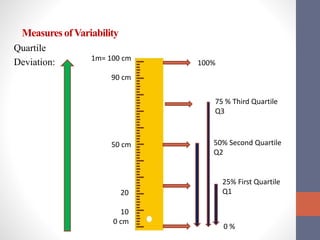
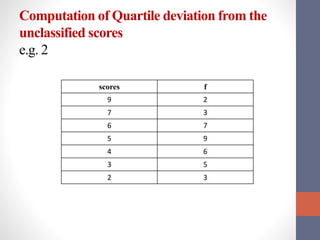
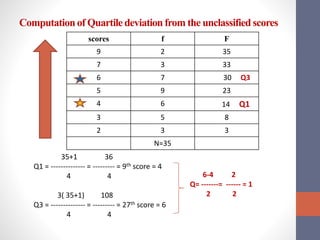
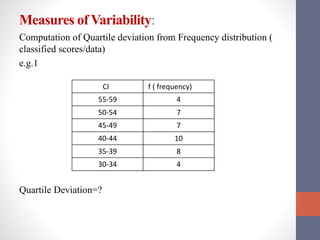
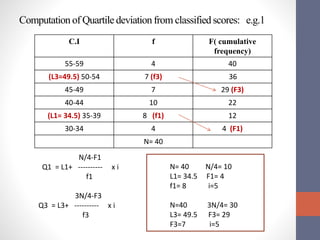
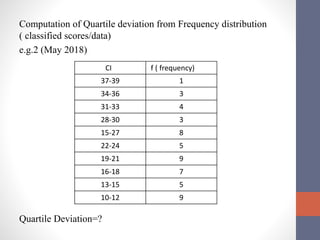
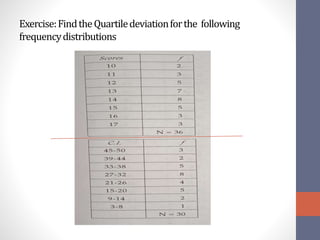
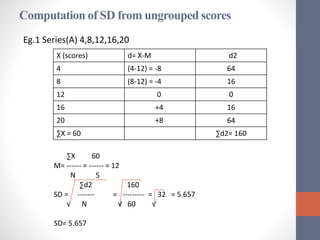
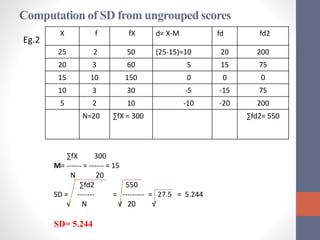
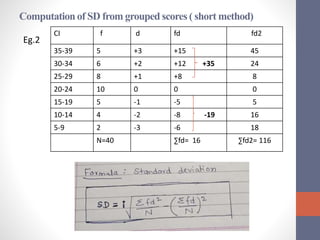
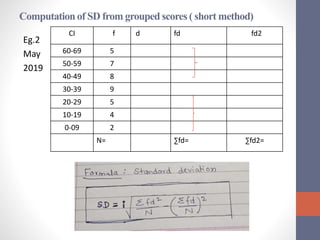
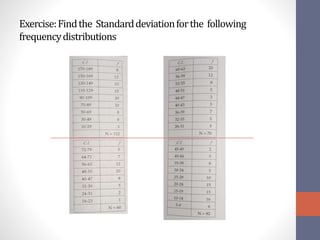
This document discusses measures of variability used to interpret test scores, including quartile deviation and standard deviation. Quartile deviation is calculated by finding the difference between the third quartile (Q3) and first quartile (Q1) and dividing by 2. Standard deviation is the most reliable measure of variability and is calculated by finding the sum of the squared deviations from the mean divided by the total number of values. Examples are provided to demonstrate computing both measures from raw data and frequency distributions.