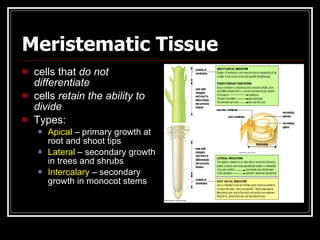
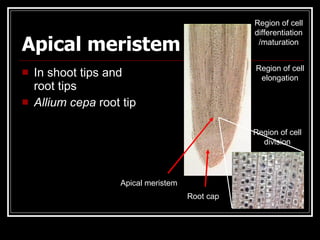
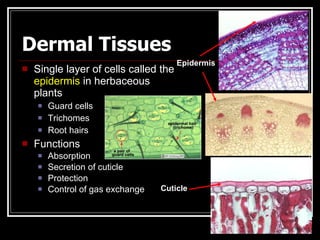
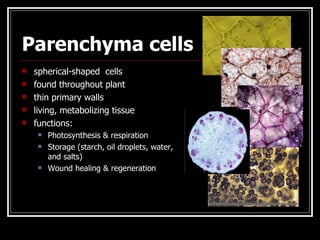
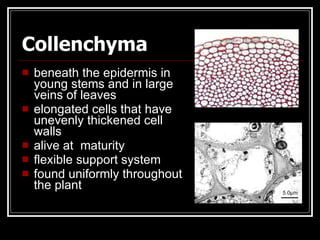
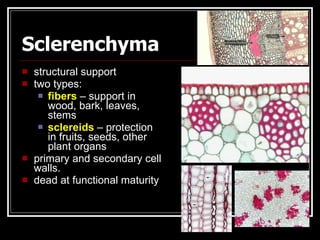
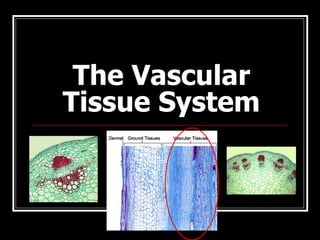
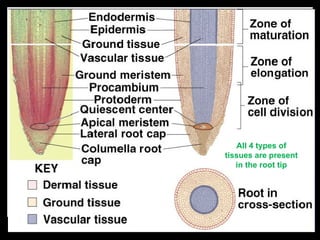
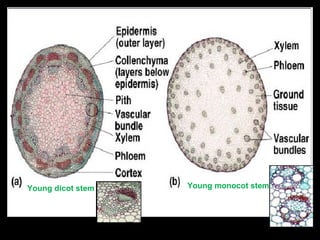
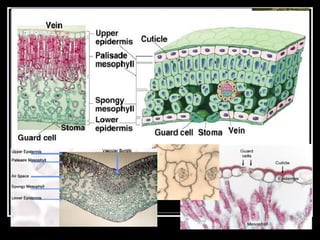
This document describes the four main types of plant tissues: meristematic, dermal, ground, and vascular tissues. Meristematic tissue contains cells that divide rapidly to facilitate growth. Dermal tissue forms the plant's outer covering. Ground tissue provides support, carries out photosynthesis, and stores food and water. Vascular tissue transports water, minerals, and food throughout the plant and strengthens its structure. Each tissue type performs distinct but interconnected functions that allow plants to grow, obtain nutrients, and transport materials throughout their bodies.