1) The document discusses the steps of the decision making process which includes identifying the problem, criteria, weighting criteria, developing alternatives, analyzing alternatives, selecting the best alternative, implementing it, and evaluating.
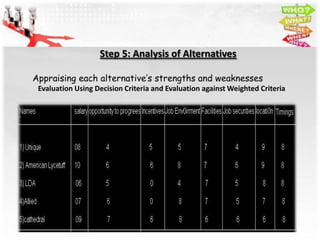
2) It provides an example of getting a job in a school and lists the relevant criteria as salary, opportunity to progress, job environment, incentives, facilities, job security, location, and timings.
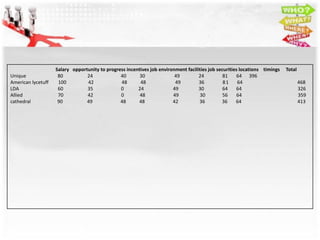
3) The alternatives provided are jobs at Unique, American Lycetuff, LDA, Allied, and Cathedral schools. Each alternative is then analyzed and weighted against the criteria to select the best option.