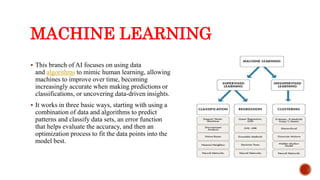
The document provides an overview of big data analytics, focusing on its definition, benefits, and the role of machine learning in extracting insights. It details the types of machine learning, particularly emphasizing supervised learning, which utilizes labeled datasets for classification and prediction. The document further discusses the various regression and classification algorithms used in supervised learning, along with their applications.