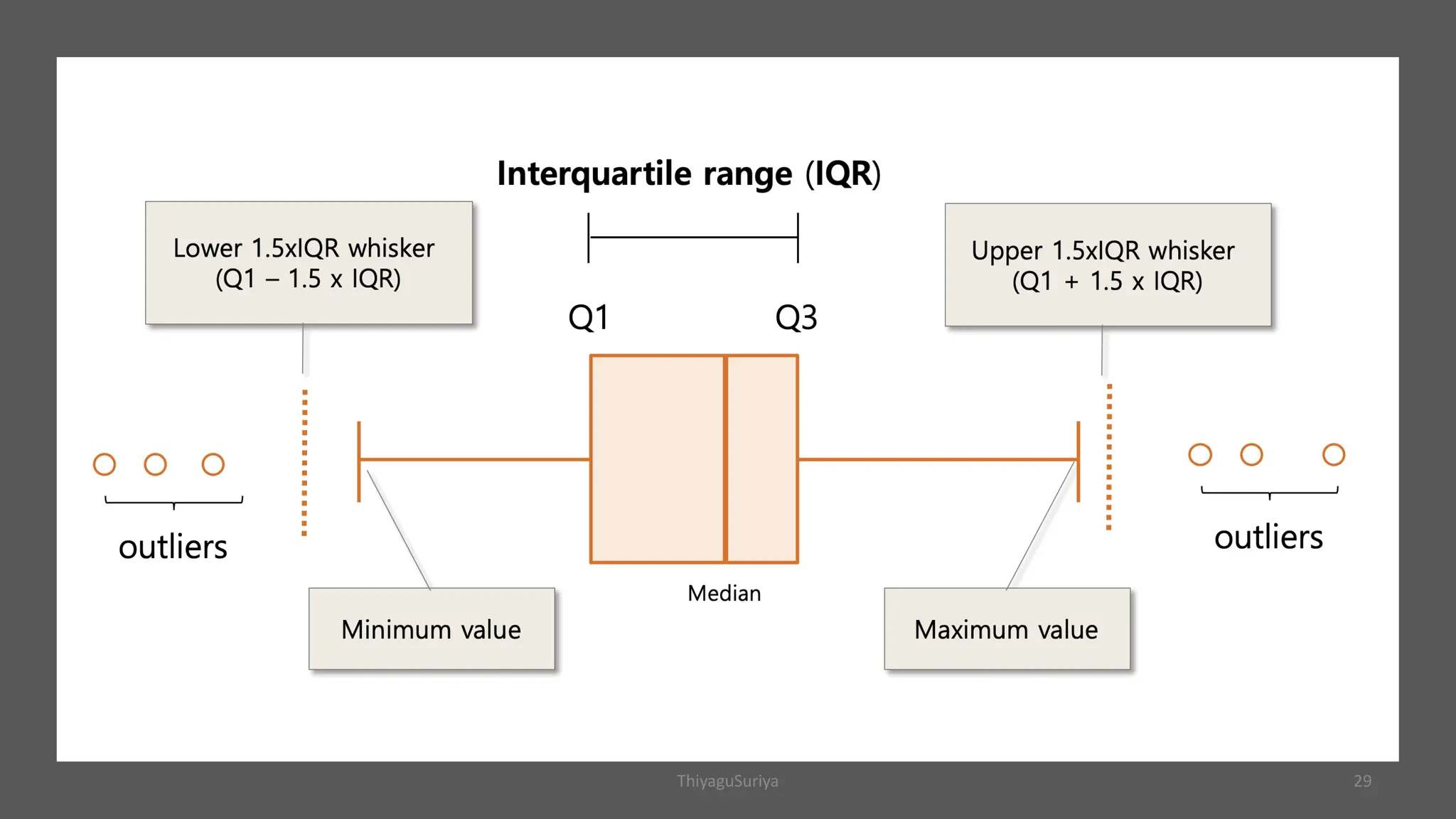
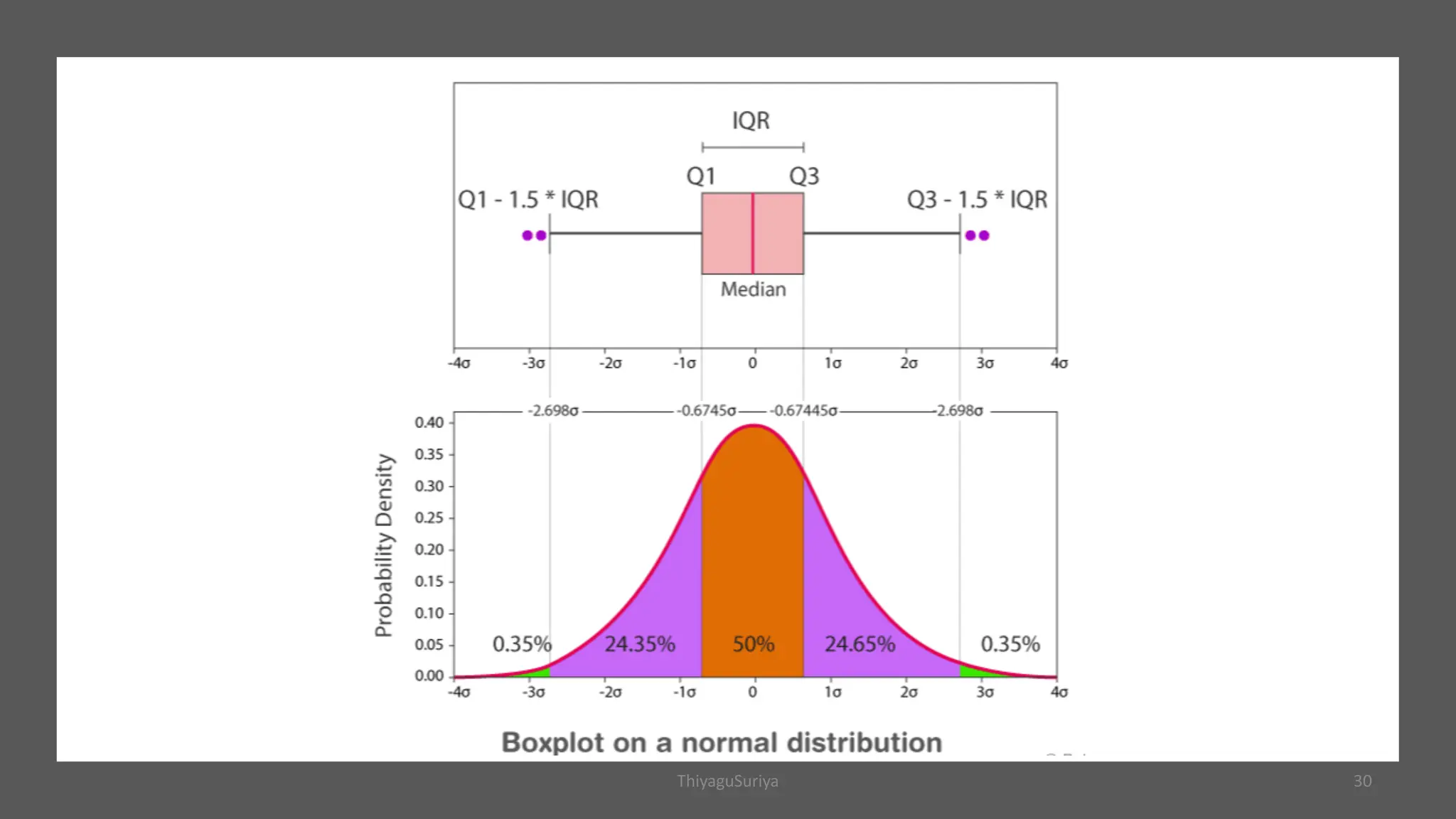
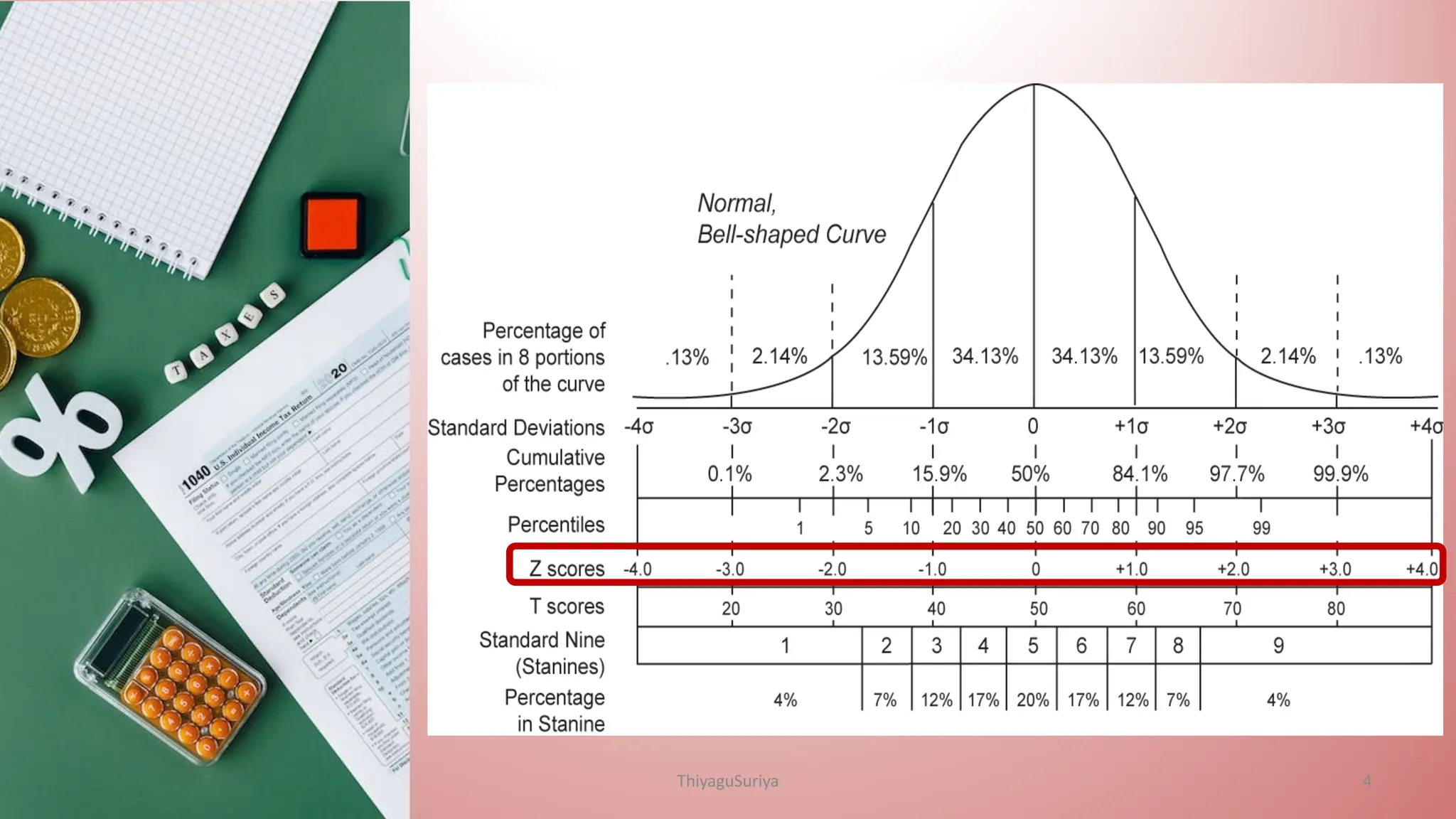
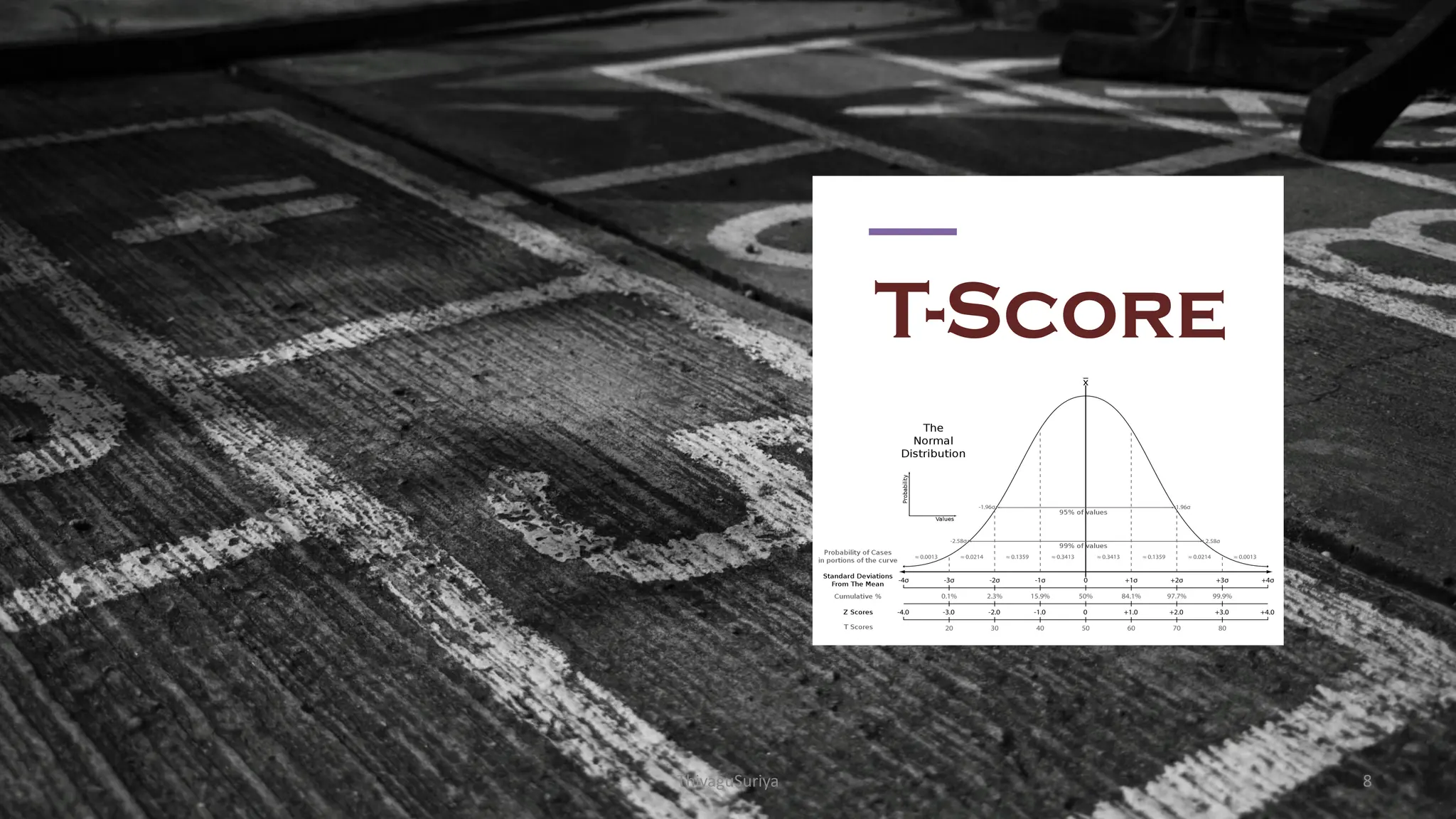
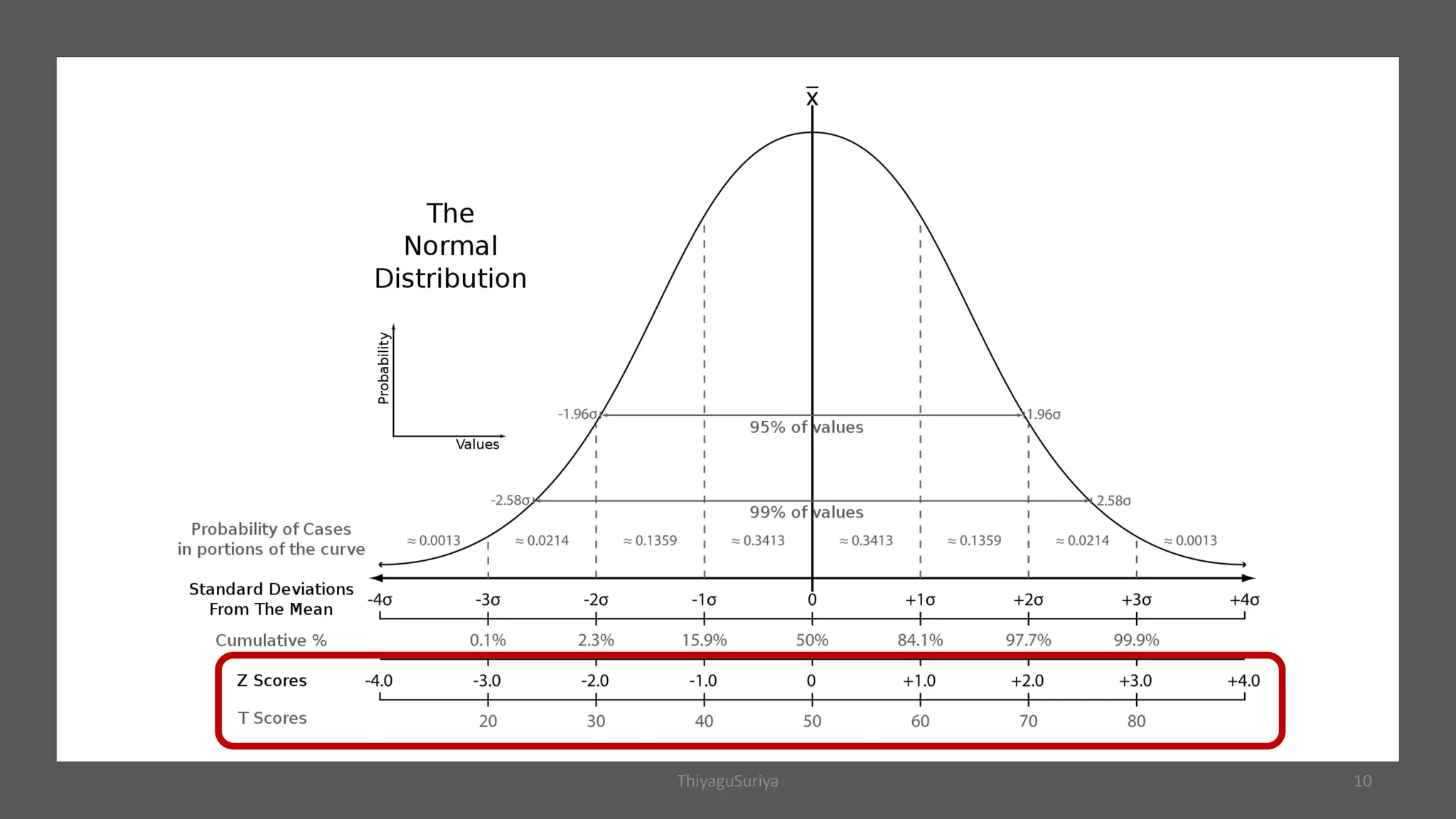
The document explains statistical concepts such as z-scores, t-scores, and percentile ranks, providing formulas and examples for their calculation. It outlines the differences between z-scores and t-scores, including when to use each based on sample size and population standard deviation. Additionally, it discusses the construction and interpretation of box plots for visualizing data distribution.











![Answer:
Amartya secures 60 in English.
Where Mean = 40 and S.D = 8
Answer:
Amartya secures 50 in Mother Tongue
Where Mean = 50 and S.D = 6
𝑇 = 10 [
𝑥 − 𝑀
𝑆𝐷
] + 50
T = 10 [
!"#!"
$
] + 50
T = 10 [
"
$
] + 50
T = 0 + 50
T = 50
𝑇 = 10 [
𝑥 − 𝑀
𝑆𝐷
] + 50 T = 10 [
$"#%"
&
] + 50
T = 10 [
/0
1
] + 50
T = 10 [
2
/
] + 50
T = 25 + 50 = 75
From the above two T-Scores, Amartya Secures better in English subject than Mother Tongue.
ThiyaguSuriya 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/zscoretscorepercentialrank-240430124917-3dedf2a2/75/Z-Score-T-Score-Percential-Rank-and-Box-Plot-Graph-15-2048.jpg)