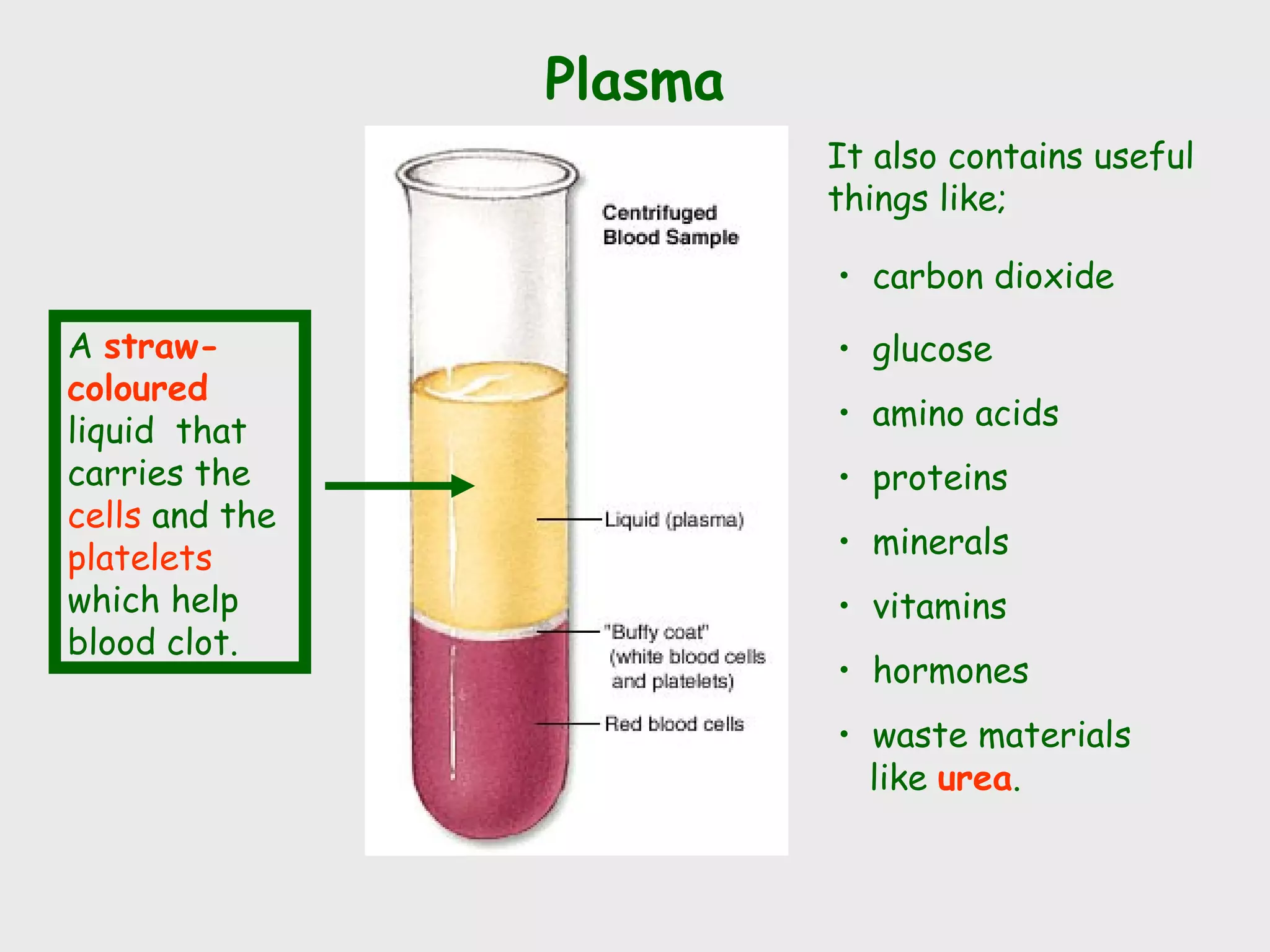
The circulatory system uses the heart to pump blood through vessels around the body. It has two circuits - pulmonary circulation between the heart and lungs, and systemic circulation between the heart and body. The heart has four chambers that pump deoxygenated blood to the lungs and oxygenated blood around the body in a continuous cycle. Blood vessels include arteries carrying blood away from the heart, veins returning it, and capillaries where exchange occurs. The circulatory system transports blood cells, platelets, plasma, oxygen, nutrients, hormones, carbon dioxide and waste products.