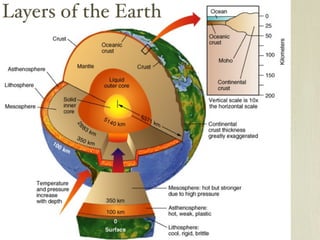
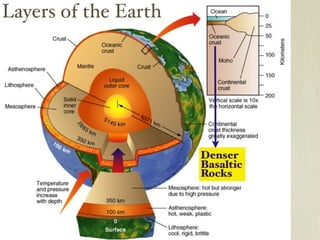
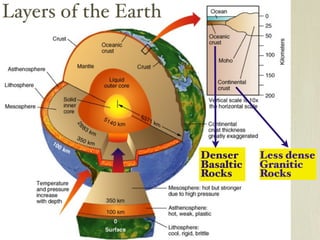
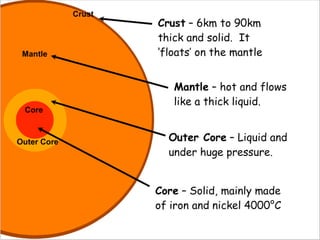
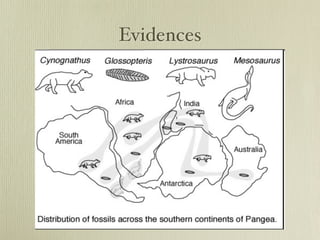
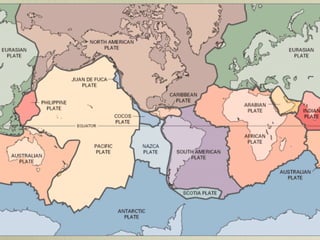
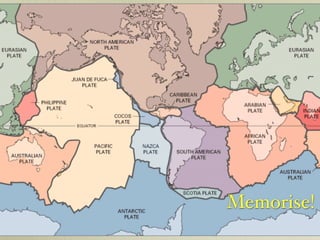
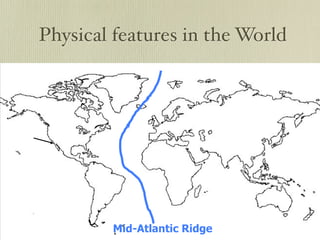
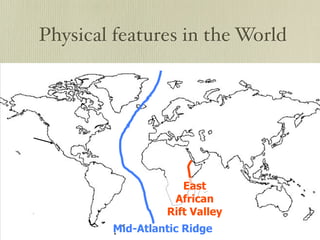
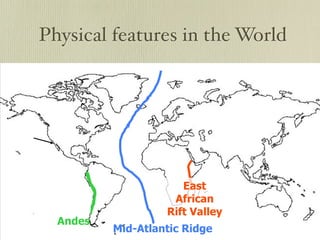
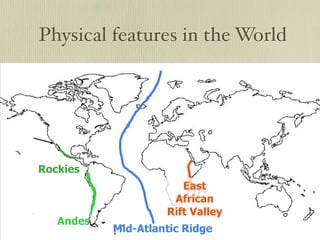
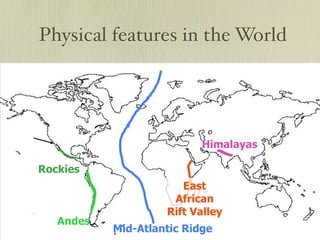
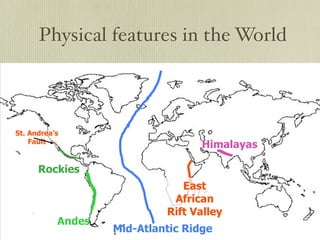
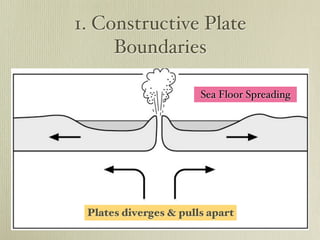
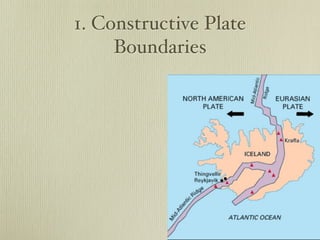
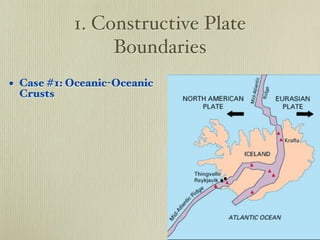
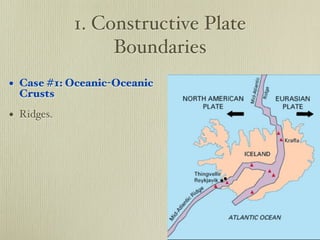
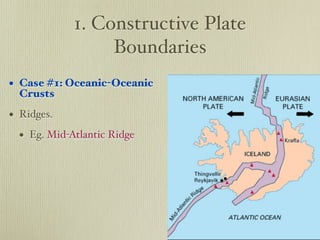
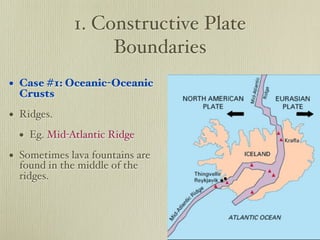
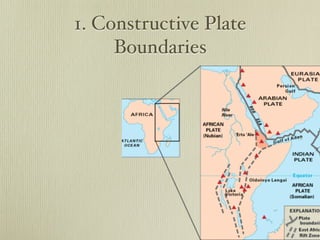
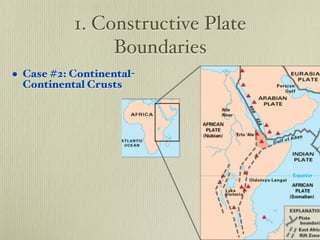
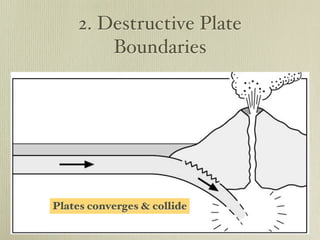
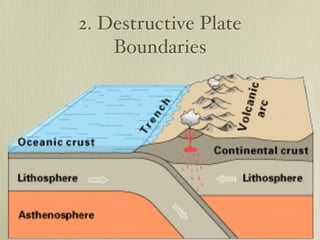
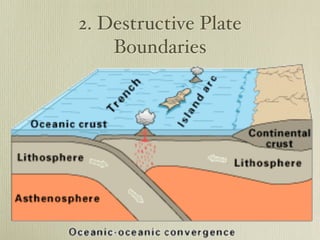
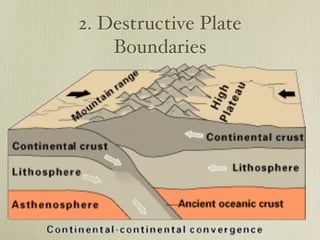
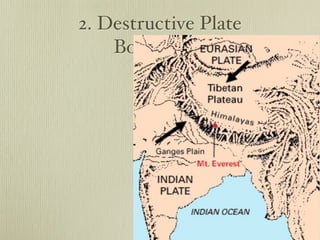
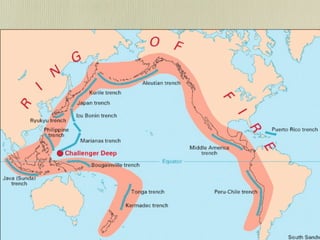
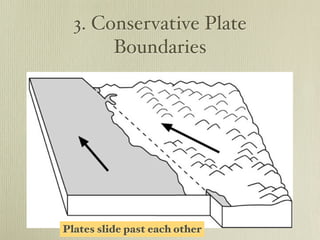
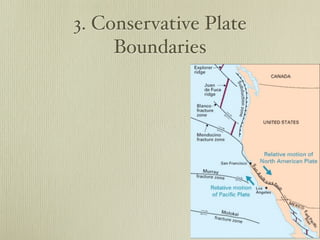
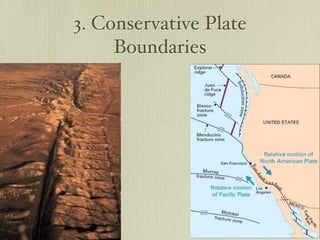
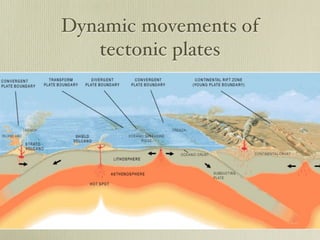
The document discusses plate tectonics and the evidence that supports continental drift. It explains that continents move as parts of tectonic plates, and describes the three types of plate boundaries: constructive where plates diverge, destructive where they converge, and conservative where they slide past each other. Examples are given of associated geological features like mid-ocean ridges, trenches, volcanoes and mountains. The movement of plates causes earthquakes and shapes the Earth's surface over time.