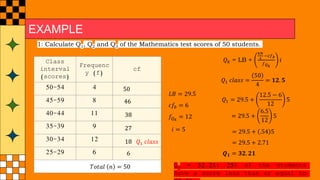
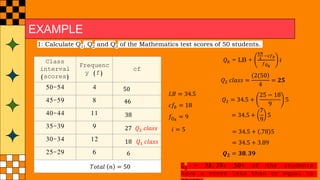
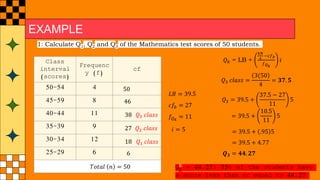
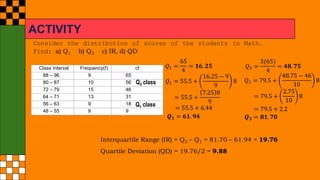
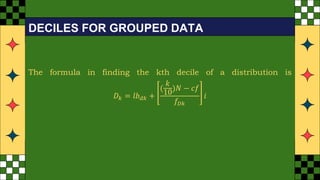
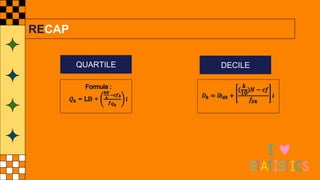
The document provides an overview of statistical concepts such as quartiles, deciles, and percentiles specifically in relation to calculating median scores from a distribution of student test scores. It includes examples and formulas for determining quartiles (q1, q2, q3), the interquartile range (IQR), and quartile deviation (QD) based on student scores. Additionally, it outlines the process for finding specific deciles within grouped data, accompanied by sample calculations.