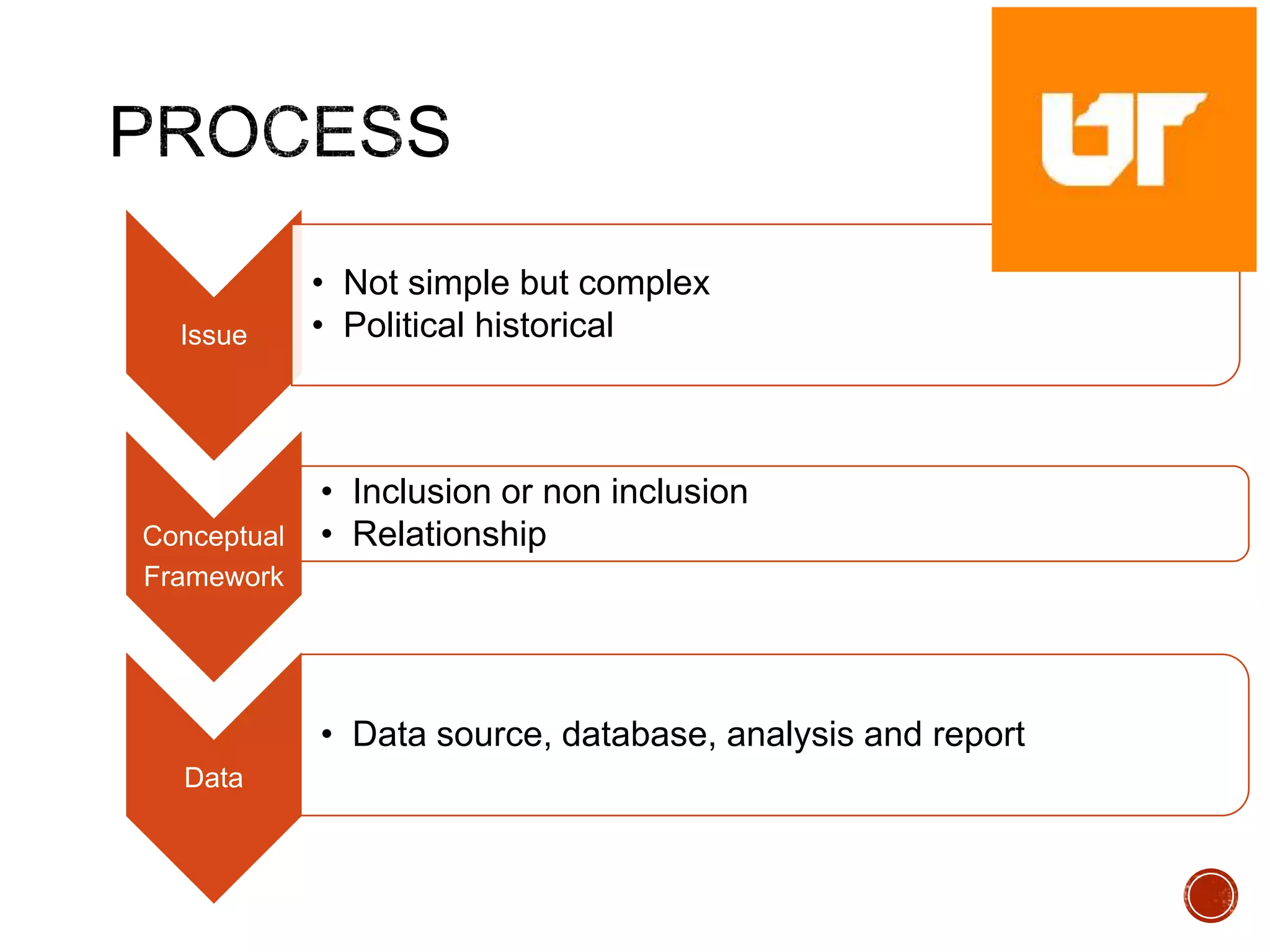
This document provides an overview of case study research. It defines case study as an in-depth examination of a phenomenon in its real-world context. The document differentiates between types of case studies such as explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive. It also discusses the relationship between theory and case studies, noting approaches can be theory-building, theory-testing, or theory-generating. The document shares examples of case study issues and methods of conducting case study research.