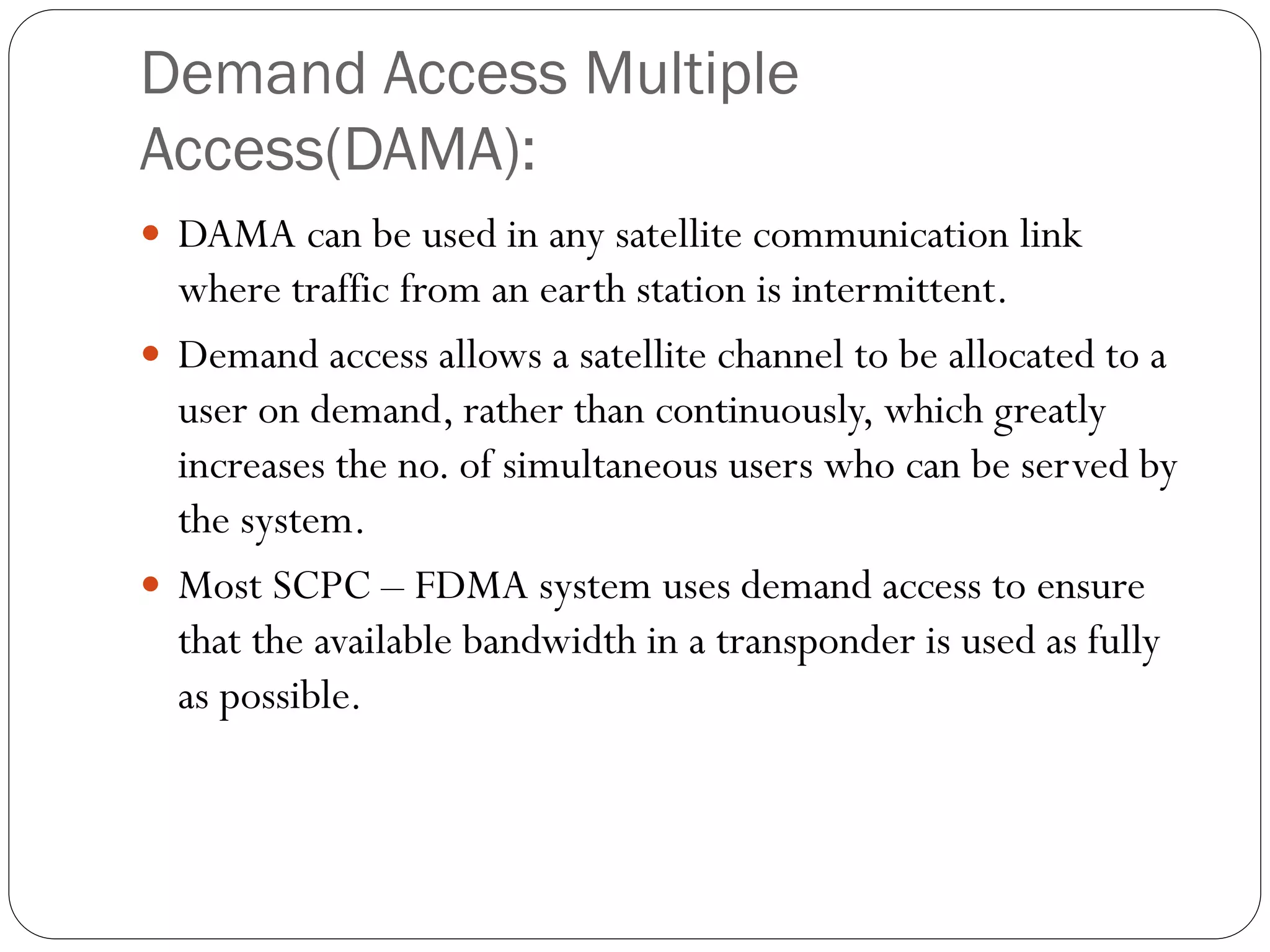
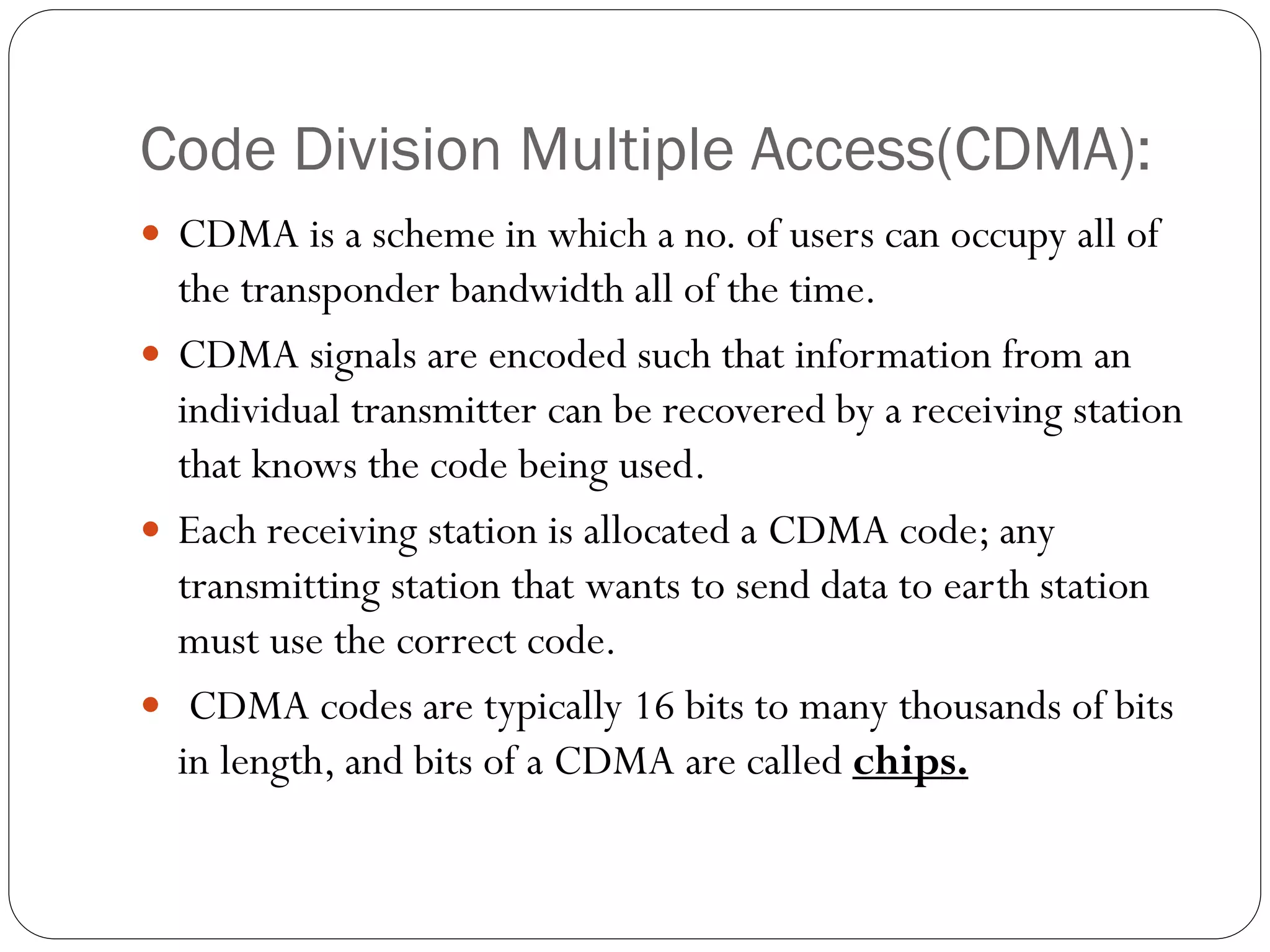
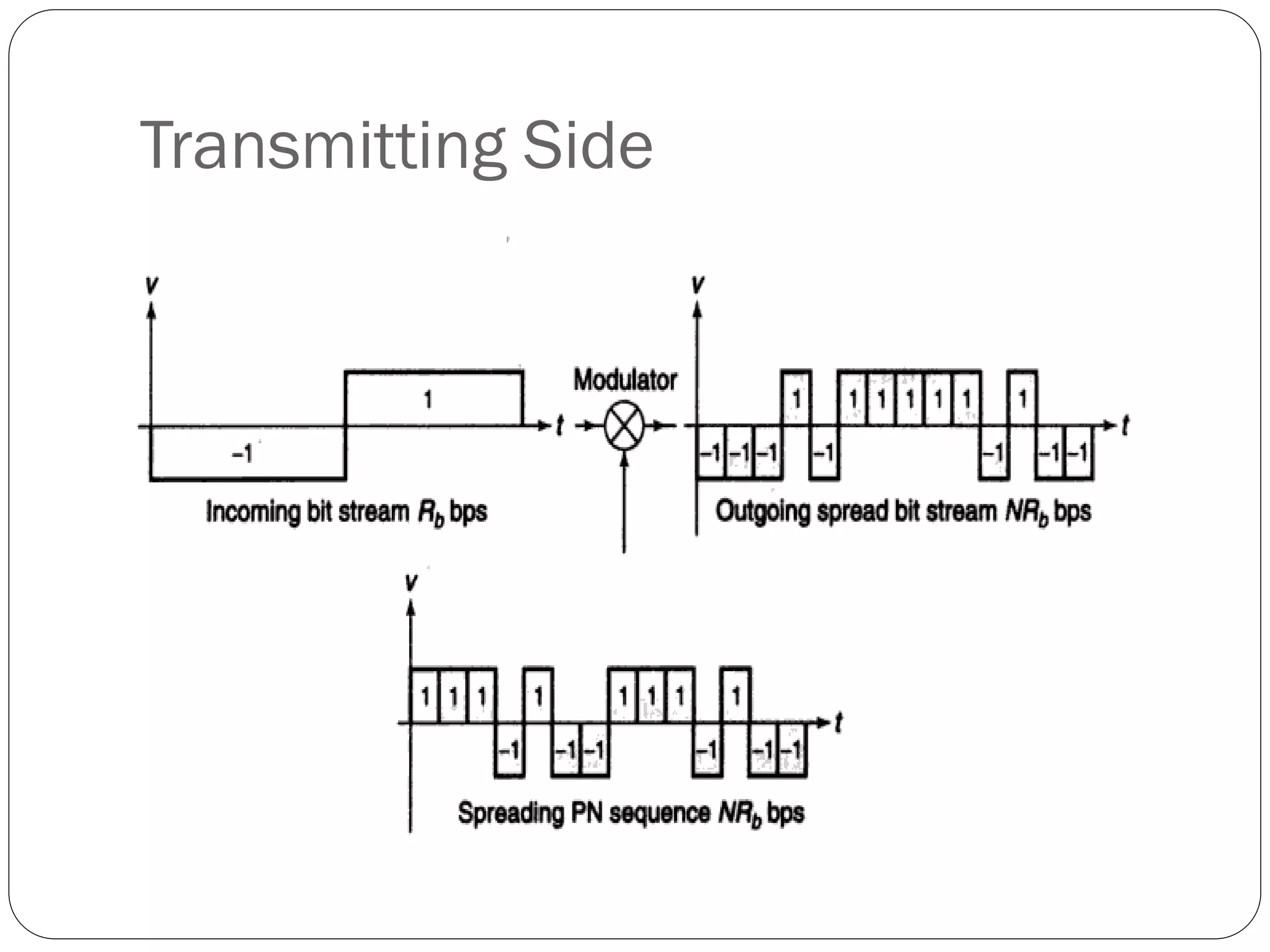
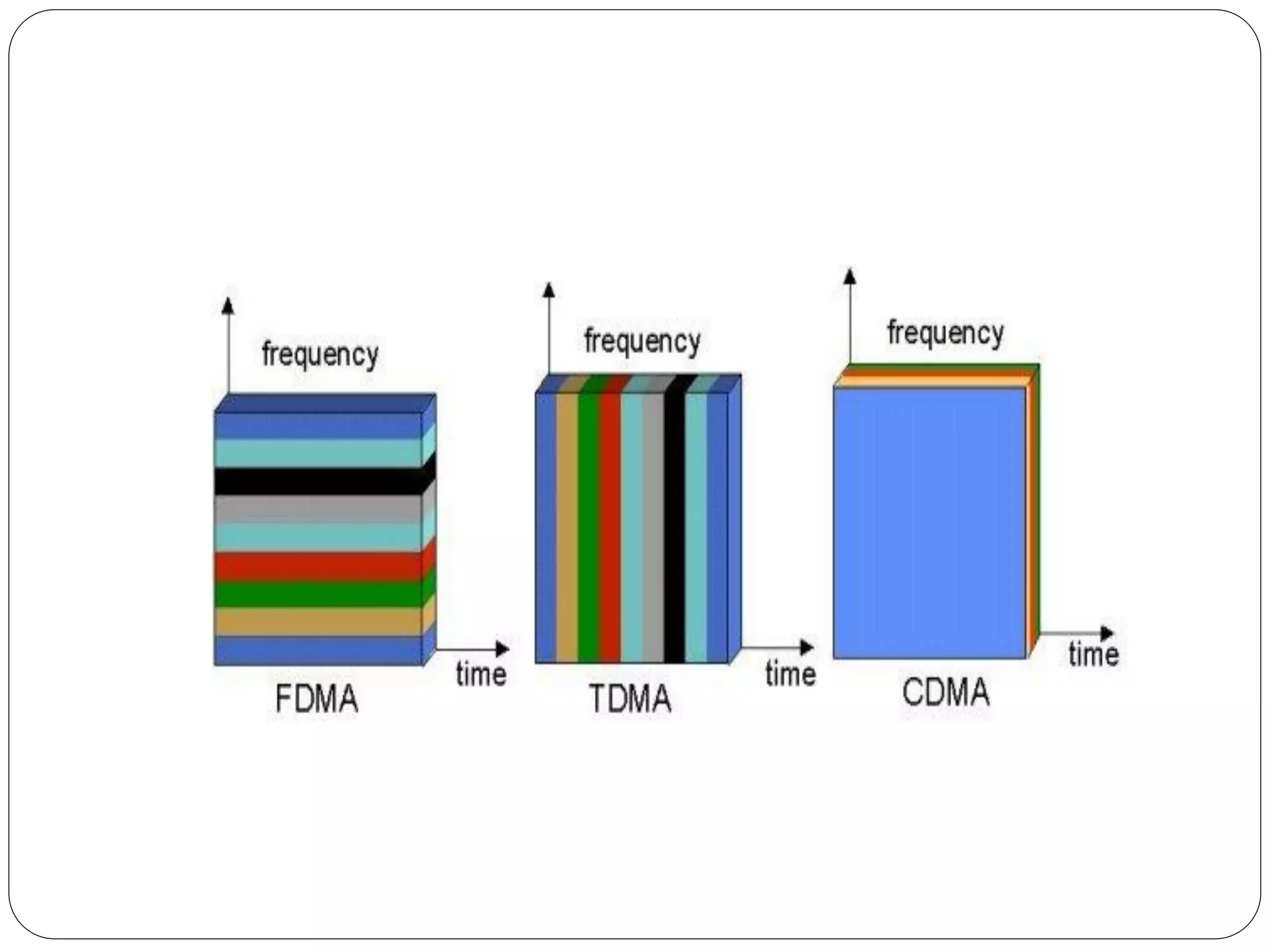
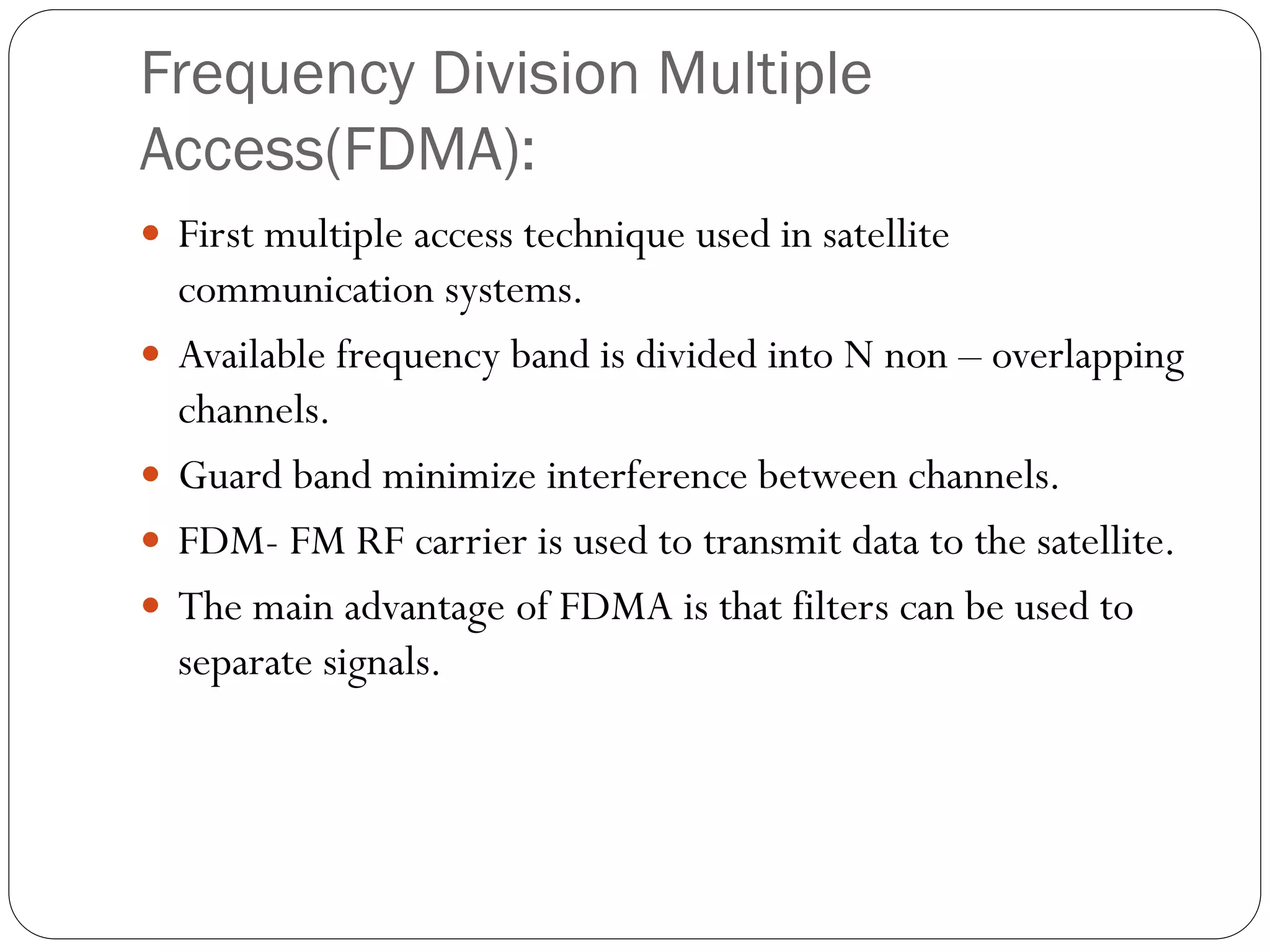
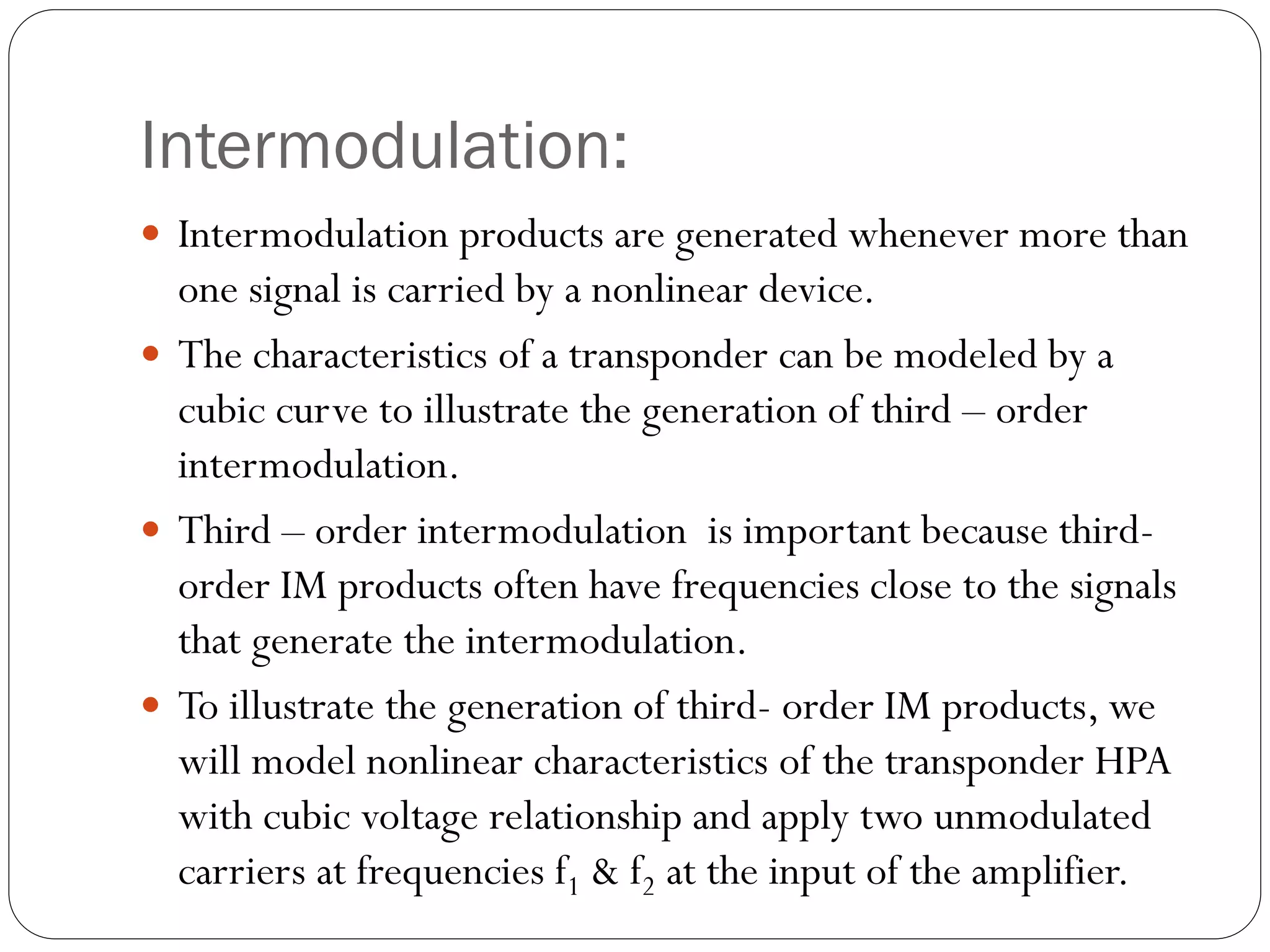
This document discusses several multiple access techniques used in satellite communications, including Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA), Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA), Demand Access Multiple Access (DAMA), and Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA). FDMA divides the available frequency band into non-overlapping channels. TDMA allows multiple earth stations to share a transponder by taking turns transmitting bursts of signals. DAMA allocates satellite channels to users on demand. CDMA encodes signals so that a receiving station can recover information from an individual transmitter using the correct code.












![Calculation of C/N with
intermodulation:
(C/N)o = 1/[1/(C/N)up + 1/(C/N)dn + 1/(C/N)IM ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/satellitecomm-180730091729/75/Multiple-Access-16-2048.jpg)

![Time Division Multiple Access:
The timeTd available in each station burst for transmission of
data bits
Td = [Tframe – N(tg + tpre )]/N seconds
In 1 s, the total no. of bits , Cb , transmitted by each earth
station is
Cb = [Tframe – N(tg + tpre )]* Rb /Tframe *N
The no. of speech channel that can be carried by each earth
station is n= [Tframe – N(tg + tpre )] * Rb /(Tframe * rsp )*N](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/satellitecomm-180730091729/75/Multiple-Access-18-2048.jpg)