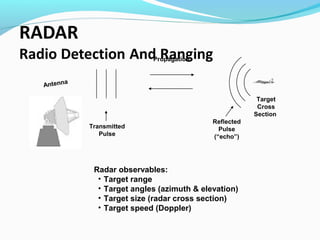
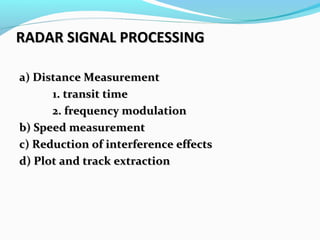
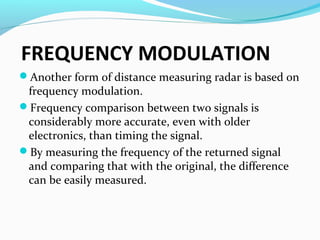
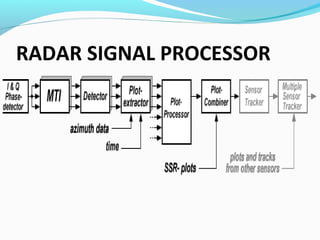
RADAR uses radio waves to detect distant objects. It transmits pulses and measures properties of the reflected pulses, including range, angles, size, and speed of targets. RADAR signal processing involves measuring distance using transit time or frequency modulation, measuring speed using Doppler effect, and reducing interference through techniques like moving target indication and constant false alarm rate processing. The signal processor separates targets from clutter based on Doppler shifts and amplitude. RADAR has military, navigation, and civilian applications including air traffic control and law enforcement.