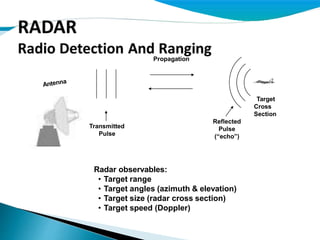
Radar signal processing techniques allow radar systems to measure key target attributes like range, speed, and direction. Transit time and frequency modulation methods are used to calculate target range. Doppler effect and change in distance over time allow measurement of target speed. Signal processing reduces interference to extract target information from clutter. Hardware implementations of fast Fourier transforms pipeline the processing.