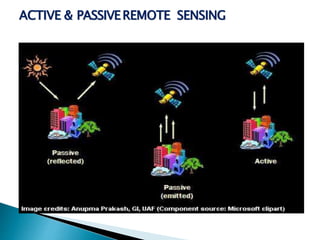
Remote sensing is a technique for obtaining information about objects without physical contact, primarily using electromagnetic radiation as a data carrier. It can be categorized into active remote sensing, which uses artificial energy sources, and passive remote sensing, which relies on natural sources like the sun. Remote sensing platforms vary from ground-based to space-borne systems, enabling a wide range of applications including agriculture, hydrology, and disaster control.