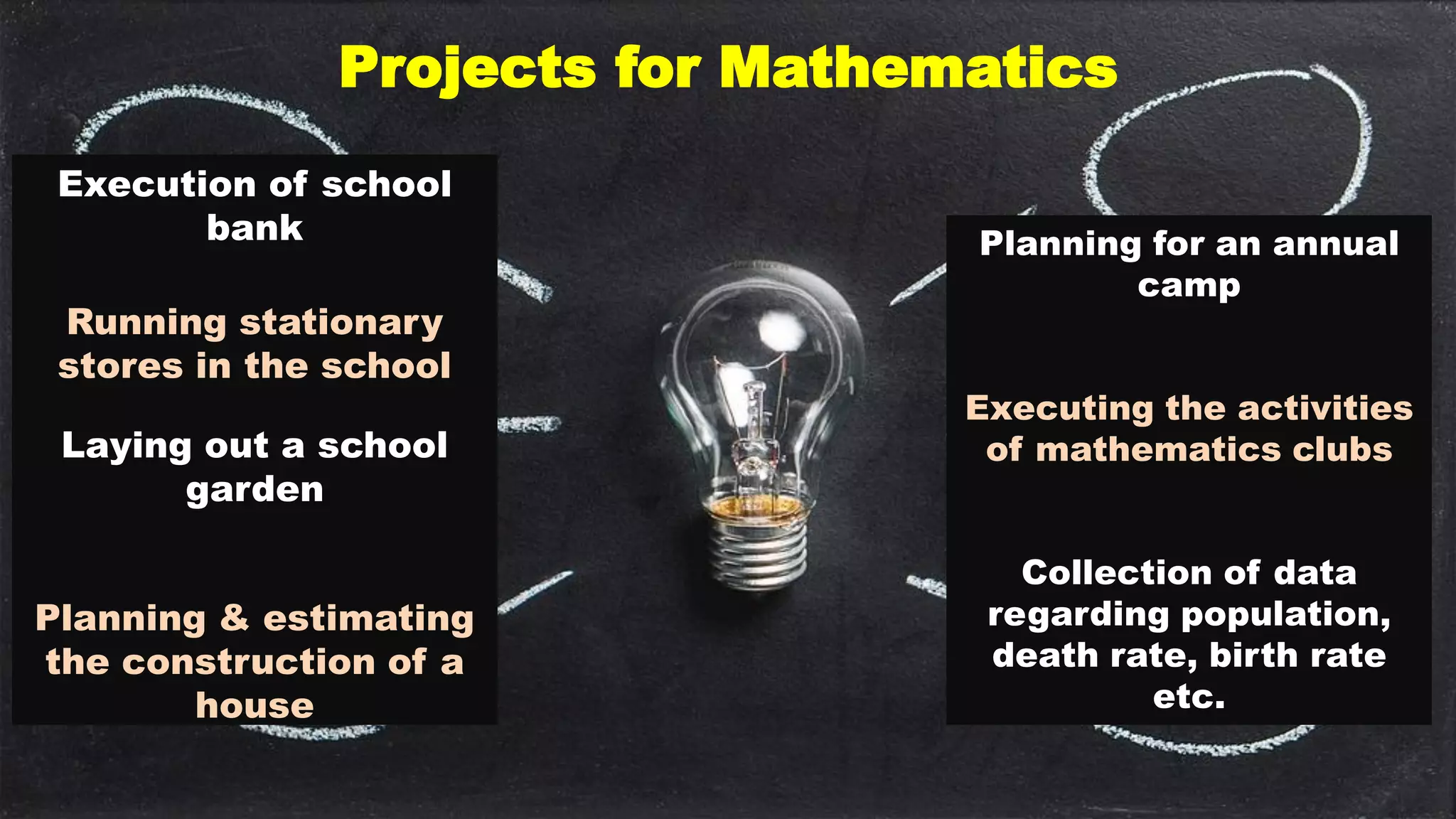
The project method of education, rooted in Dewey's philosophy and developed by Dr. Kilpatrick, emphasizes learning through real-life projects that engage students in purposeful activities. It involves several steps: creating problem situations, choosing projects relevant to students, planning, executing, and evaluating the project, while promoting self-confidence, critical thinking, and independent work. Despite its merits, the method can be time-consuming and may not align with fixed curricula or provide necessary drills for students.