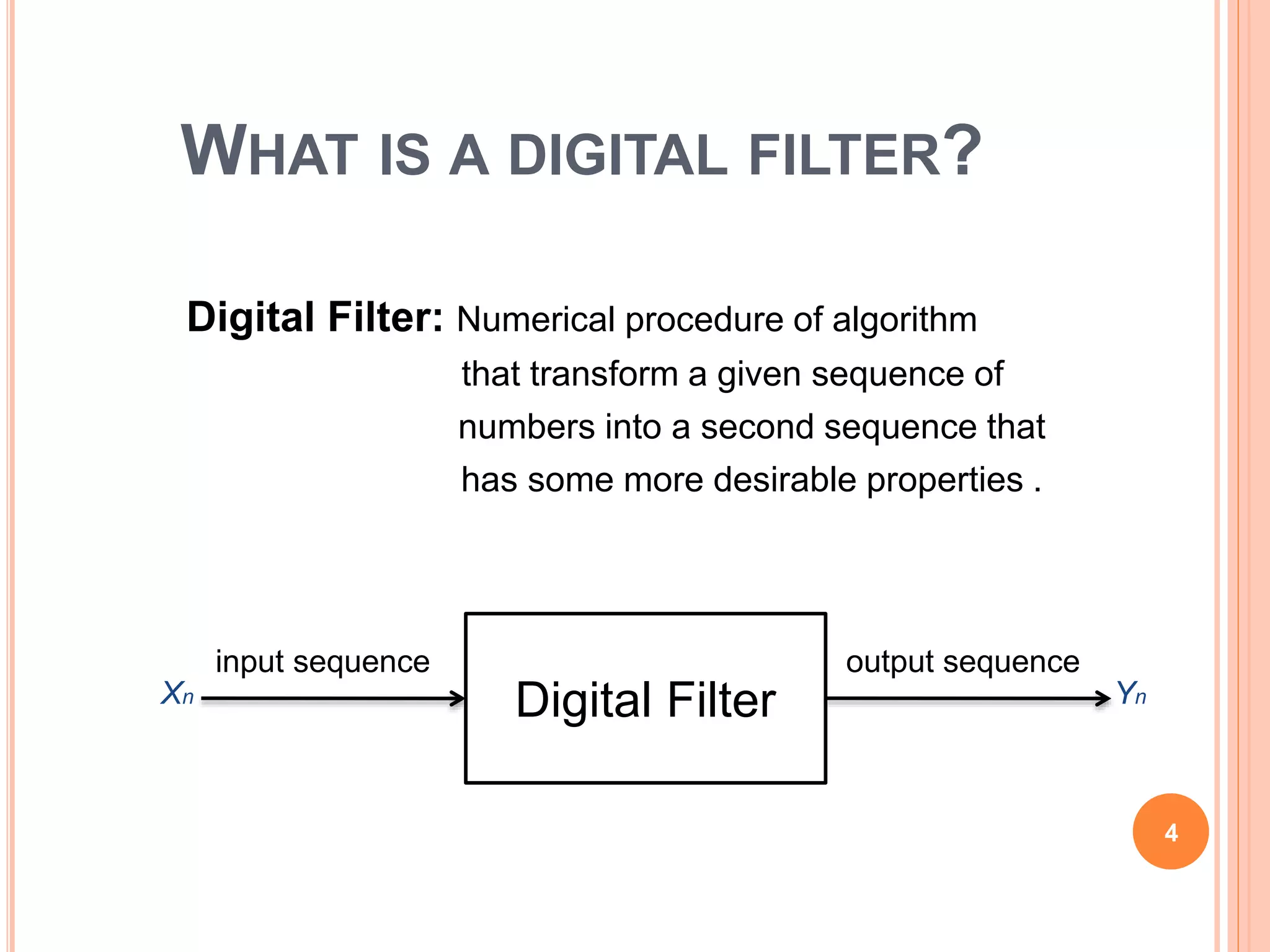
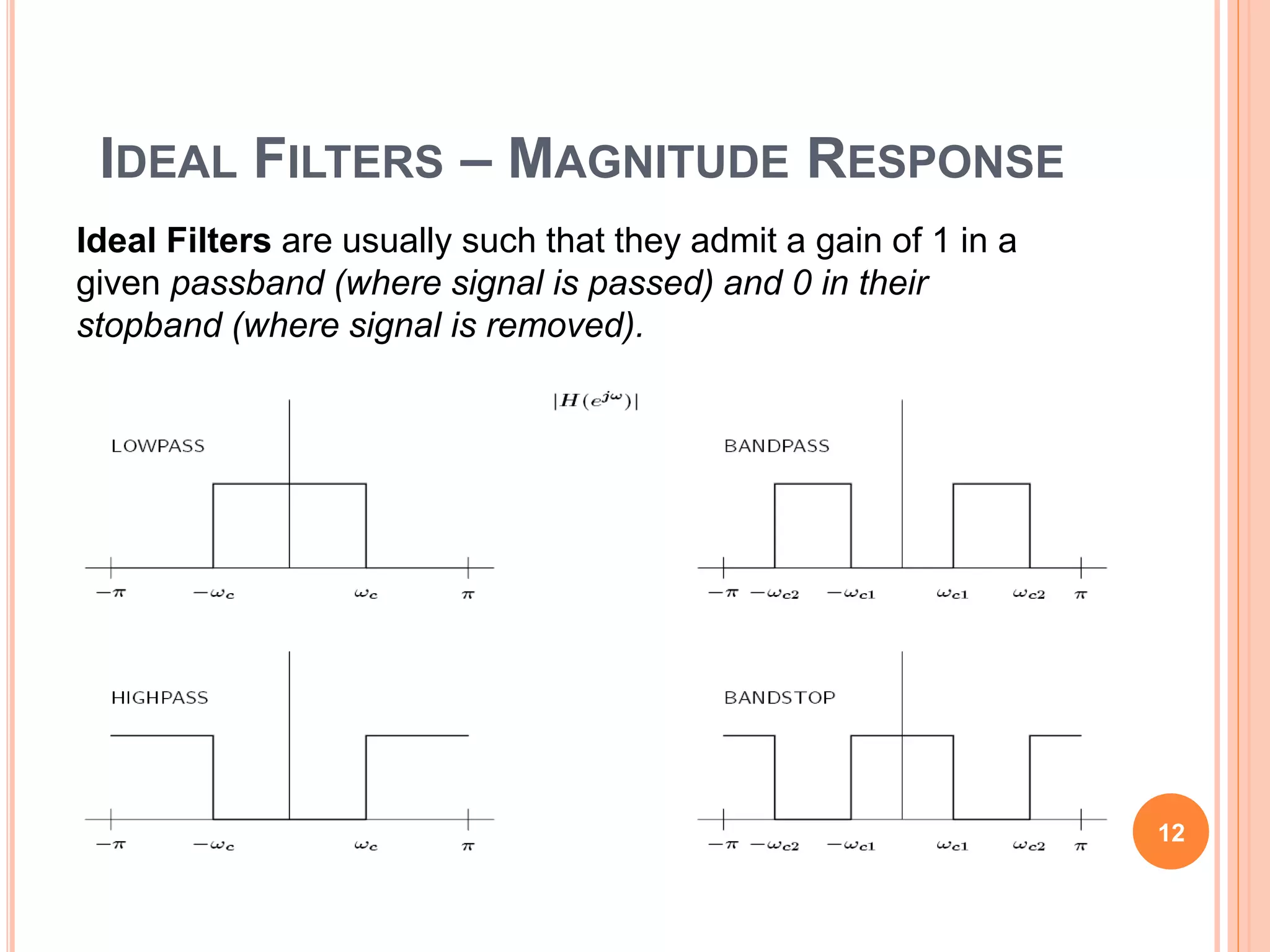
The document provides an overview of digital filters, including their definitions, features, and types such as FIR (Finite Impulse Response) and IIR (Infinite Impulse Response) filters. It discusses the importance of filter specifications and how ideal filters cannot be realized due to practical limitations. Examples of filtering applications include noise suppression in audio signals and image processing enhancements.