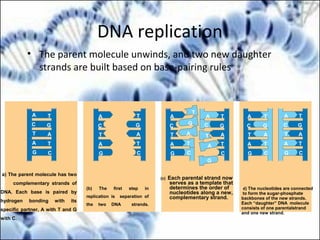
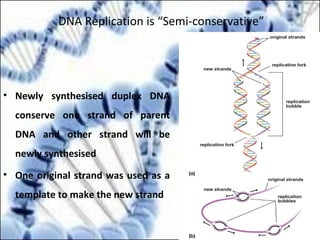
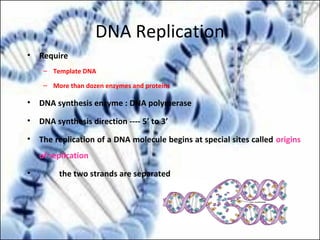
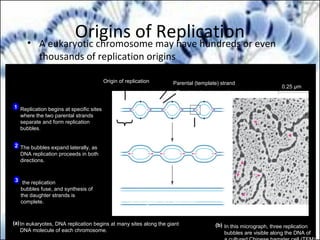
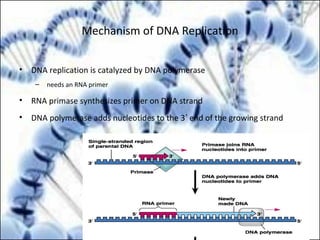
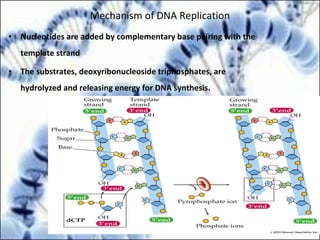
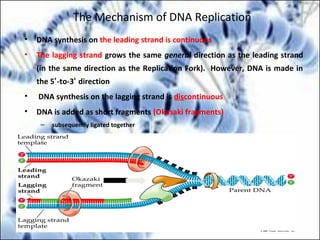
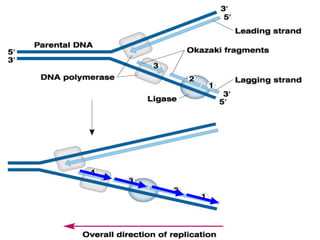
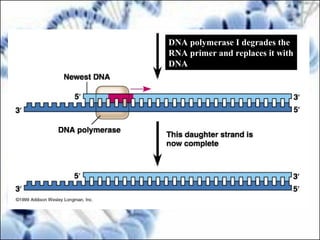
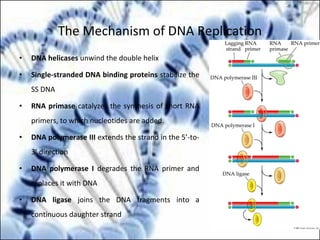
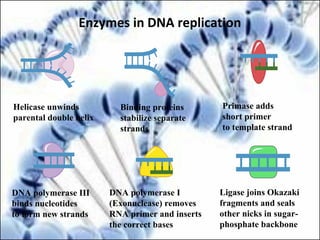
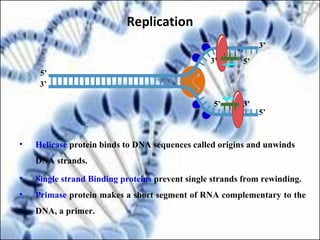
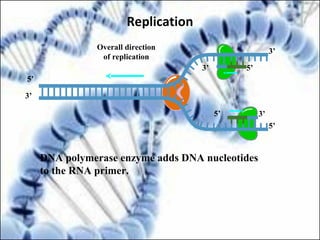
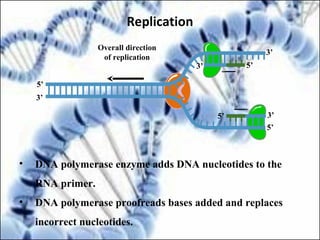
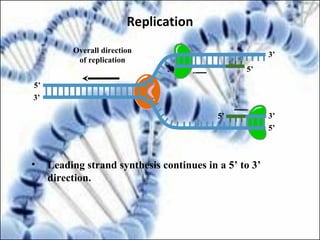
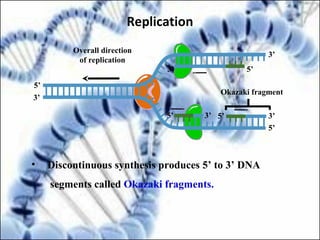
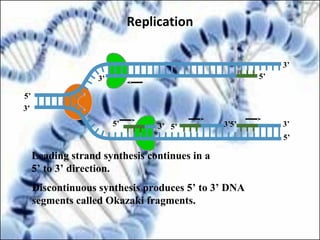
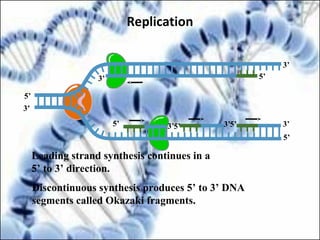
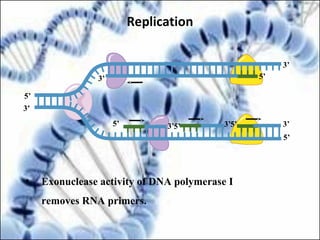
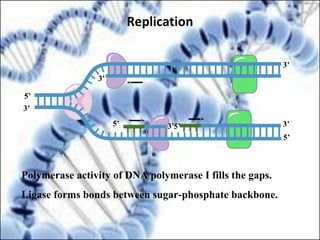
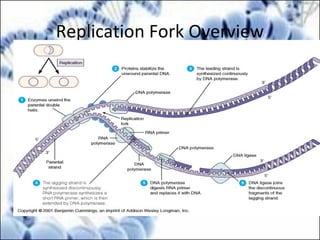
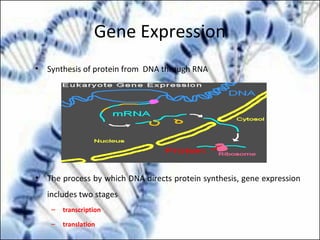
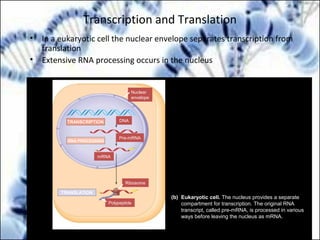
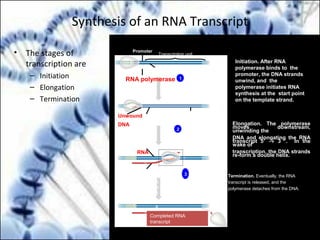
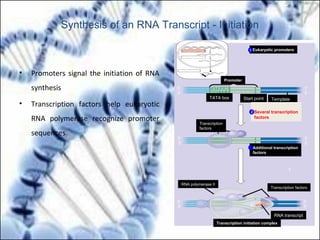
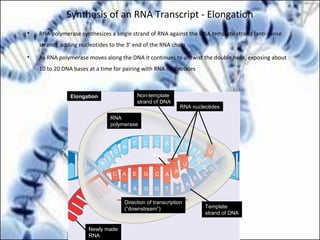
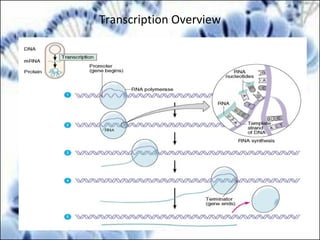
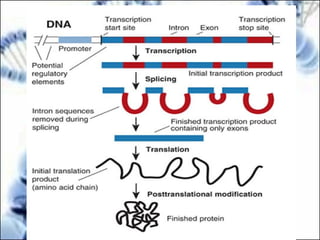
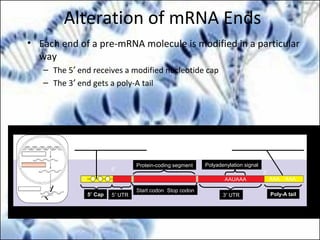
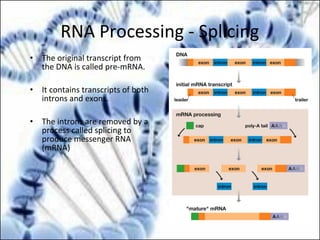
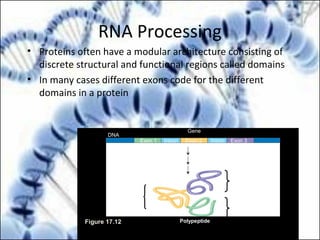
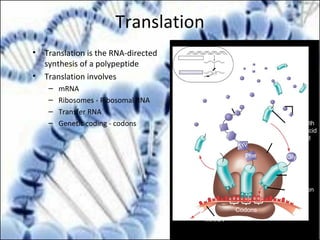
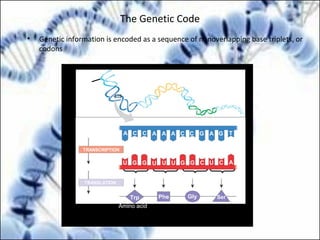
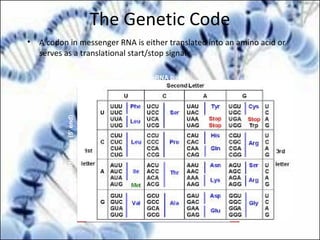
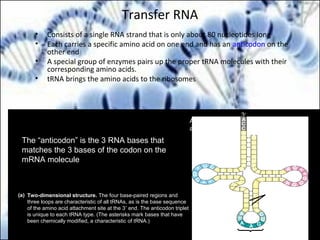
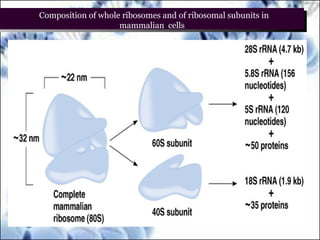
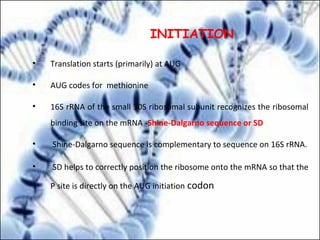
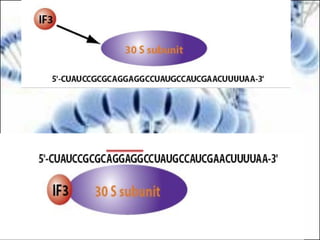
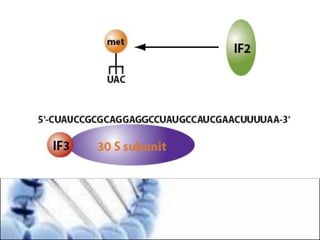
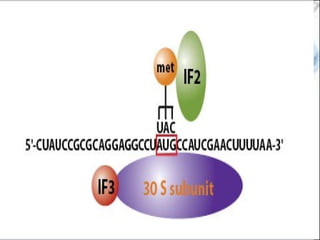
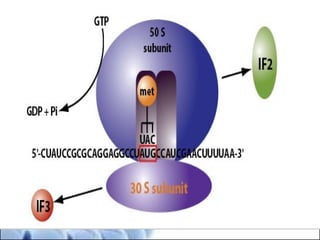
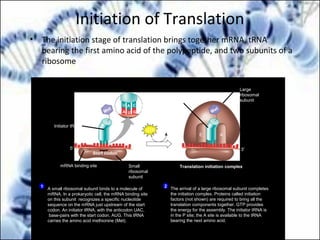
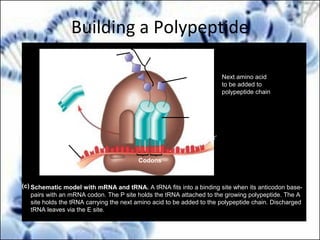
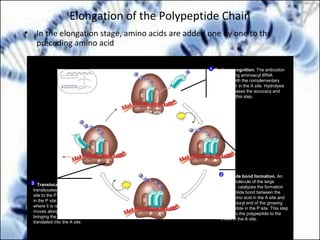
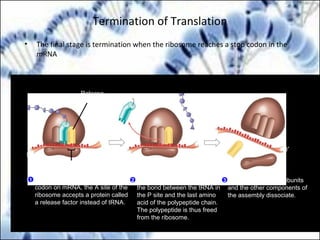
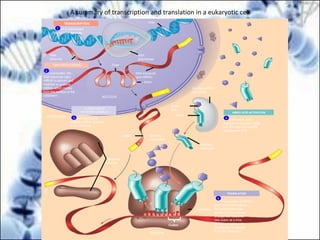
DNA replication and gene expression are the two main processes by which DNA is copied and expressed. DNA replication involves unwinding the parental DNA strands, synthesizing new complementary strands according to base pairing rules, resulting in two identical copies of the original DNA. Gene expression involves transcription of DNA into RNA and translation of RNA into protein. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and involves RNA polymerase making an RNA copy of a gene. The RNA then undergoes processing before being exported to the cytoplasm for translation by ribosomes into a polypeptide chain according to the genetic code.