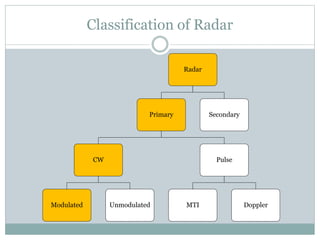
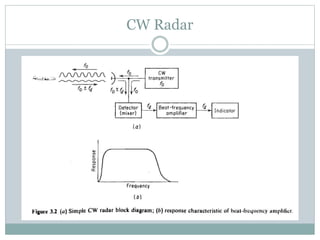
This document discusses continuous wave (CW) radar and frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) radar. It defines radar as an electromagnetic device that can detect objects hidden from view using radio waves. Radar is classified into primary types including CW and modulated radar. CW radar uses the Doppler effect to detect moving targets based on changes in transmitted frequency. However, CW radar cannot determine range. FMCW radar modulates the transmitted frequency over time and compares the received frequency to determine both range and radial velocity of targets. Key applications of radar include military surveillance, weather monitoring, air traffic control and more.