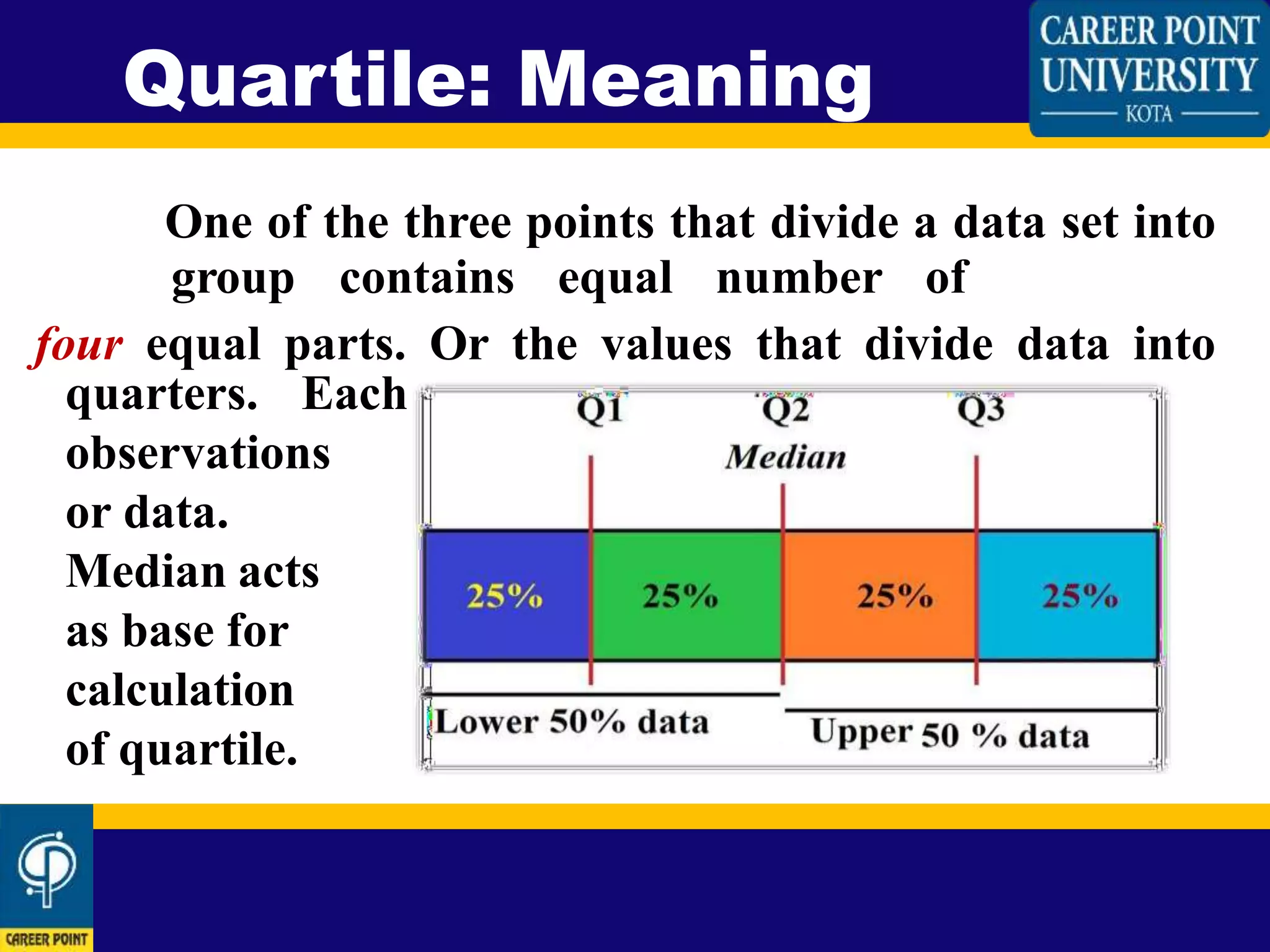
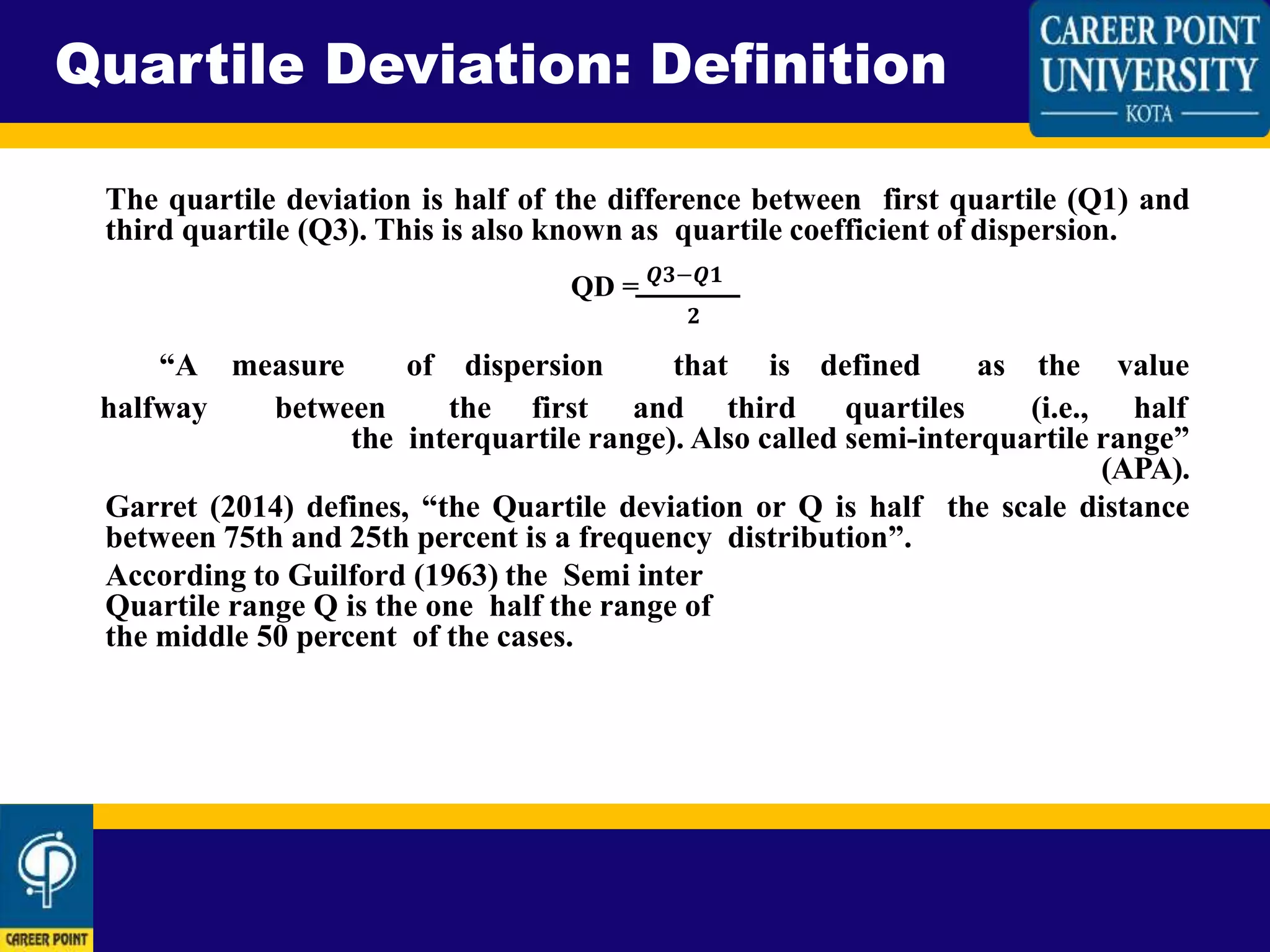
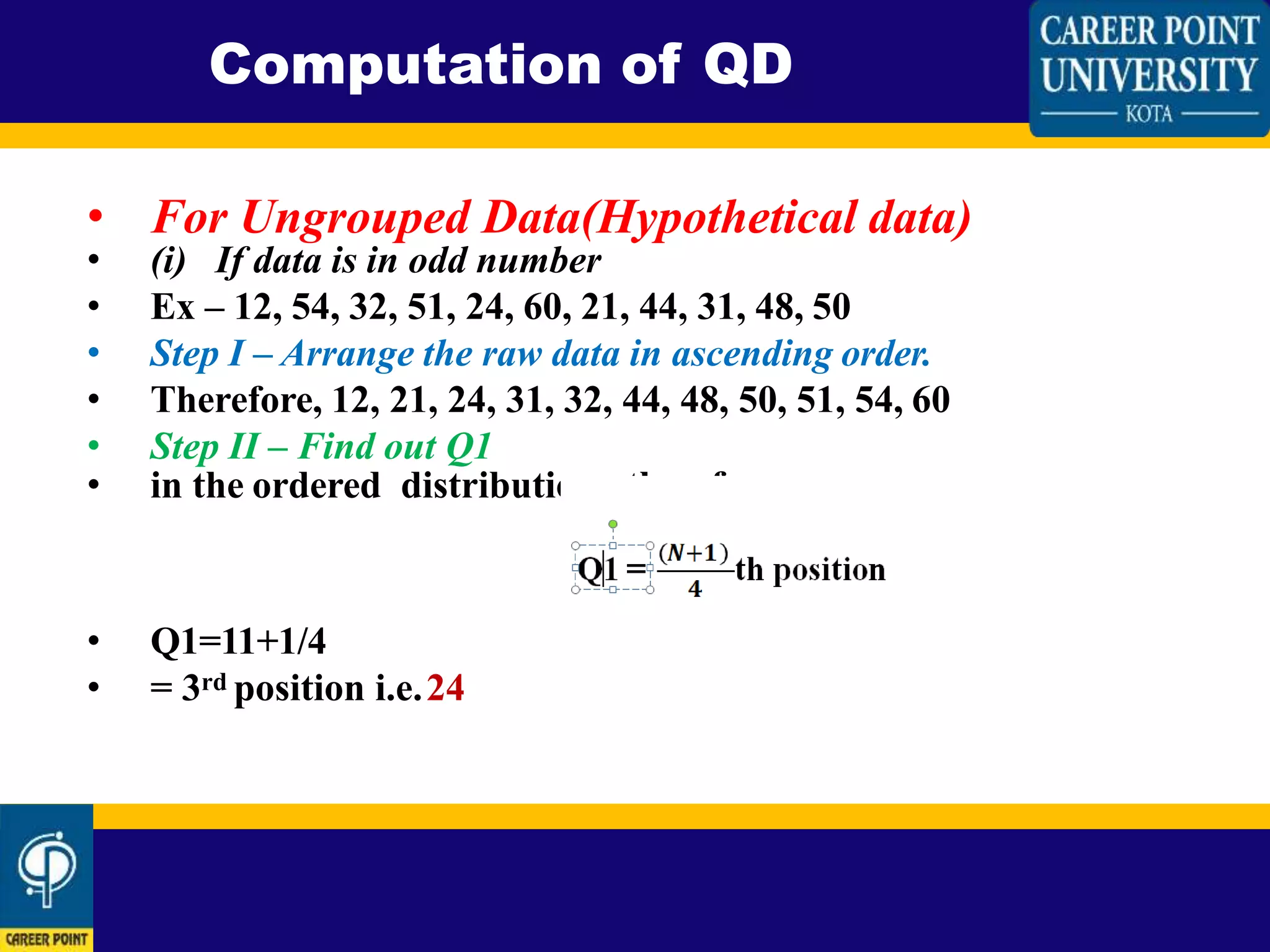
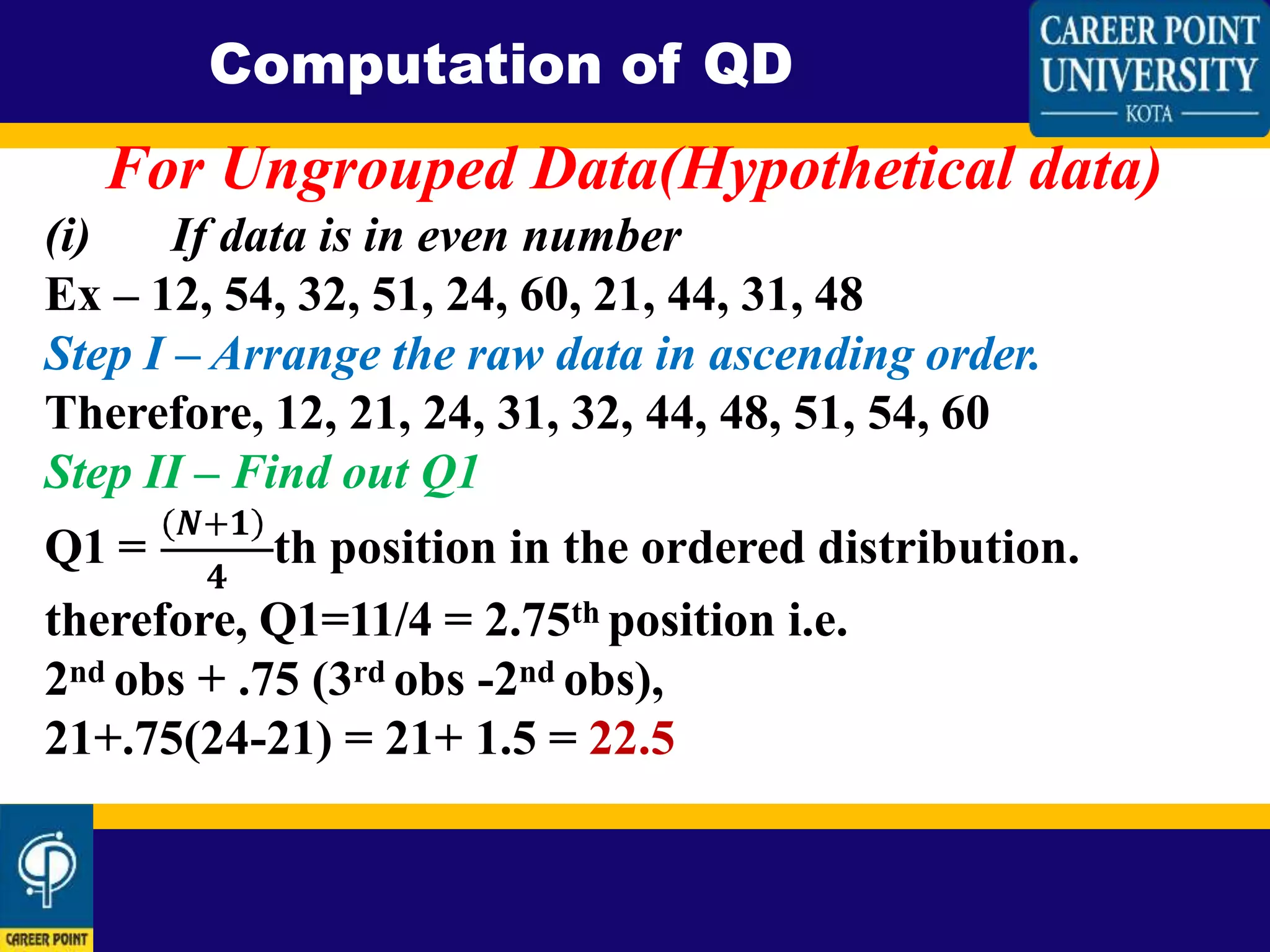
This document defines and explains how to calculate quartile deviation (QD). It begins by defining quartiles as the three points that divide a data set into four equal parts. The median acts as the base for calculating quartiles. Quartile deviation is then defined as half the difference between the first quartile (Q1) and third quartile (Q3). The document provides the formula for calculating QD as QD=(Q3-Q1)/2. It then explains how to calculate Q1, Q2, and Q3 for both odd-numbered and even-numbered data sets by arranging the data in ascending order and determining the values that divide the data into four equal parts. Sample calculations are shown for both odd