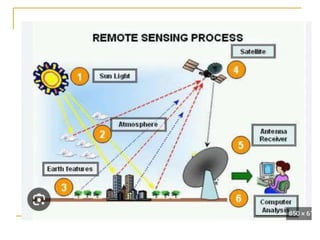
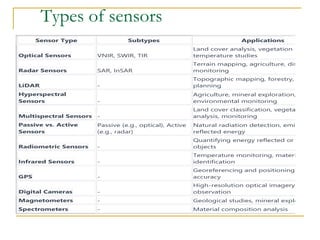
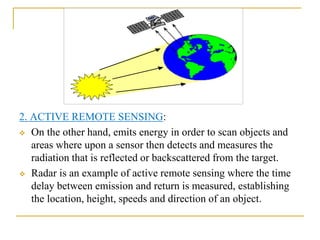
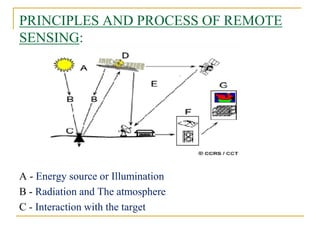
Remote sensing is the science of acquiring images and data about objects from a distance using sensors. It involves recording electromagnetic radiation reflected or emitted from objects using platforms like satellites, aircraft, and drones. There are two main types - passive sensing, which detects natural radiation, and active sensing, which emits energy and measures its reflection. Remote sensing has various applications like mapping land use, monitoring agriculture and forests, and studying geology, oceans, and the environment. It provides data over large and inaccessible areas quickly and cost-effectively. However, interpretation requires skill and data may need ground verification.