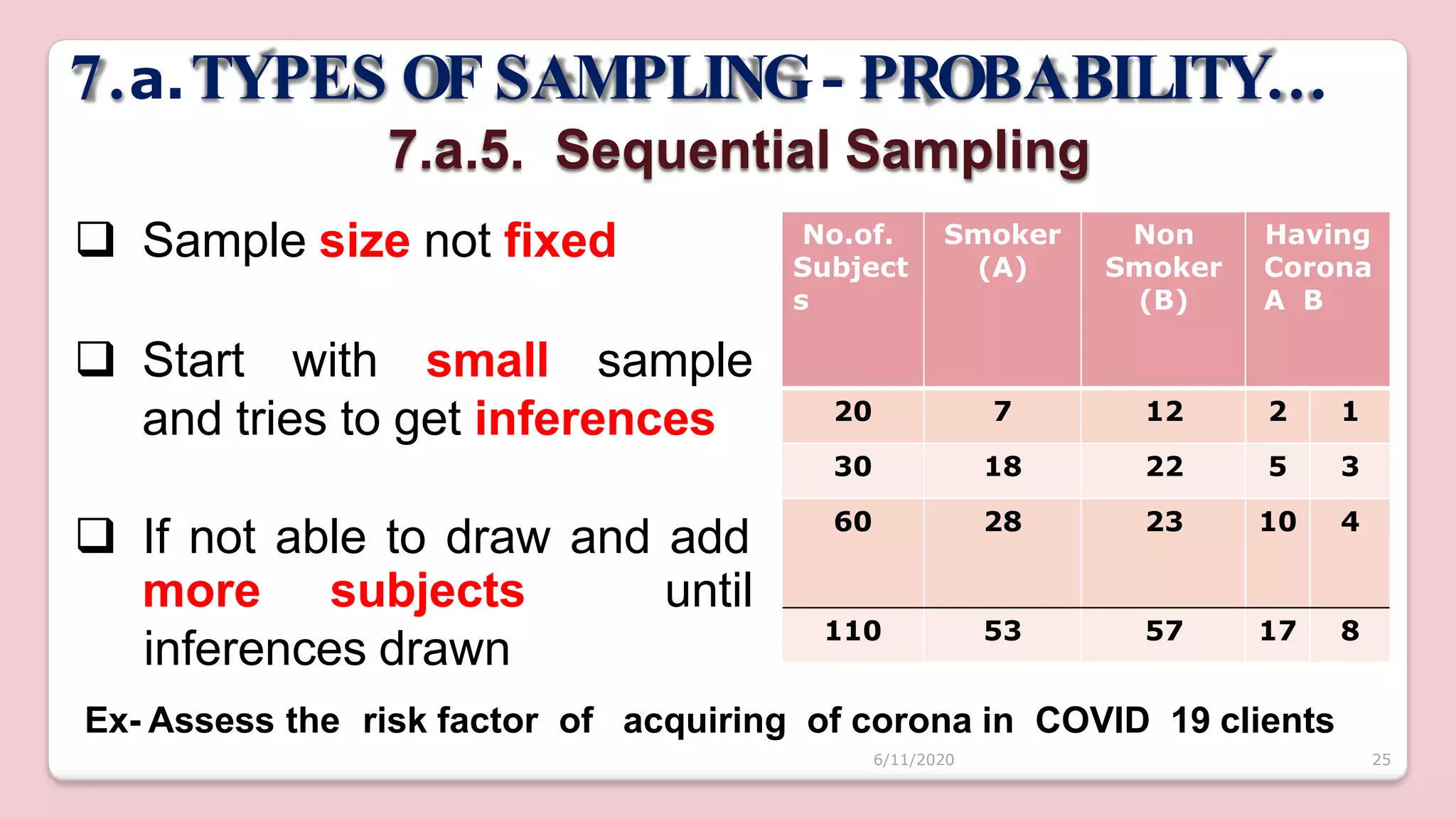
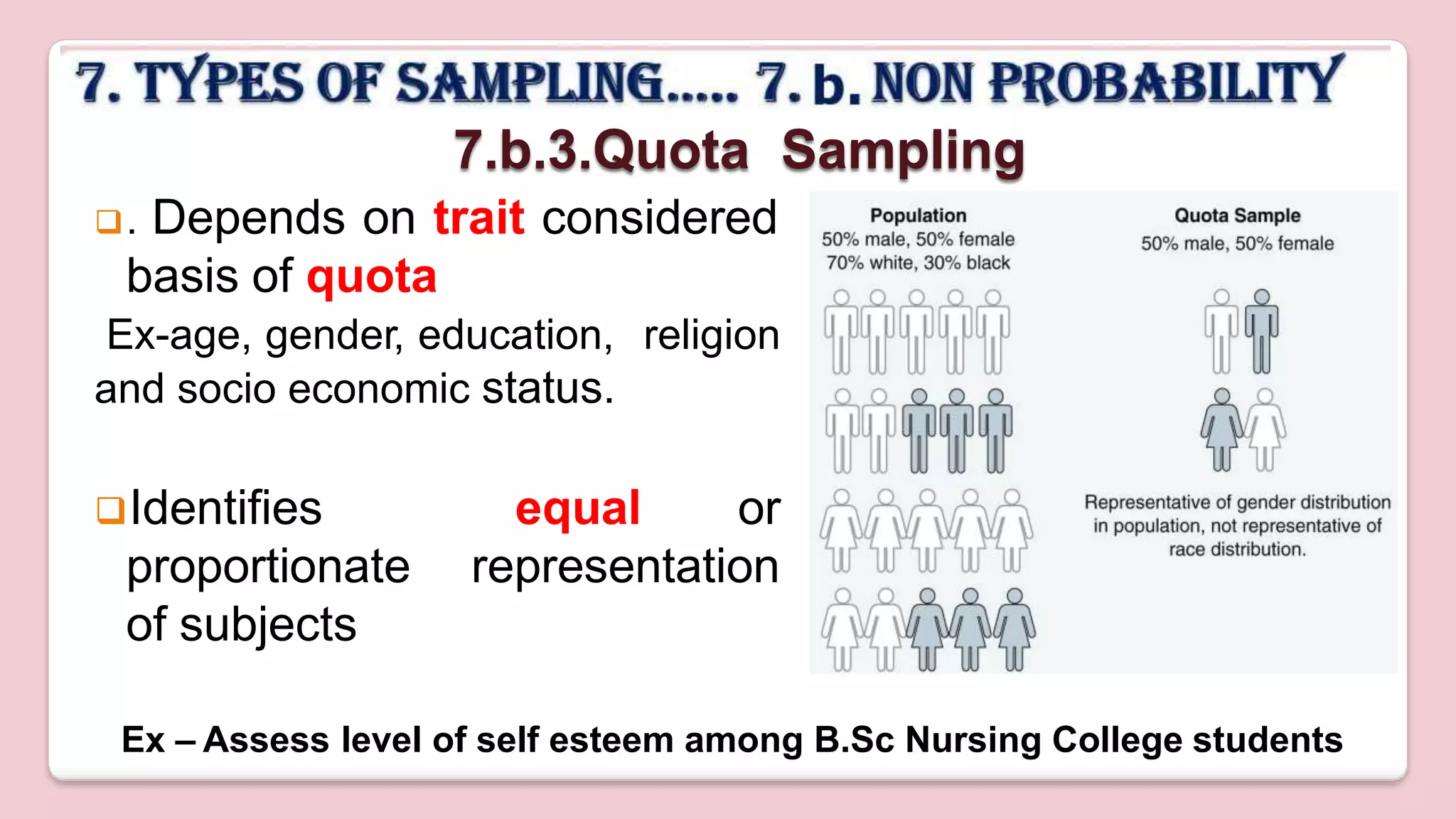
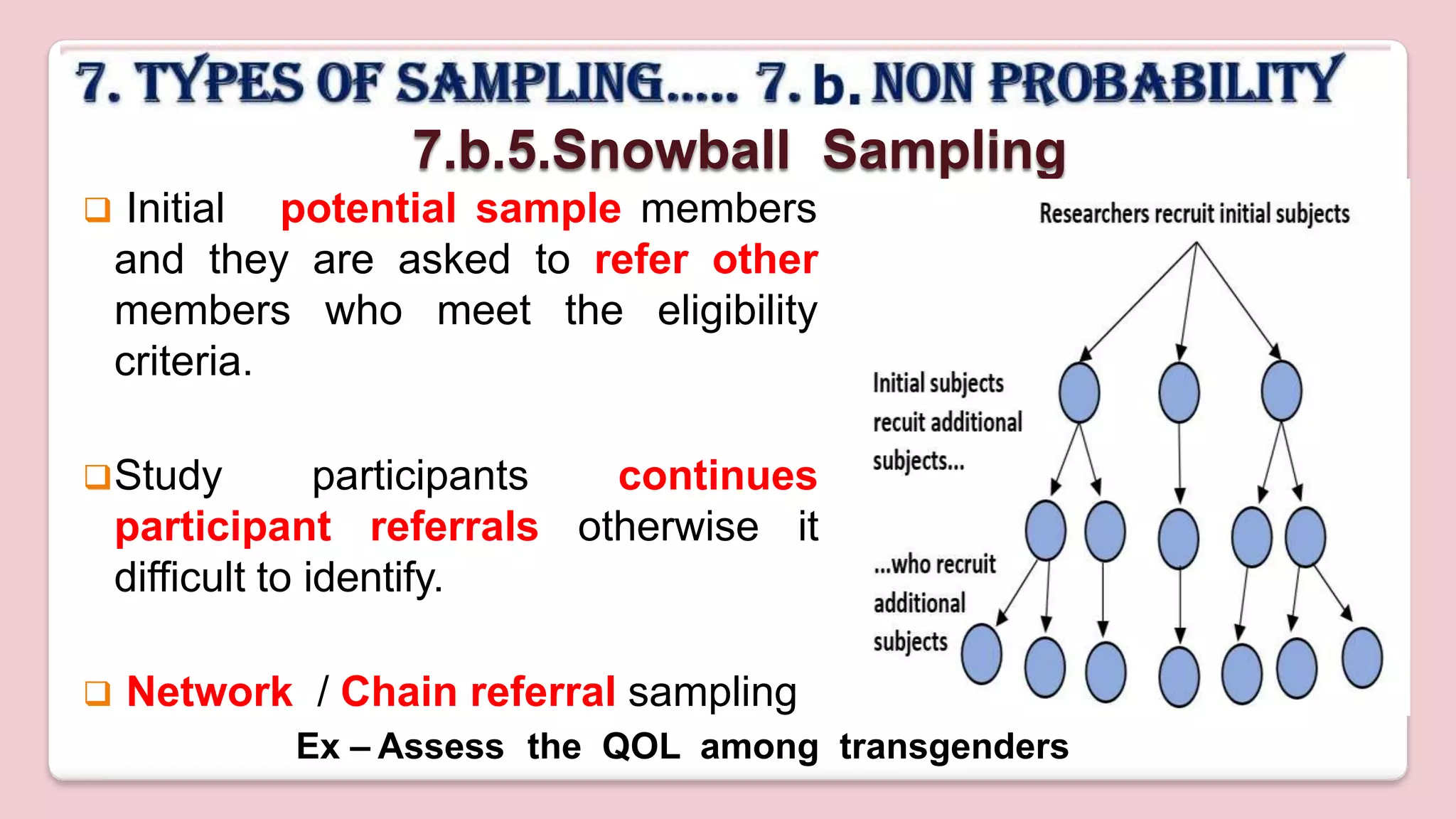
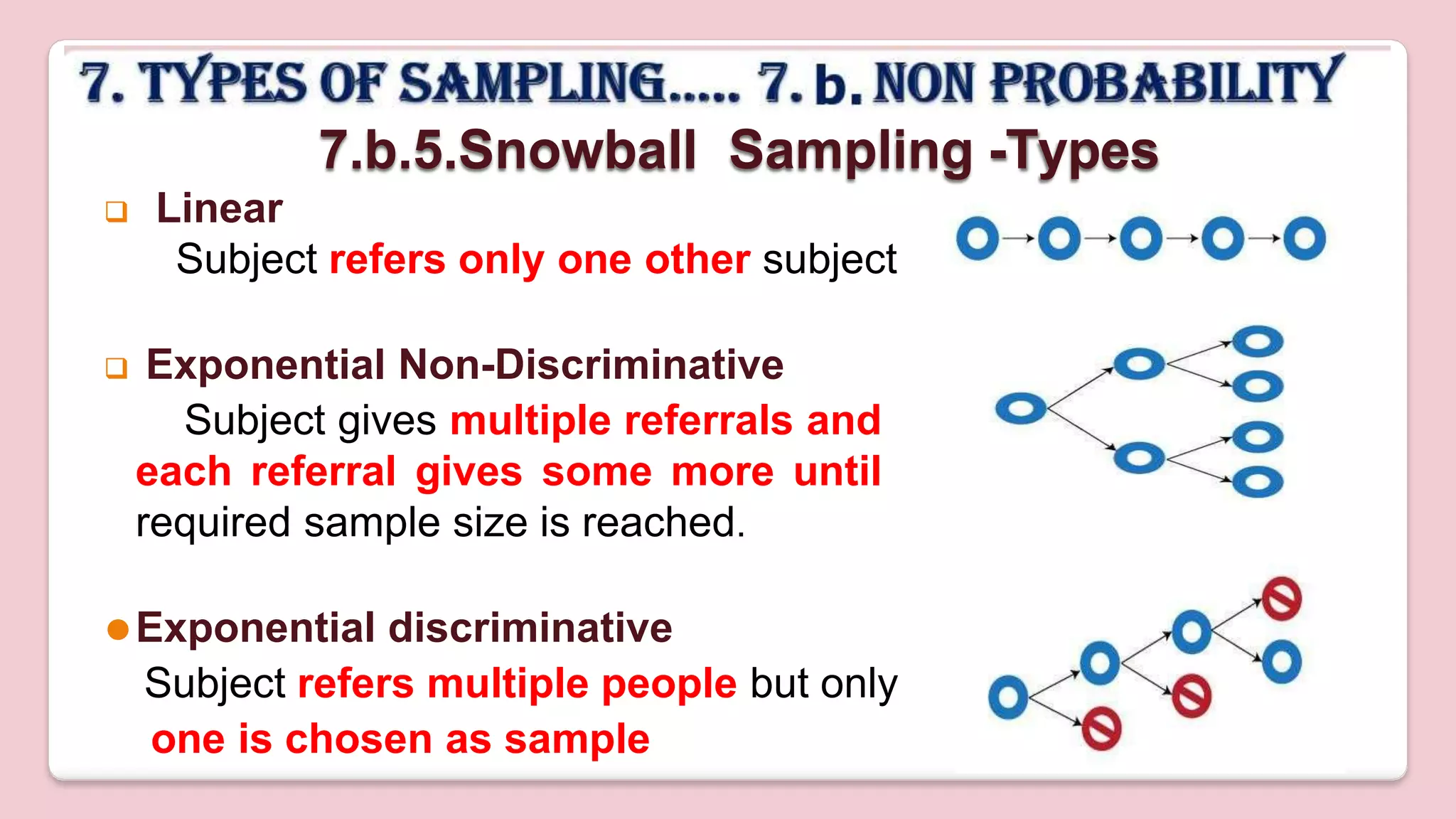
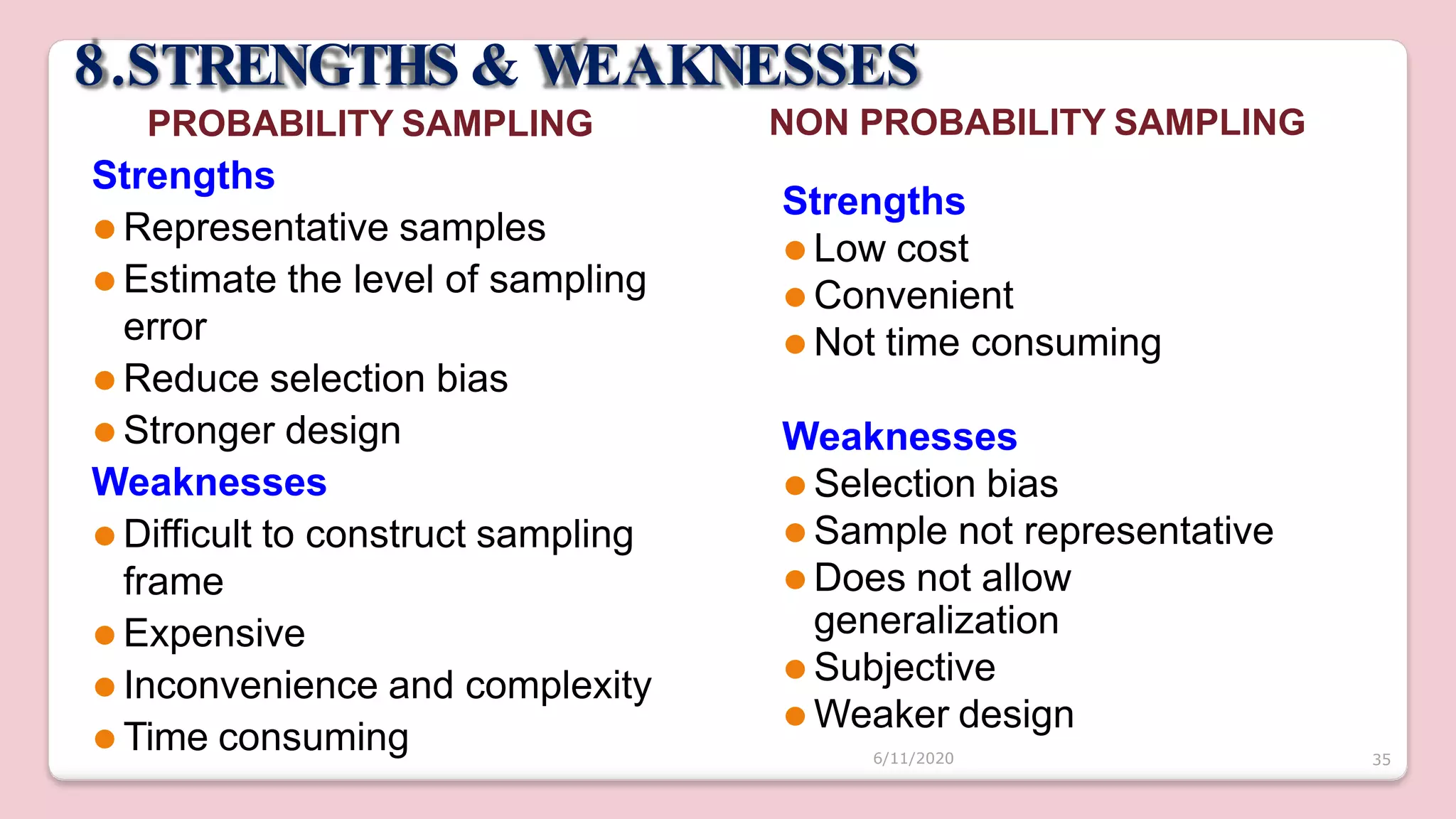
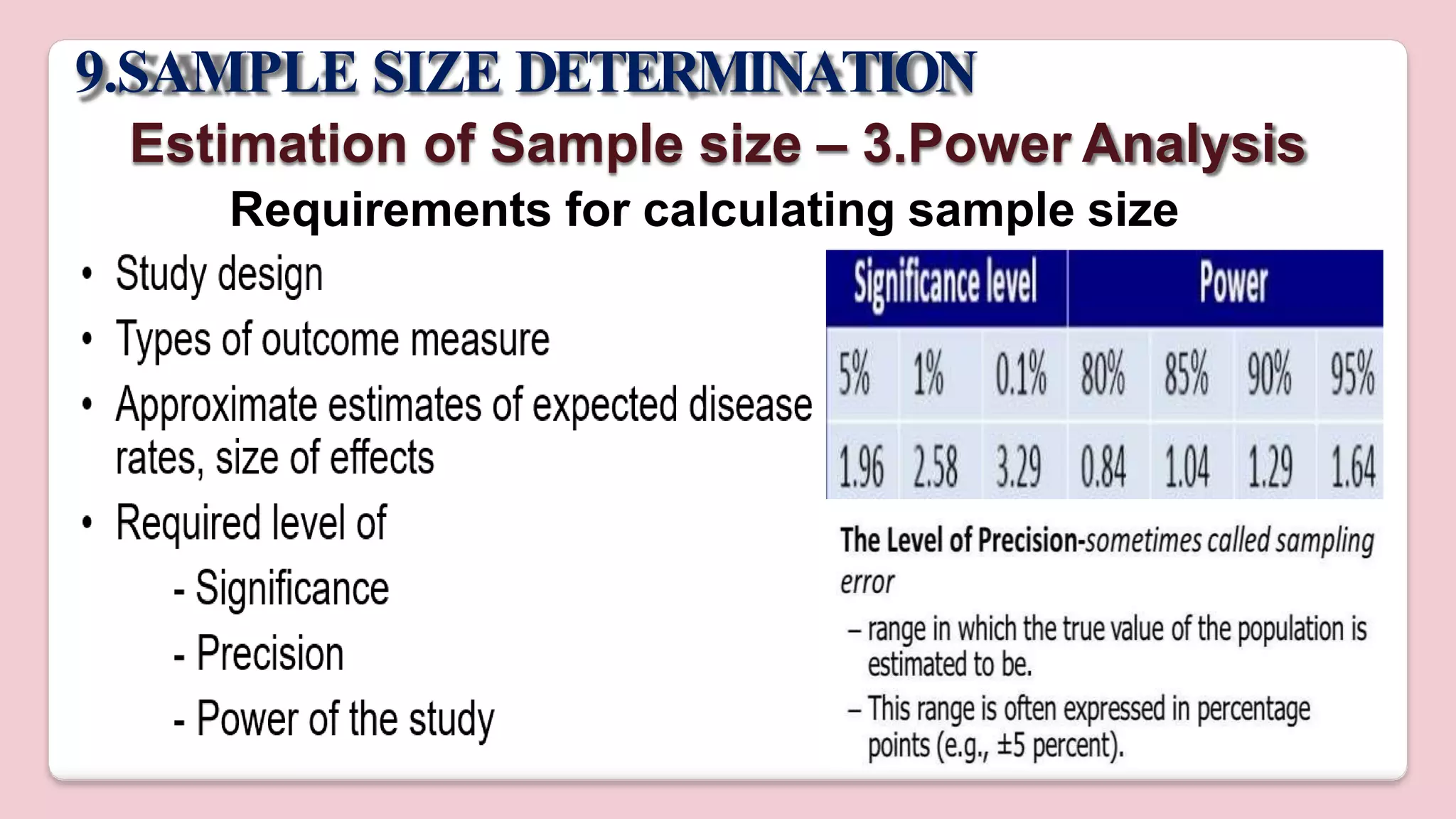
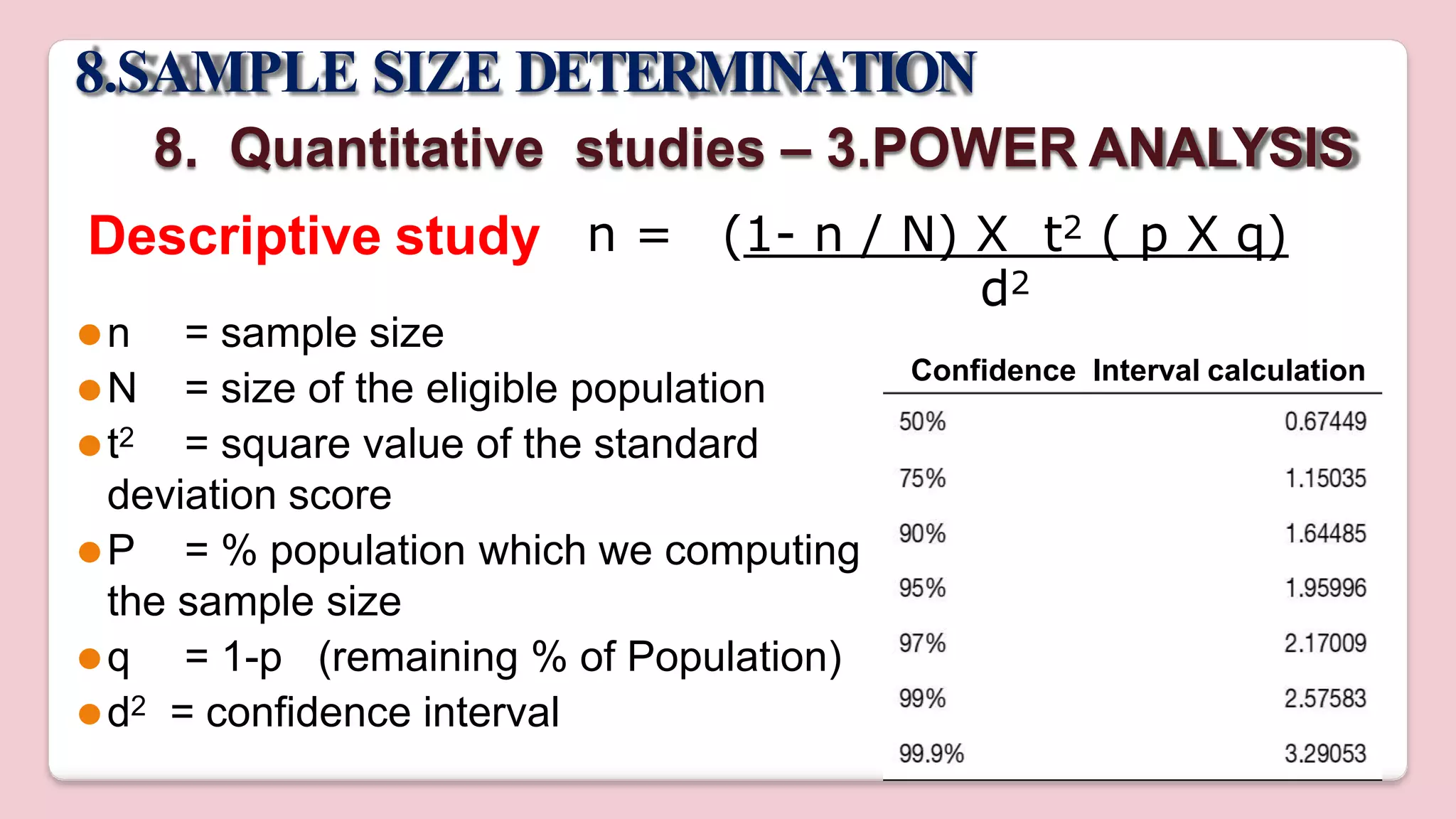
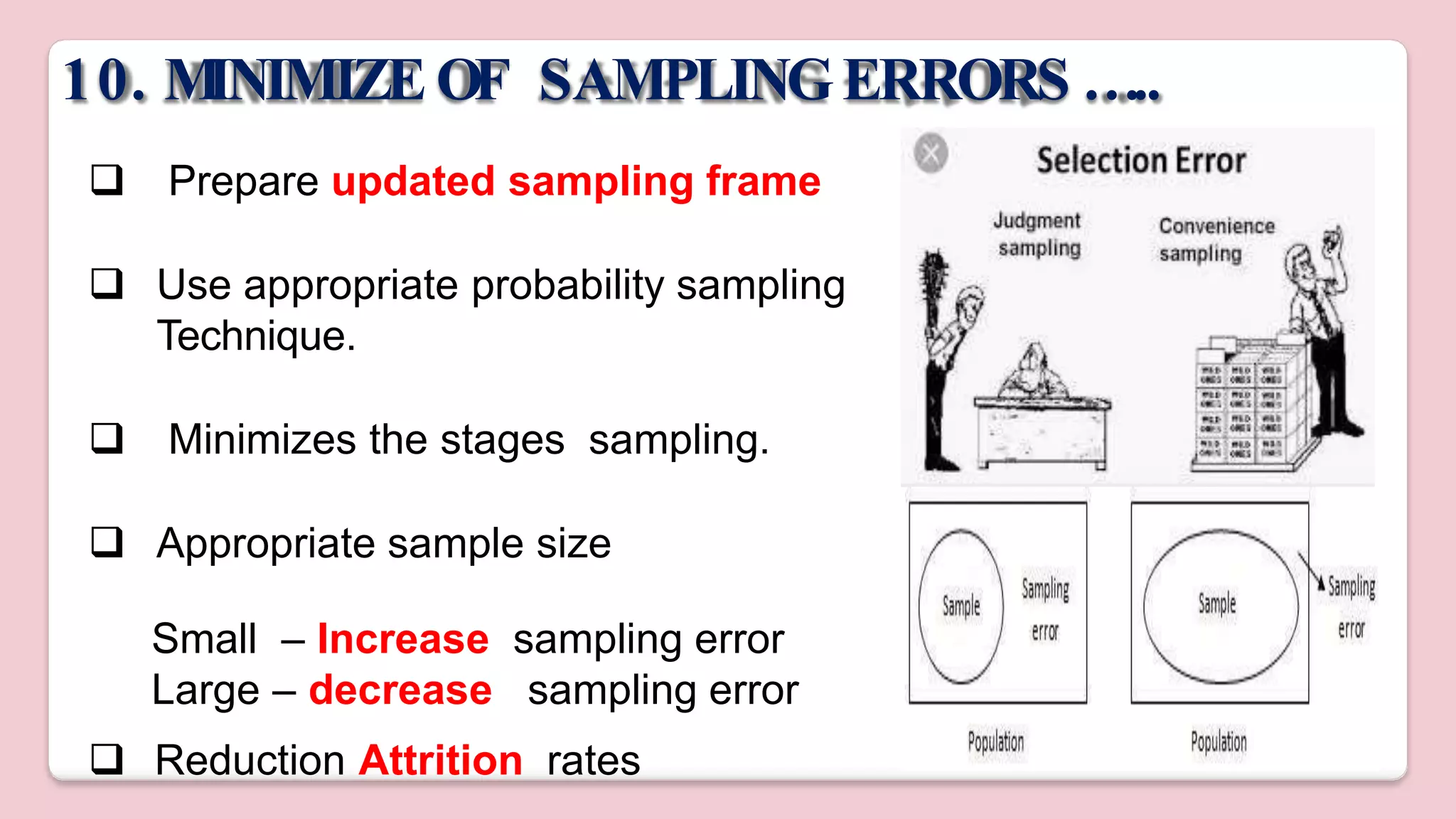
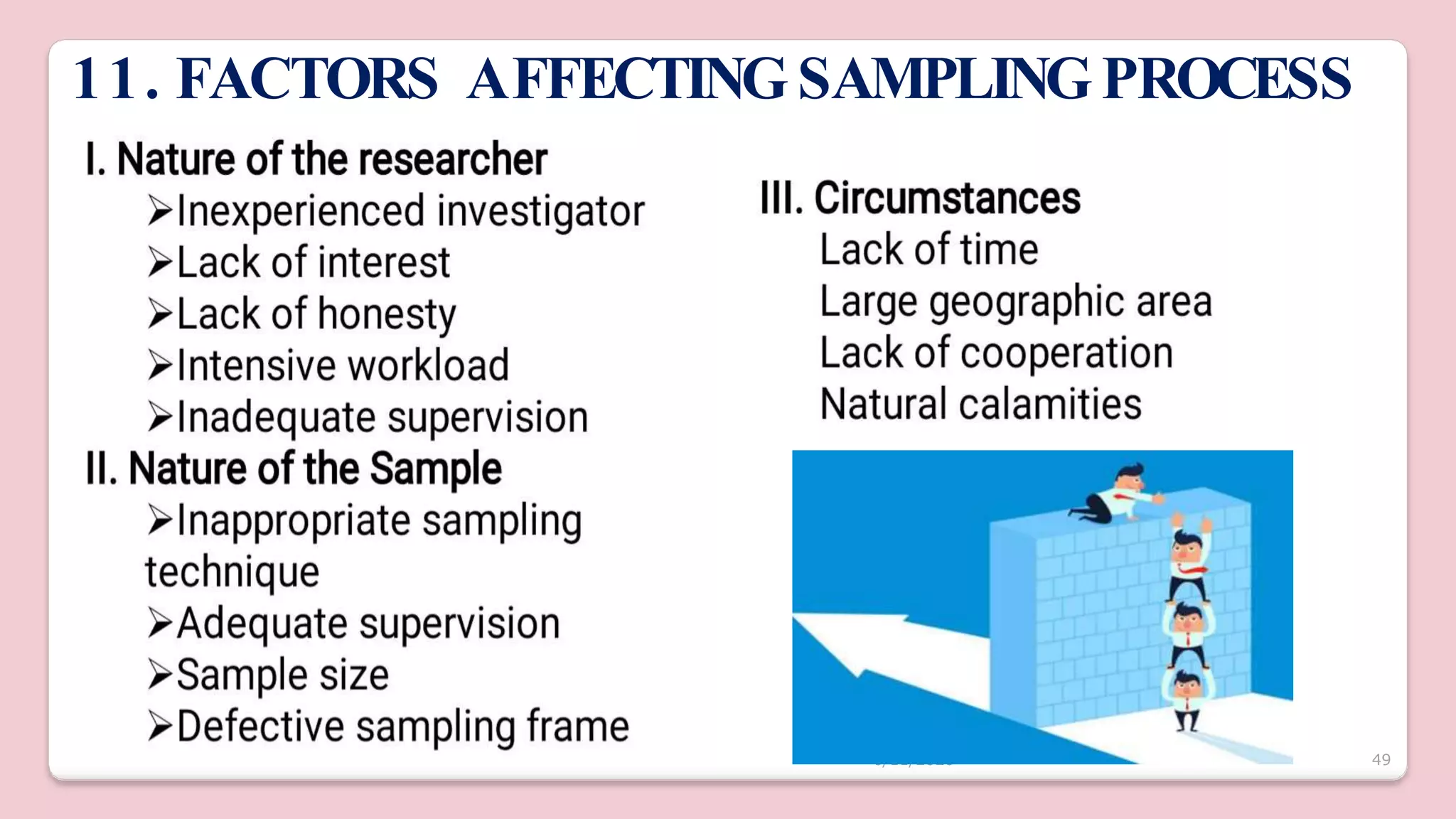
This document discusses various methods of sampling in research. It begins by defining sampling as selecting a portion of the population to represent the whole and notes its importance for statistical inferences. It then covers the purposes of sampling such as being economical and improving data quality. The document outlines characteristics of a good sample such as being representative and free from bias. It also discusses principles of sampling and the sampling process. The main types of sampling techniques for quantitative and qualitative research are described in detail, including probability, non-probability, and specific techniques within each. The strengths and weaknesses of different approaches are compared. Factors to consider for determining sample size and minimizing errors are also reviewed.