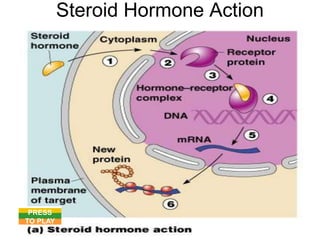
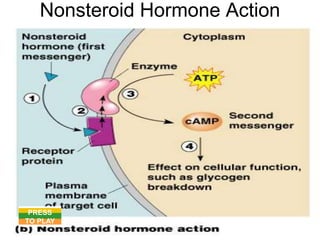
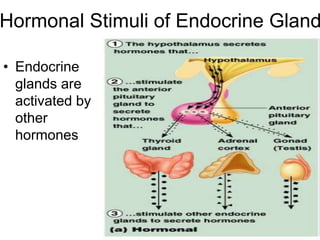
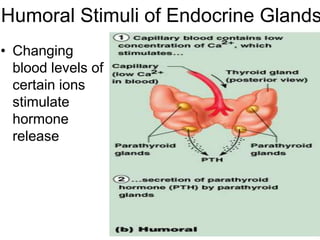
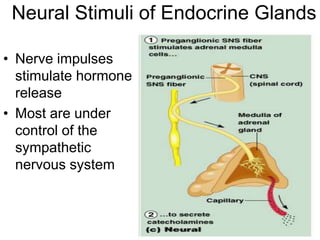
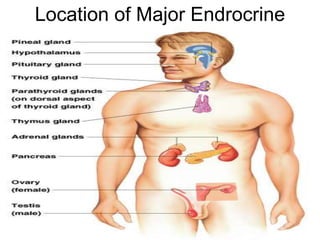
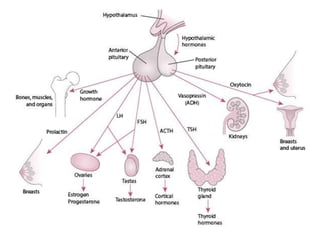
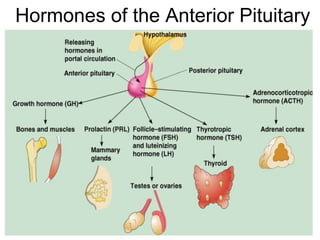
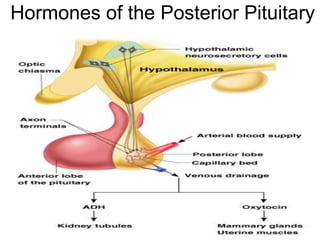
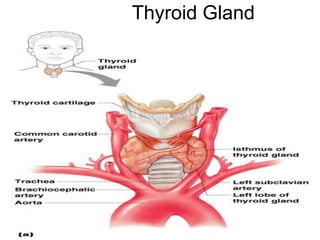
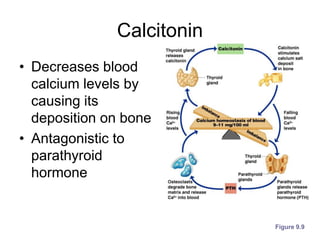
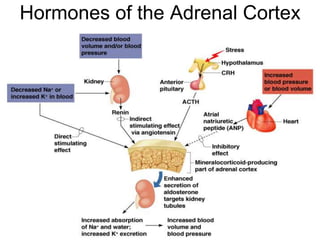
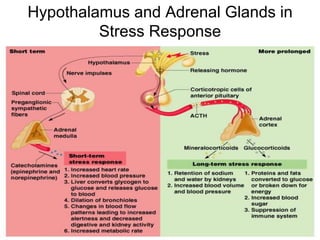
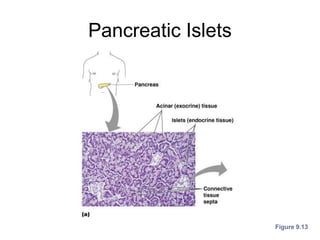
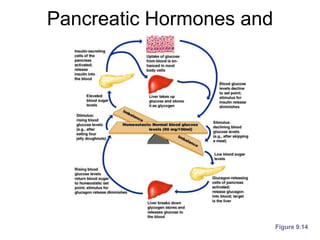
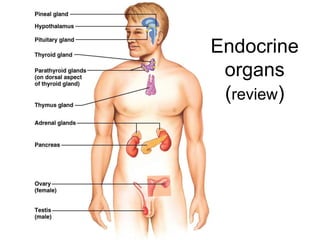
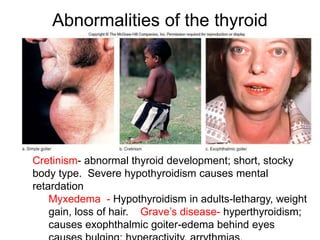
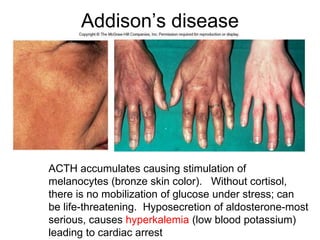
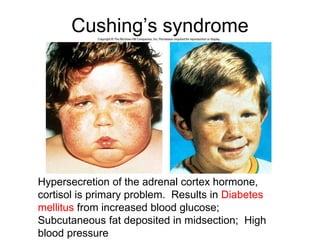
The document provides an overview of the endocrine system, detailing the roles and functions of various hormones, their sources, and mechanisms of action. It explains the regulatory processes for hormone release and describes key endocrine organs such as the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and others, along with their respective hormones and effects. Additionally, it covers developmental aspects and potential disorders related to hormone production and function.