This document provides a tutorial on classification machine learning using Python. It defines classification as categorizing input data into predefined classes or labels. It discusses several common classification algorithms like logistic regression, k-nearest neighbors, support vector machines, decision trees, random forests, gradient boosting machines, Gaussian naive Bayes, and multinomial naive Bayes. It also covers key evaluation metrics, applications, challenges, and future trends in classification machine learning. Code examples are provided for implementing various classification models in Python and R.




![1.Logistic Regression
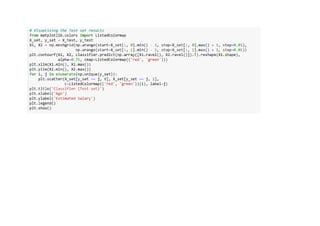
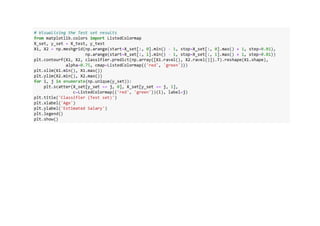
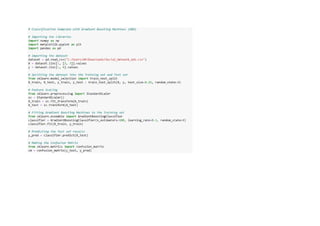
• Logistic Regression is a statistical method used for binary classification, predicting the probability of
an instance belonging to one of two classes. Unlike linear regression, which predicts a continuous
outcome, logistic regression employs the logistic function to squash the predicted values into the
range of [0, 1]. This makes it particularly well-suited for problems where the dependent variable is
binary, such as spam detection or medical diagnosis. The model estimates coefficients for input
features, which represent the log-odds of the target class. Through a process called logistic
transformation, these log-odds are converted into probabilities. Logistic Regression is widely
employed due to its simplicity, interpretability, and efficiency in handling linear relationships between
features and the log-odds of the target class.
Data is from the social network ads.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythoncodeforclassificationsupervisedmachinelearning-231217124426-9e867e6c/85/Python-Code-for-Classification-Supervised-Machine-Learning-pdf-5-320.jpg)