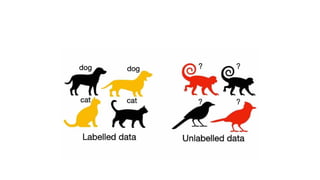
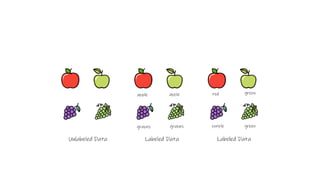
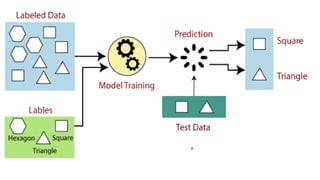
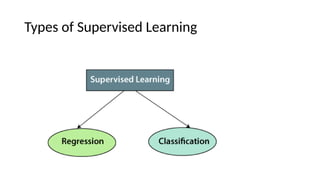
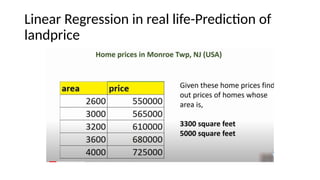
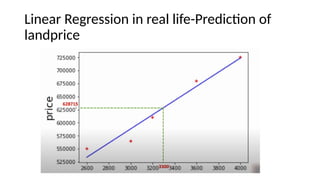
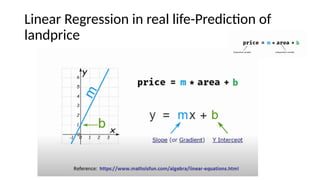
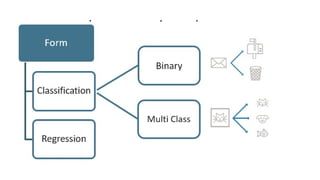
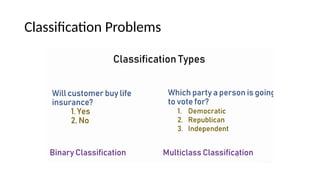
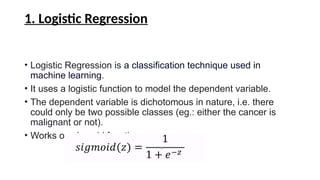
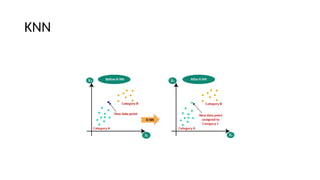
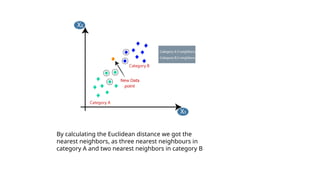
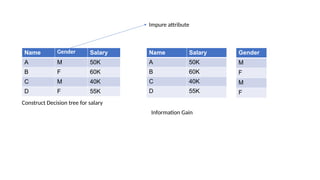
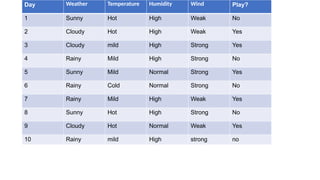
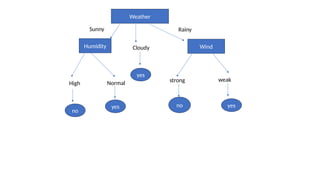
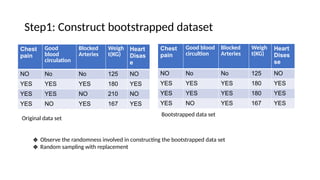
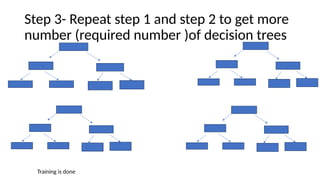
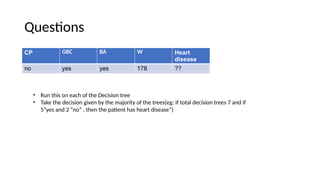
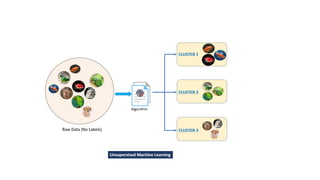
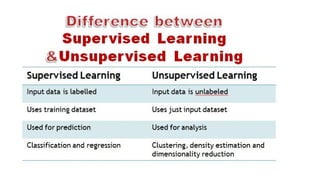
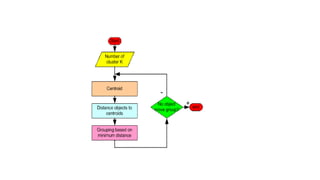
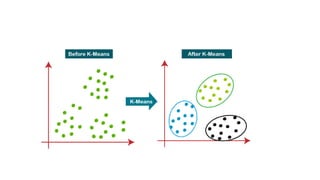
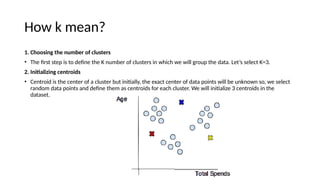
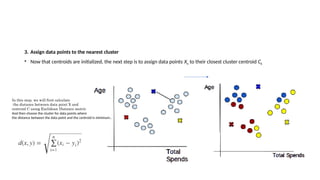
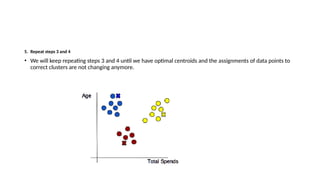
The document provides an overview of machine learning and artificial intelligence, emphasizing the crucial role of data in training models. It differentiates between supervised and unsupervised learning, detailing various algorithms used for tasks such as classification and regression. The text also covers important concepts like data preprocessing, feature scaling, and specific algorithms like linear regression, decision trees, and k-means clustering.