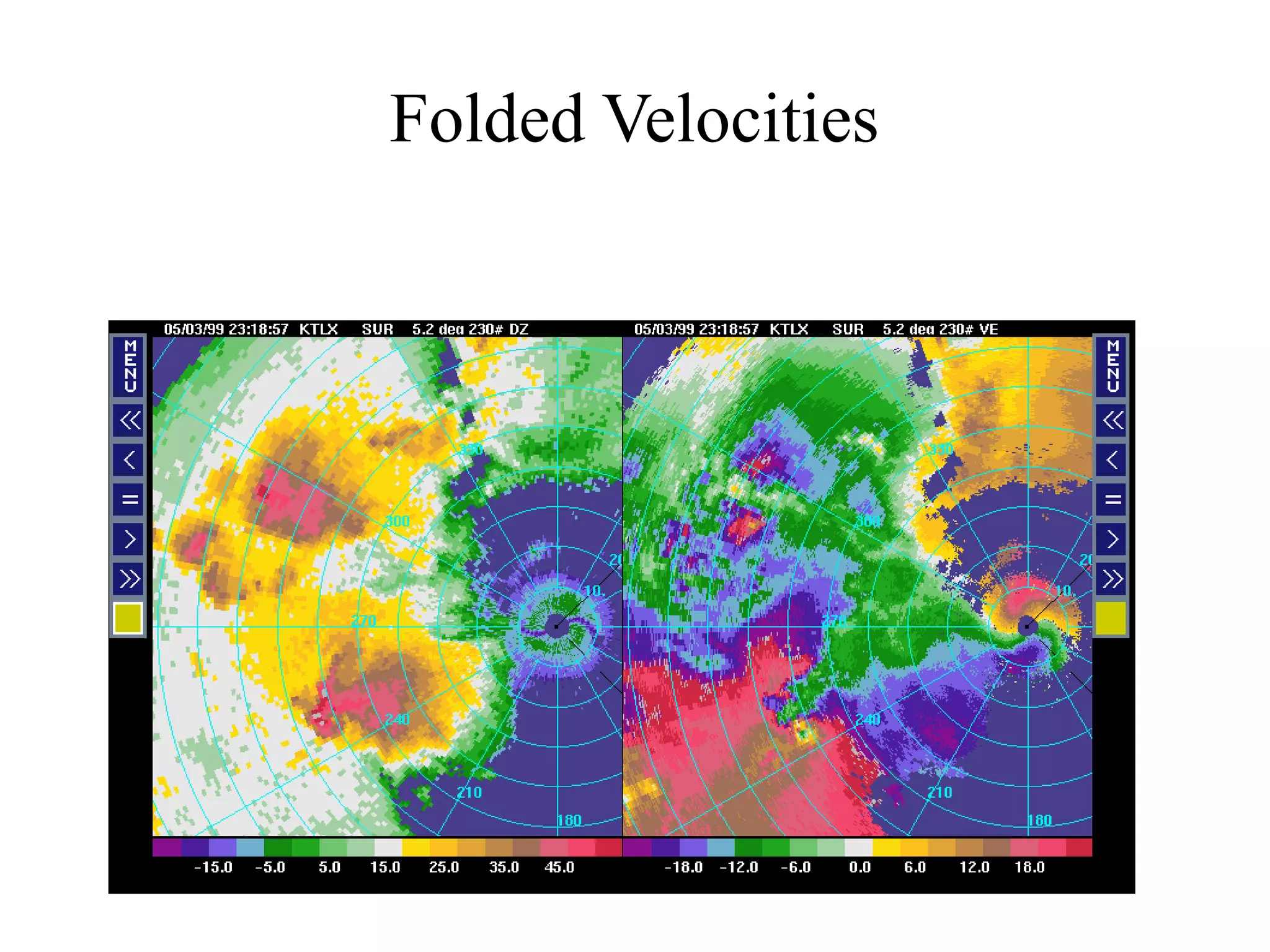
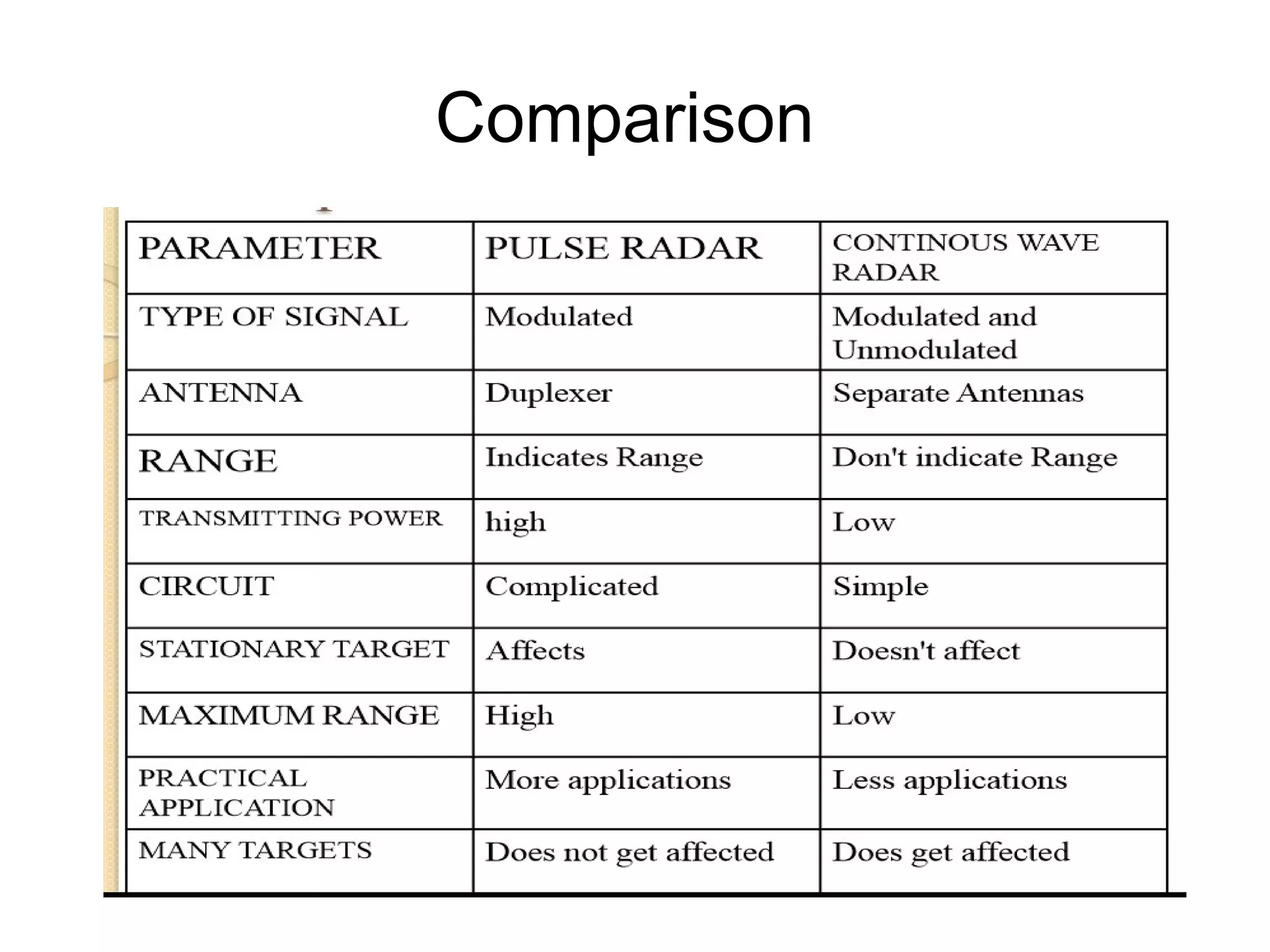
This document discusses different types of pulse radar. It begins with an introduction to radar and its advantages and disadvantages. It then describes pulse radar, which transmits high power pulses to determine a target's range and velocity. Two types of pulse radar are moving target indicator (MTI) radar and pulse Doppler radar. MTI radar uses the Doppler effect and low pulse repetition frequency to distinguish between moving and stationary targets. Pulse Doppler radar uses a high pulse repetition frequency to avoid Doppler ambiguities but can cause range ambiguities. The document compares MTI and pulse Doppler radar and their applications including for unmanned aerial vehicles.



















![References
● “Types of Radar”, Engineers Garage,2012[online].
Available: http://www.engineersgarage.
com/articles/type-of-radars
● “Types of Radar”, Cristian Wolff, June 10,
2012[online]. Available:http://www.radartutorial.
eu/02.basics/rp05.en.html
● “Radar Basics”, Infoplease, September 22, 2012
[online]. Available: http://www.infoplease.
com/ce6/sci/A0860616.html
● “Principles of communication”,Nptel,IITB(online)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulsedopplerradar-141011140258-conversion-gate01/75/Pulse-Doppler-Radar-22-2048.jpg)
