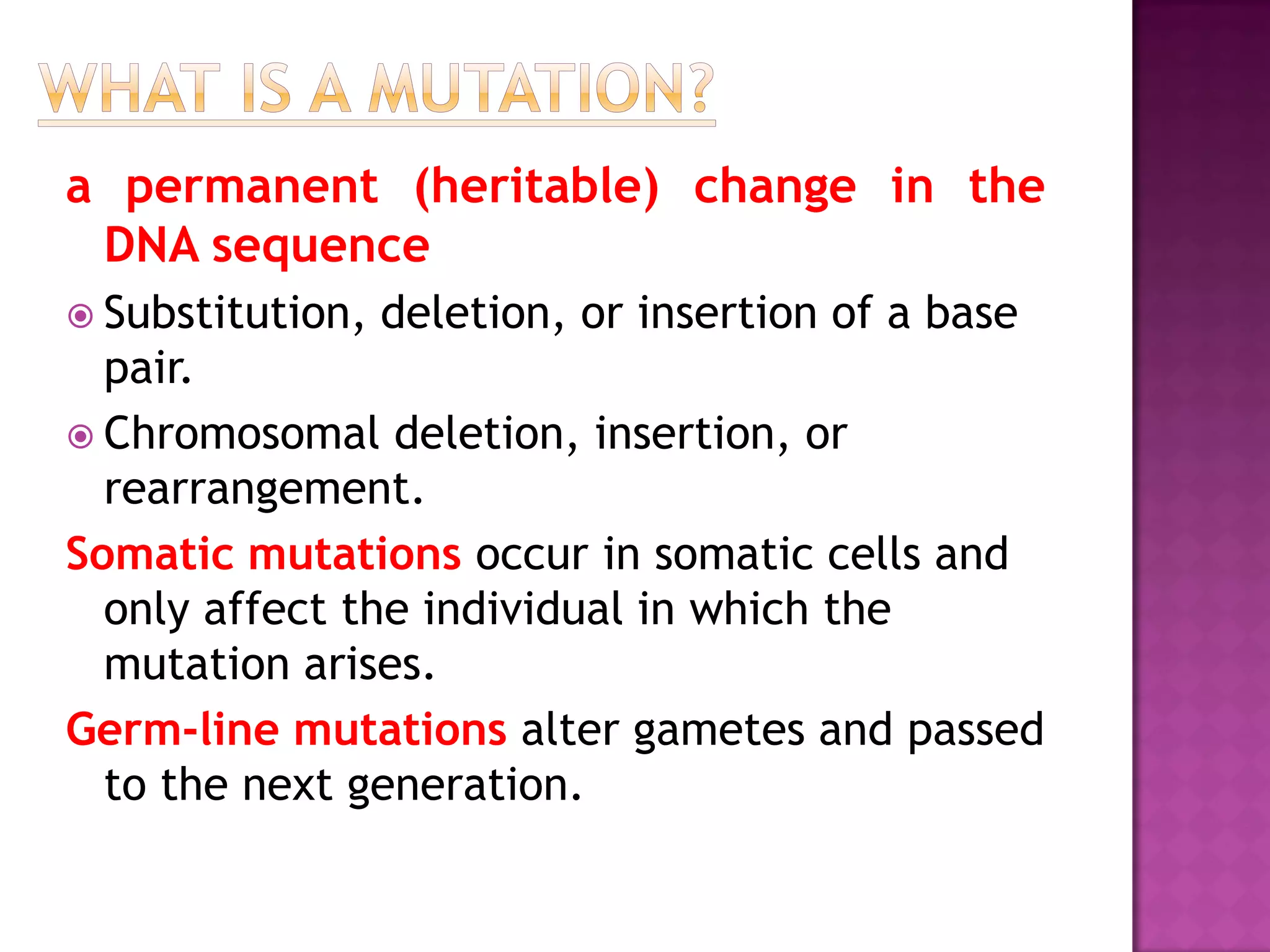
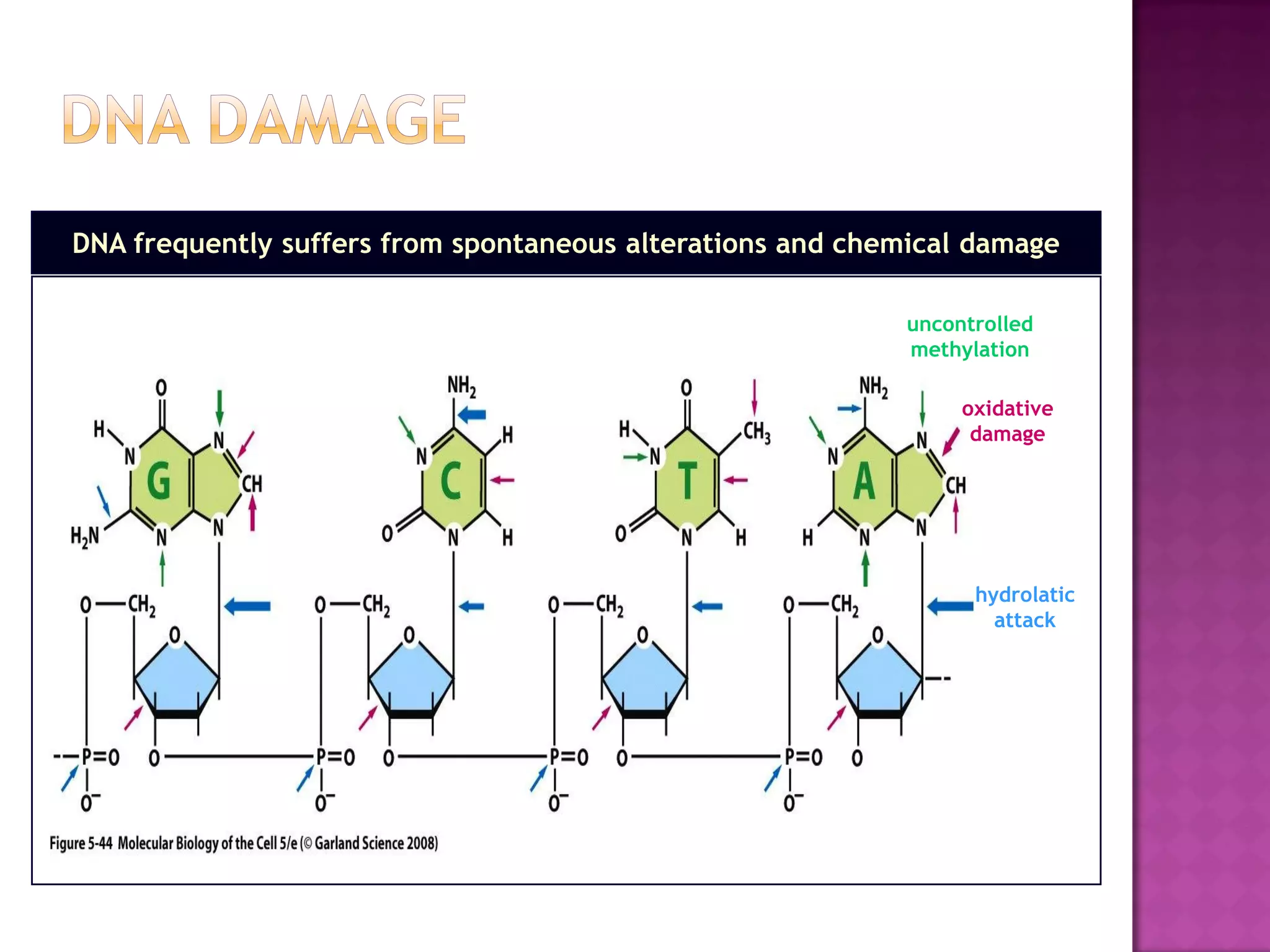
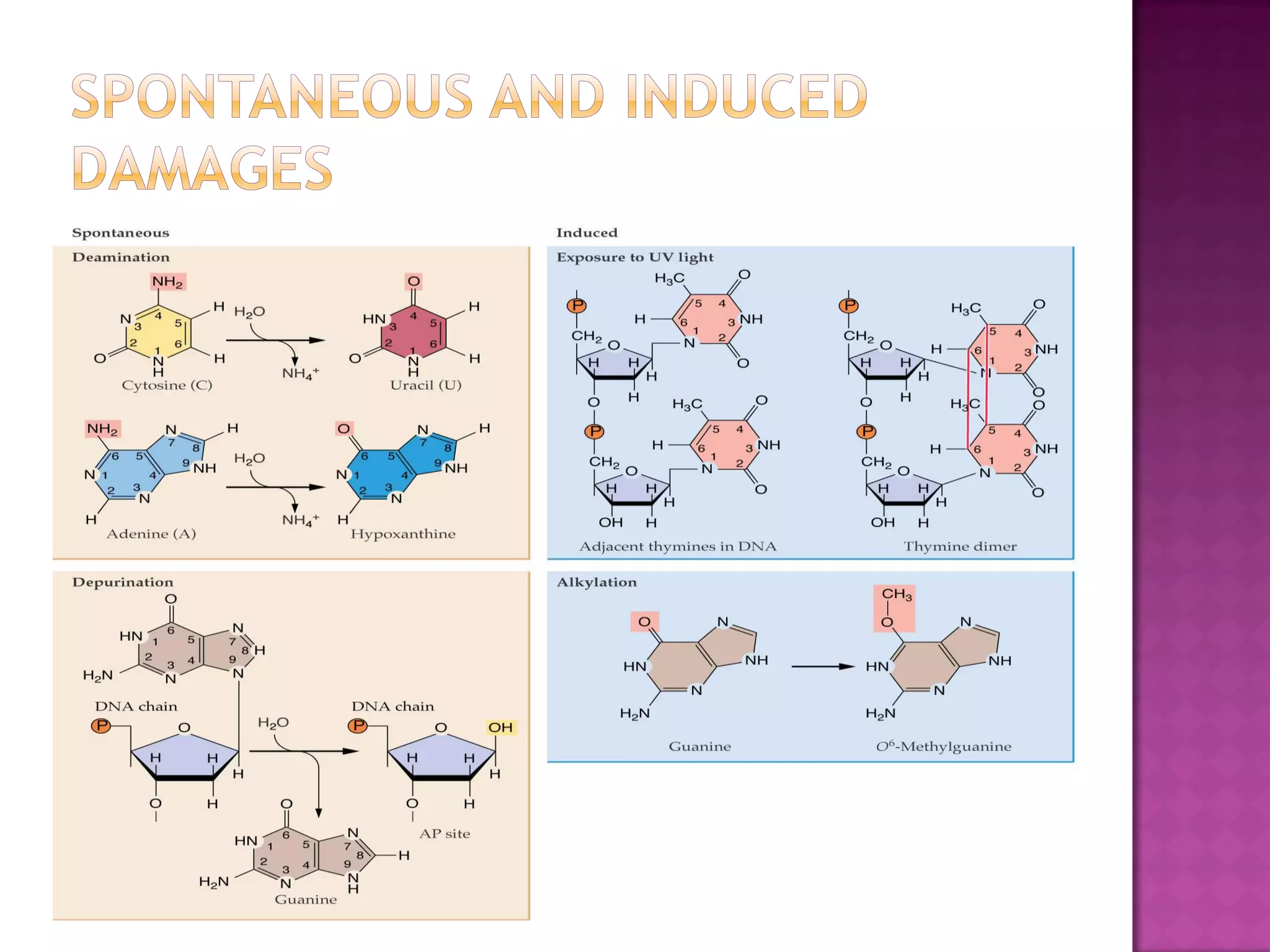
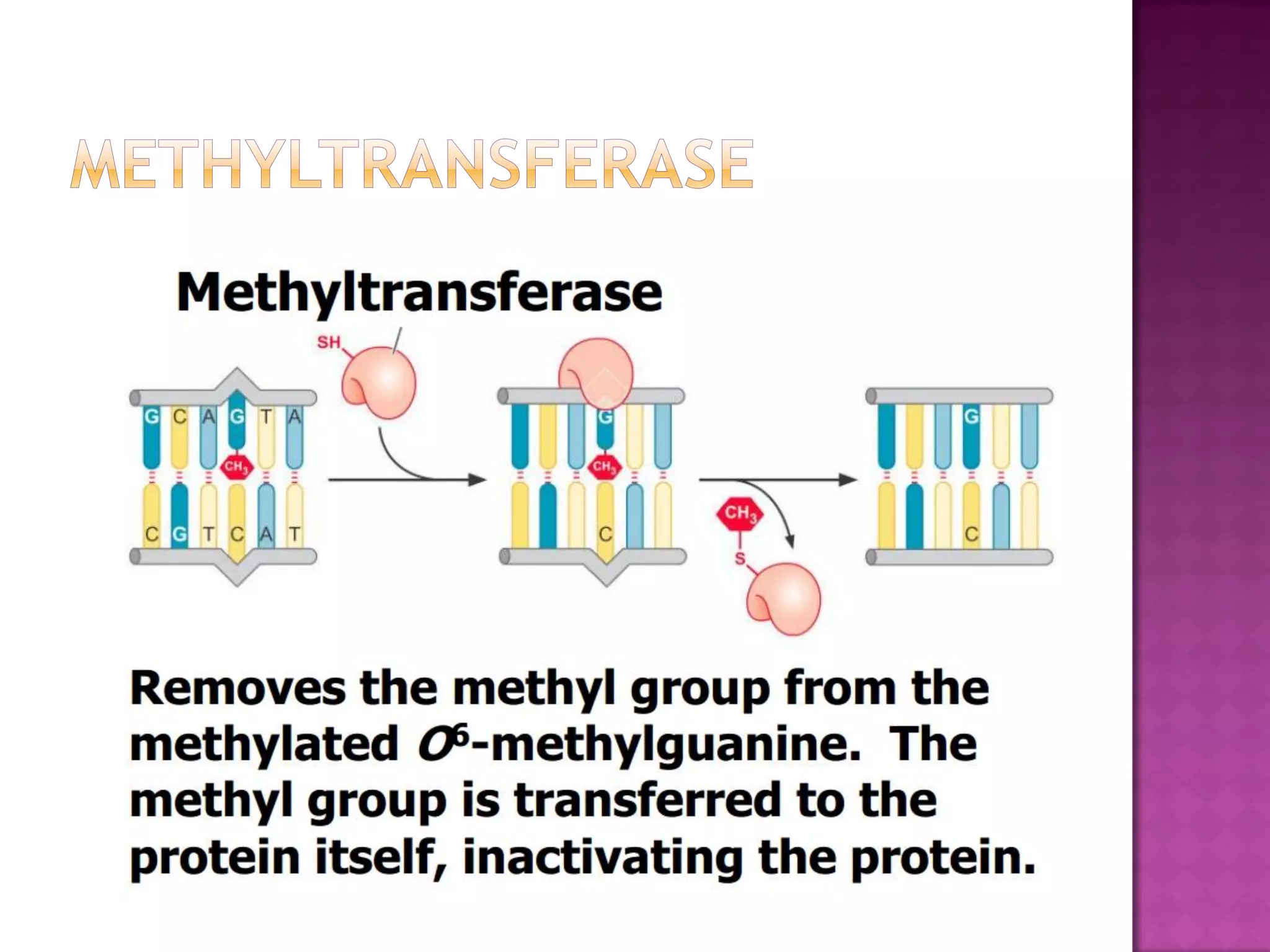
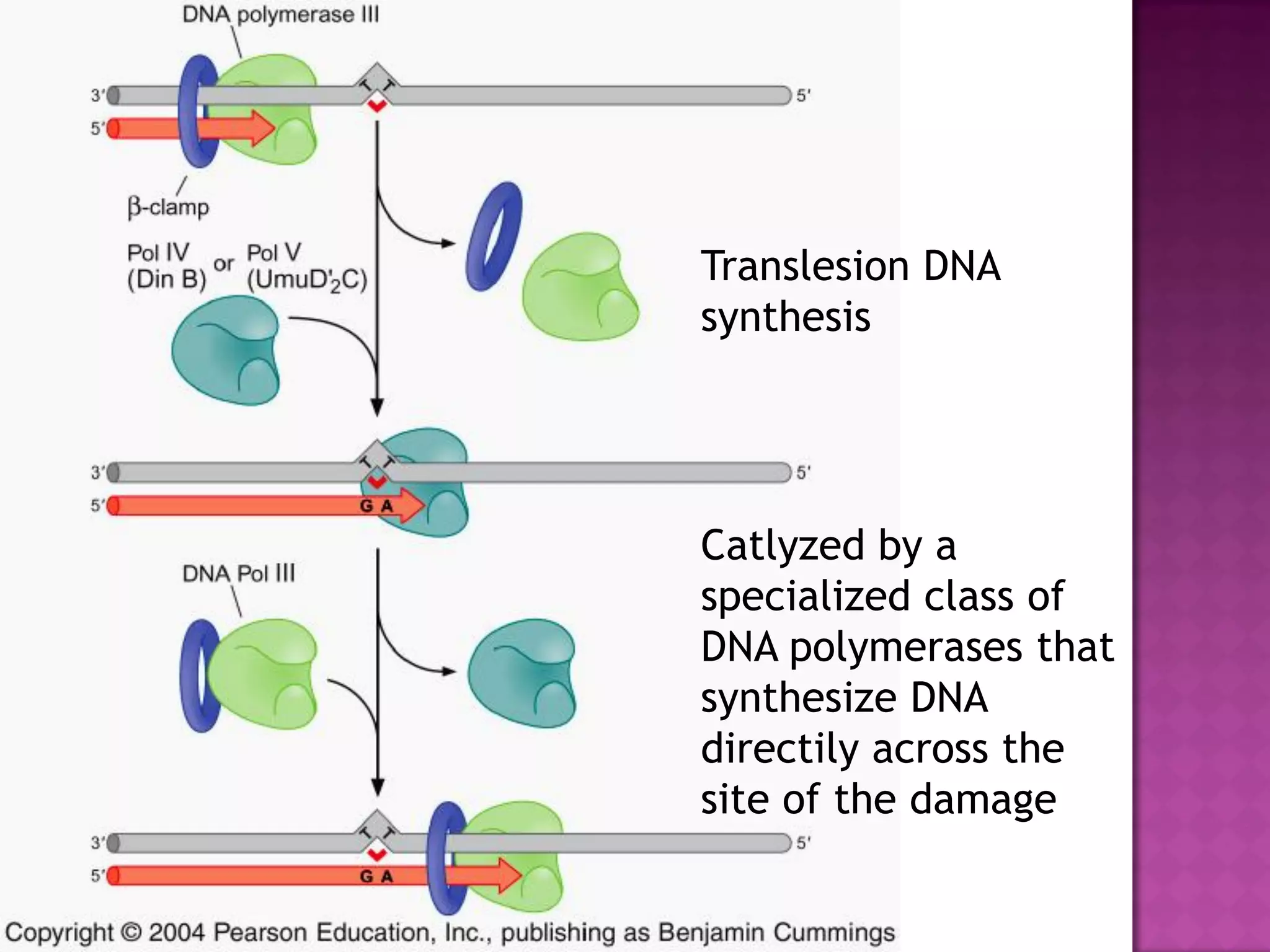
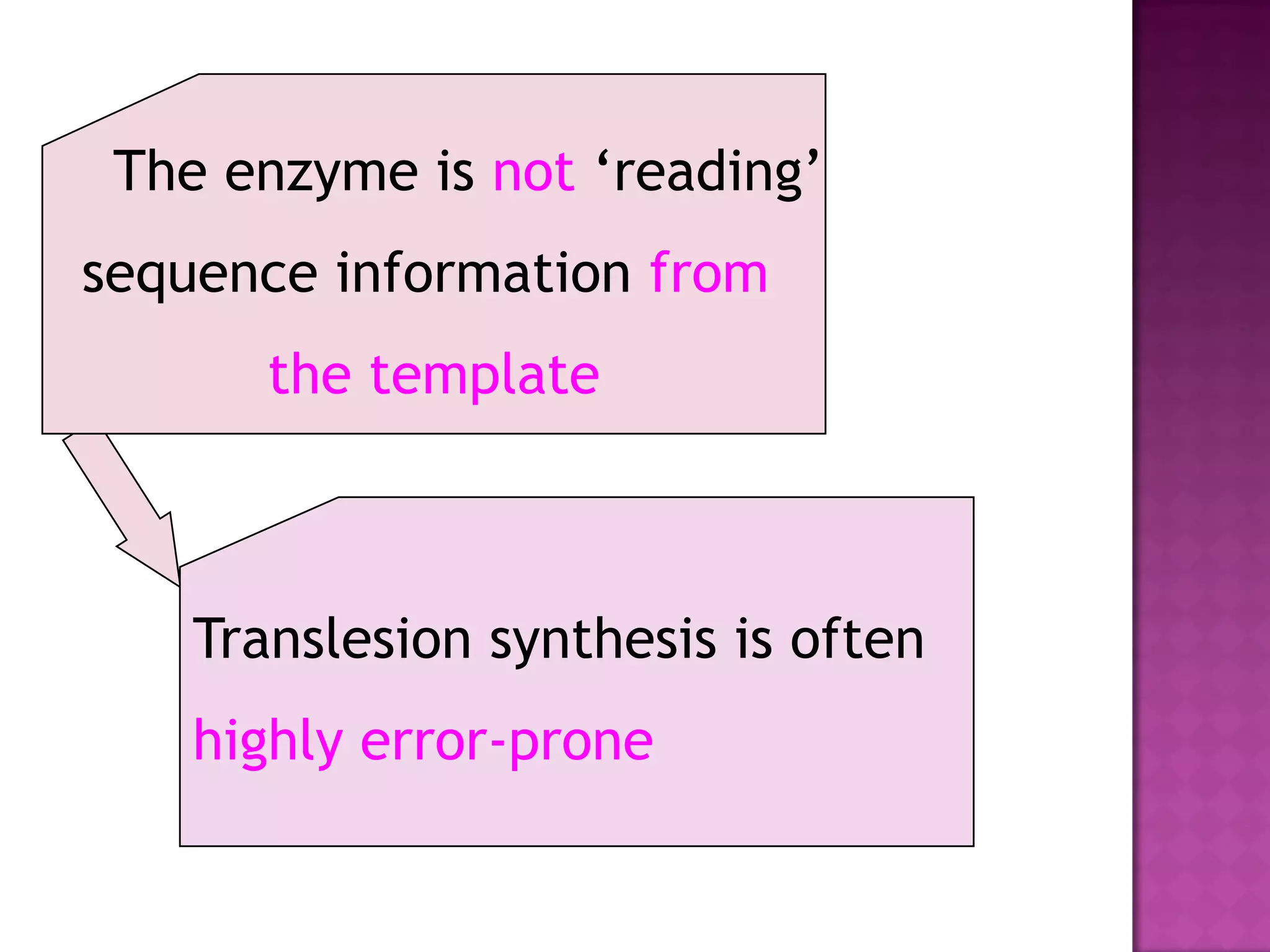
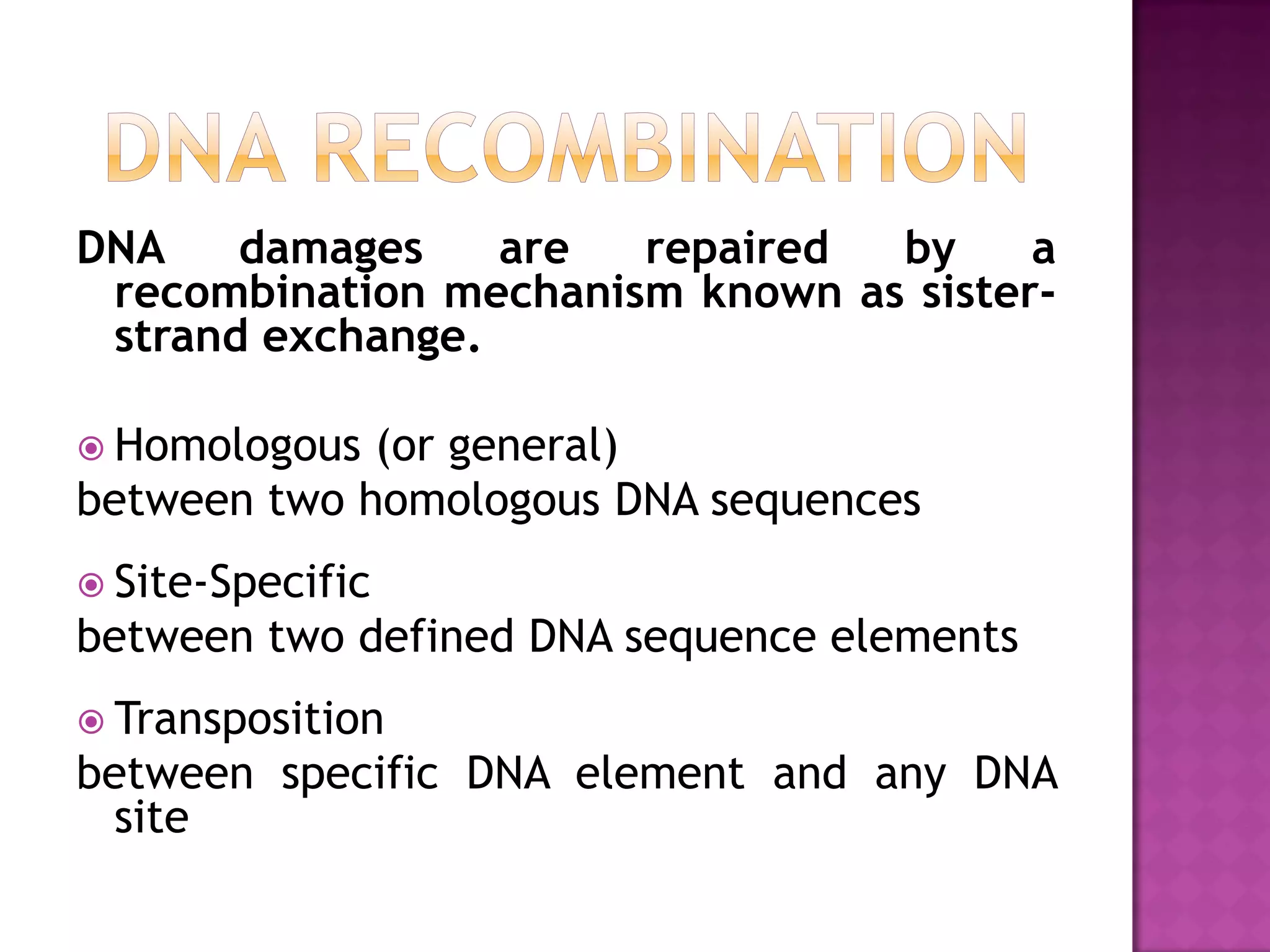
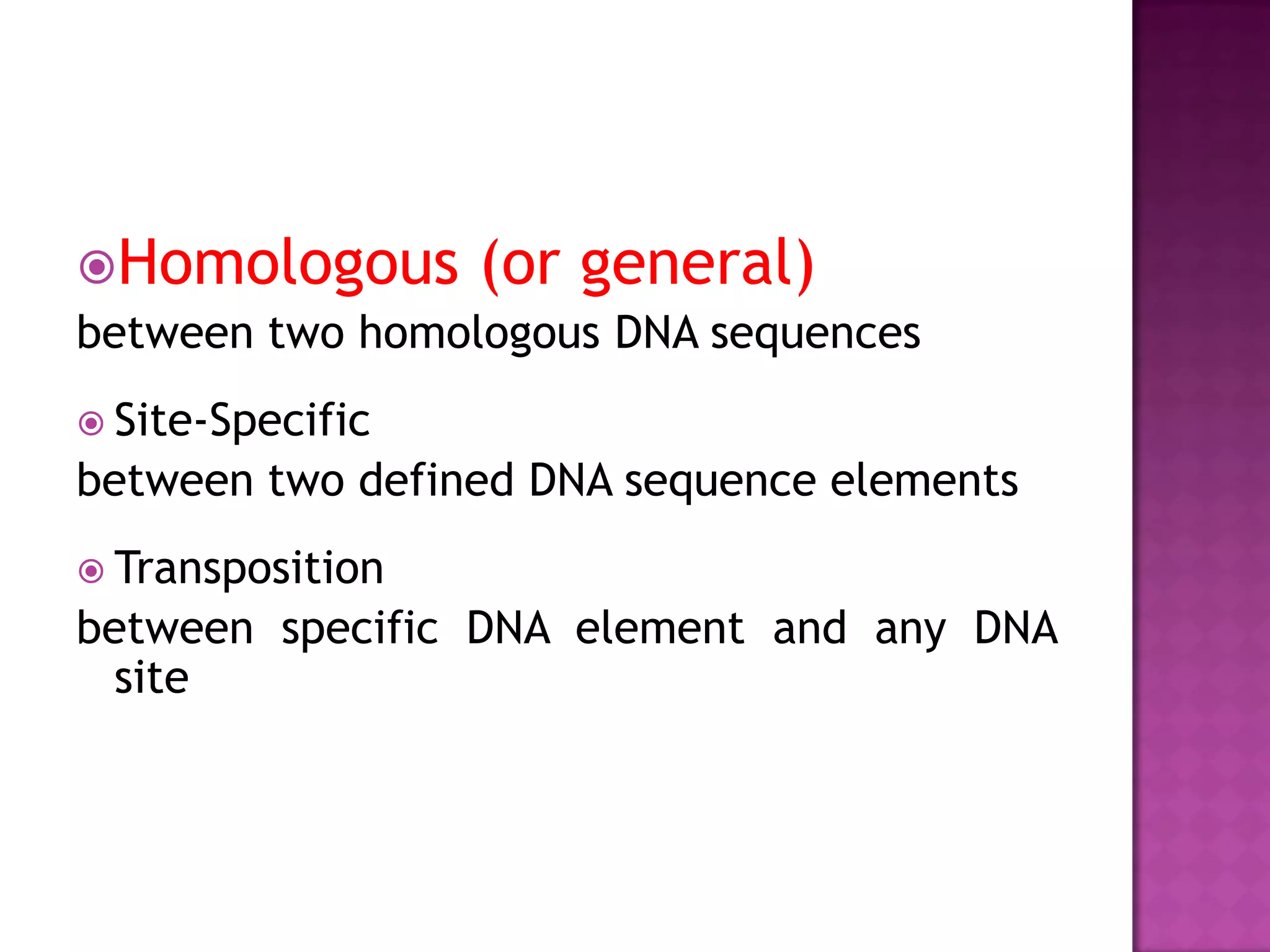
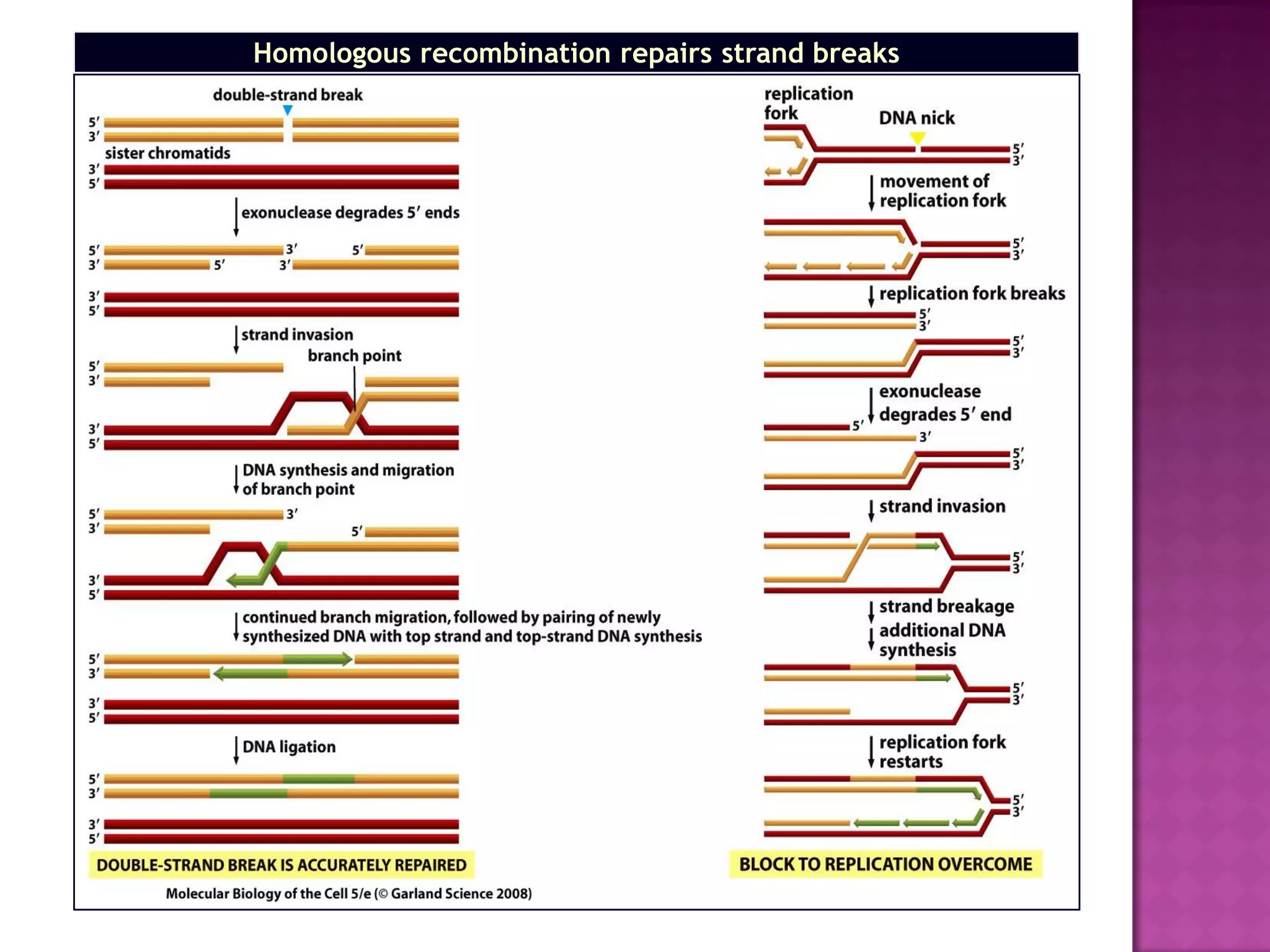
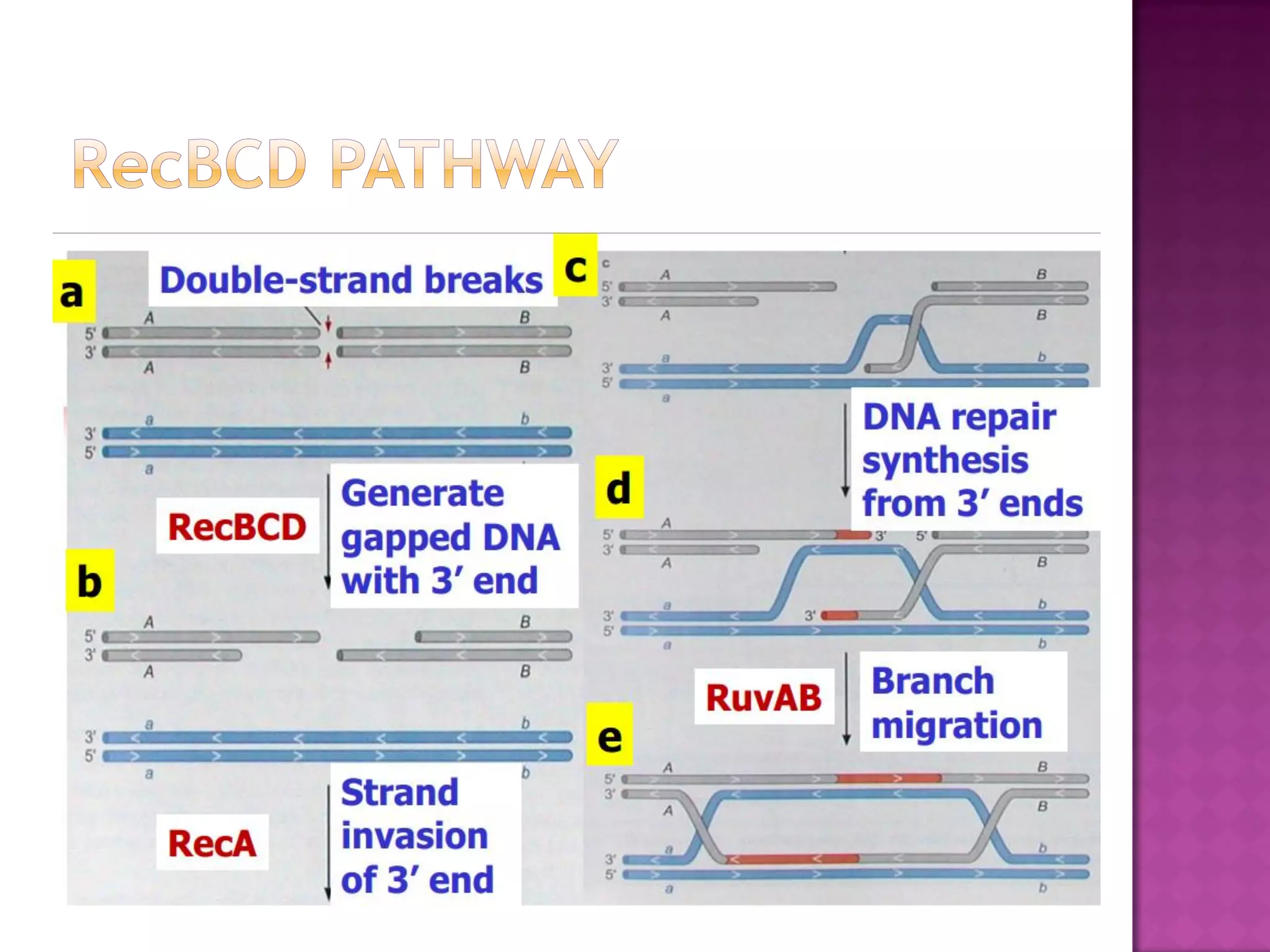
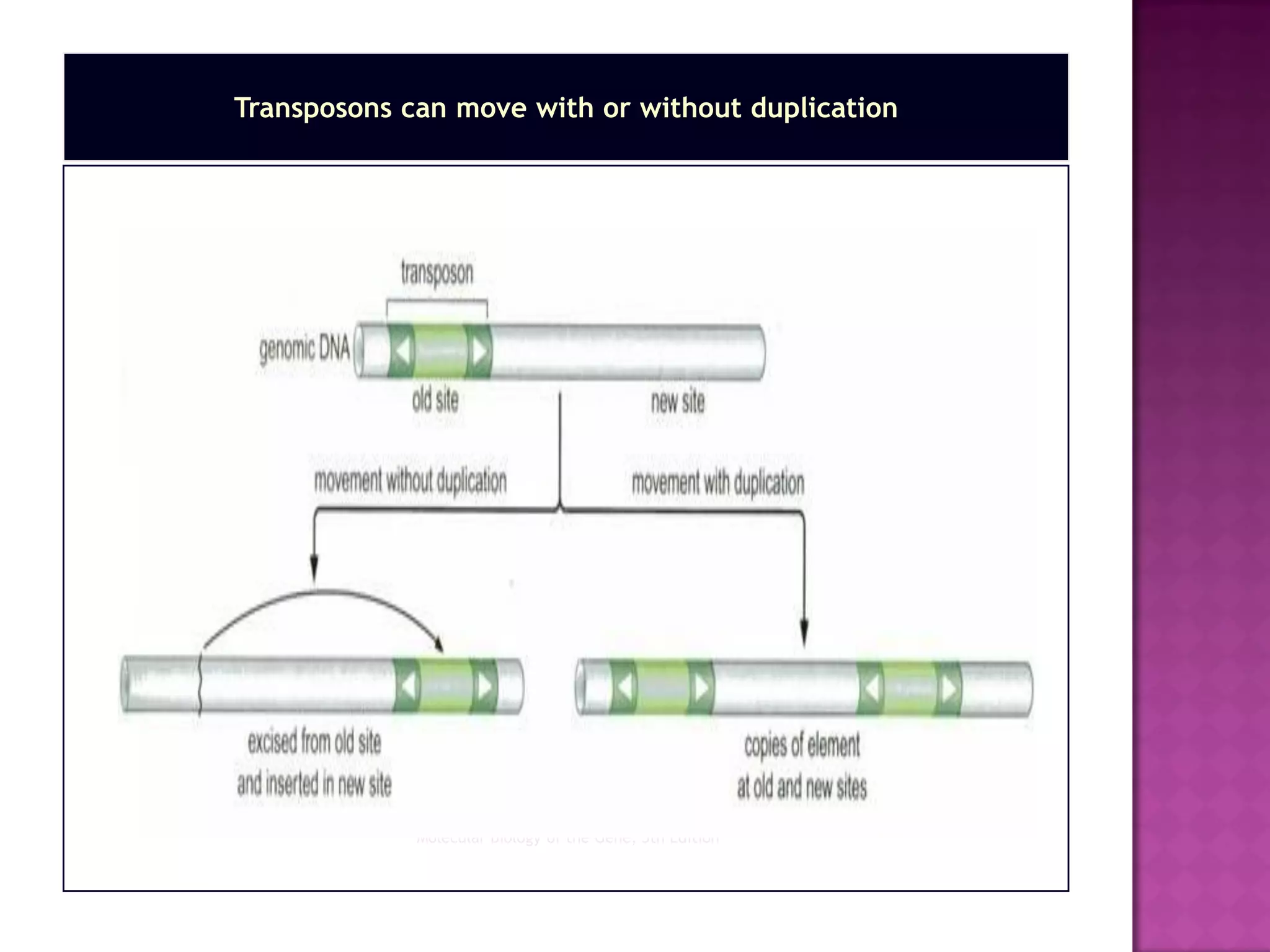
DNA repair is a collection of processes cells use to identify and correct damage to DNA. Failure to repair damaged DNA leads to mutations, which are permanent changes in the DNA sequence. There are several types of DNA damage including mismatches, modified DNA bases, and single or double strand breaks. Cells use multiple repair pathways like direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, recombination repair, and translesion DNA synthesis to fix different types of DNA damage. Homologous recombination repairs double strand breaks by exchanging DNA between similar molecules, while site-specific and transposon recombination involve movement of DNA between defined sequences.