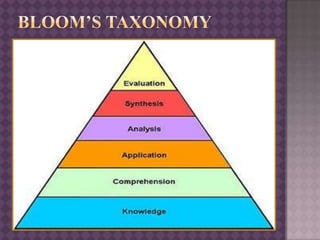
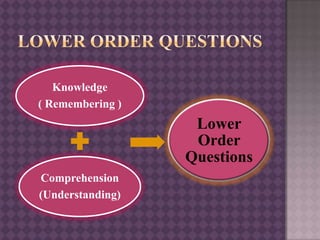
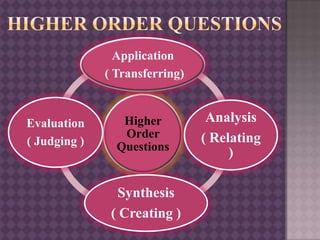
This document provides guidance on effective questioning techniques for teachers. It discusses that teachers ask an average of 400 questions per day, with one-third of teaching time spent on questioning. The document outlines key tactics for questioning like structuring questions, pitching them clearly, directing and distributing questions, and pausing and pacing. It also discusses Bloom's Taxonomy and designing higher and lower order questions. Effective questioning is presented as important for interaction, challenge, influence and assessment of students. The document encourages coming out of comfort zones to develop as a teacher.