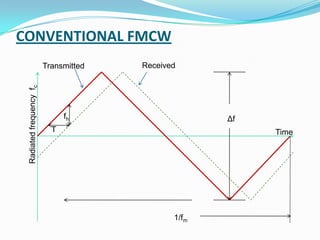
This document discusses different types of aircraft altimeters. It describes three main types: pulse type radio altimeter, conventional FMCW altimeter, and constant difference frequency FMCW altimeter. It focuses on explaining the basic principle and operation of conventional FMCW altimeters. The conventional FMCW altimeter measures altitude by varying the carrier frequency linearly over time and determining the change in frequency during the round trip travel time to calculate altitude. The beat frequency detected is directly proportional to the aircraft's altitude.