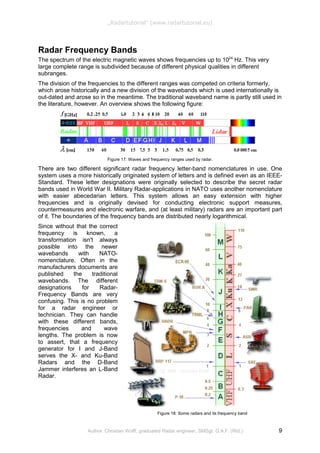
This document provides an overview of different types of radar systems. It describes primary radar, which transmits and receives its own signals, and secondary radar, which requires transponders on targets. Primary radar can determine location, distance, and sometimes altitude of targets, while secondary radar can provide more information like identification codes. Pulse radar transmits high power pulses while pulse compression radar uses weaker longer pulses. Radar can also be classified as imaging or non-imaging, monostatic or bistatic, and is used for purposes like air traffic control, weapons targeting, and weather monitoring. The goal is to understand the differences between primary and secondary radars and how various radar configurations achieve different objectives.

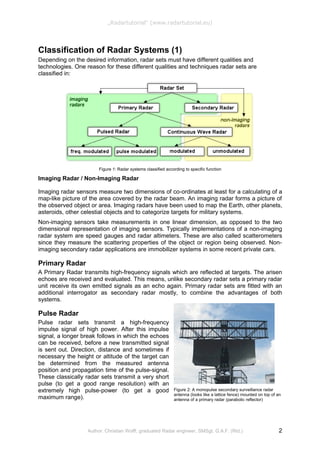
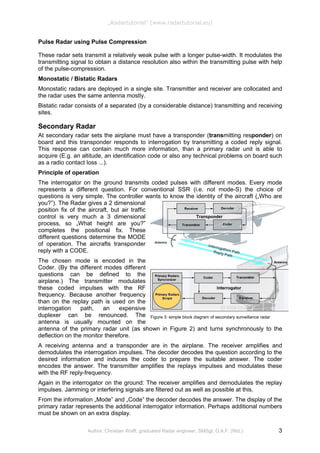


![Figure 8: Diagram of a typical 2D-Radar, the
rotating cosecant squared antenna pattern
Figure 9: Diagram of a typical 3D-Radar, a
mix of vertical electronic beam steering and
mechanically horizontal movement of a
pencil-beam
„Radartutorial“ (www.radartutorial.eu)
0
2
c t
R
∆⋅
= Where: c0 = speed of light = 3·108
m/s
Δt = measured time-difference [s]
R = distance altimeter to terrain [m] (2)
This kind of radar is used as “radar altimeter” often. The radar altimeter is used to measure
the exact height during the landing procedure of aircraft. Radar altimeters are also a
component of terrain avoidance warning systems, telling the pilot that the aircraft is flying too
low or that terrain is rising to meet the aircraft.
Classification of Radar Sets (2)
Radar systems may be divided into types based on the designed use. This section presents
the general characteristics of several commonly used radar systems:
Figure 7: Classification of radar sets according its use
Although any and every radar can be abused as military radar, the necessary distinction as
military or civil radar has legal causes often.
Air-defense Radars
Air-Defense Radars can detect air targets and determine
their position, course, and speed in a relatively large
area. The maximum range of Air-Defense Radar can
exceed 300 miles, and the bearing coverage is a
complete 360-degree circle. Air-Defense Radars are
usually divided into two categories, based on the amount
of position information supplied. Radar sets that provide
only range and bearing information are referred to as
two-dimensional, or 2D, radars. Radar sets that supply
range, bearing, and height are called three-dimensional,
or 3D, radars.
Air-Defense Radars are used as early-warning devices
because they can detect approaching enemy aircraft or
missiles at great distances. In case of an attack, early
detection of the enemy is vital for a successful defense
against attack. Antiaircraft defenses in the form of anti-
aircraft artillery (abbreviated to „AAA”), missiles, or fighter
planes must be brought to a high degree of readiness in
time to repel an attack. Range and bearing information, provided by Air-Defense Radars,
used to initially position a fire-control tracking radar on a target.
Another function of the Air-Defense Radar is guiding combat air patrol (CAP) aircraft to a
position suitable to intercept an enemy aircraft. In the case of aircraft control, the guidance
information is obtained by the radar operator and passed to the aircraft by either voice radio
or a computer link to the aircraft.
Author: Christian Wolff, graduated Radar engineer, SMSgt. G.A.F. (Rtd.) 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/radartutorial-130925075341-phpapp01/85/Radar-tutorial-6-320.jpg)