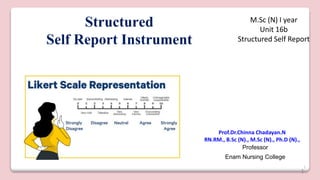
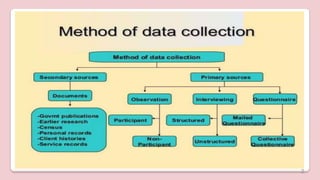
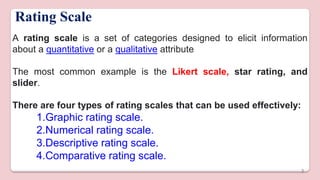
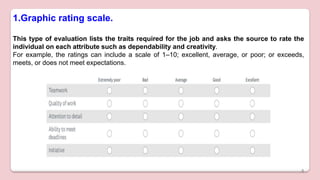
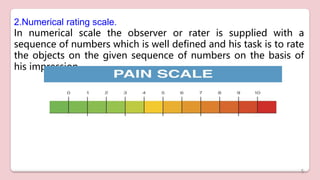
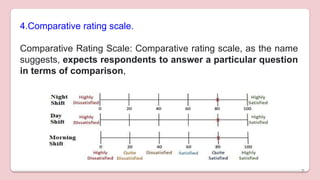
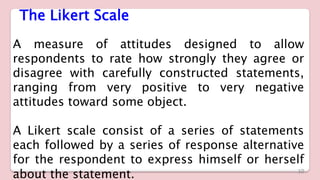
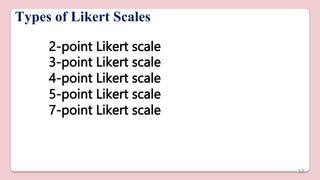
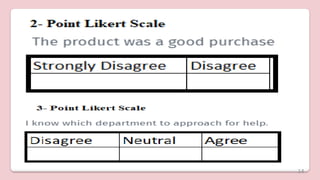
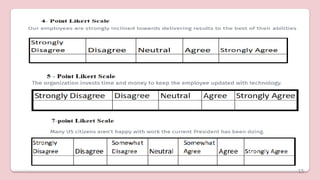
This document discusses different types of structured self-report instruments and rating scales that can be used to collect information. It describes four main types of rating scales: graphic rating scales, numerical rating scales, descriptive rating scales, and comparative rating scales. A common example of a rating scale discussed is the Likert scale, which uses a series of statements followed by response options to assess attitudes. The document outlines the uses, characteristics, types (including common 5-point scales), advantages, and disadvantages of Likert scales as a structured self-report instrument.