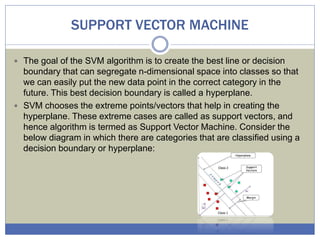
The document provides an overview of machine learning (ML), detailing its role as a branch of artificial intelligence that utilizes data analysis to make predictions, classify data, and improve through experience. It categorizes ML into supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning, highlighting various applications such as speech recognition, medical analysis, and game playing. Additionally, it discusses specific algorithms like artificial neural networks, decision trees, support vector machines, naïve Bayes, and logistic regression, emphasizing their significance in classification and predictive modeling.