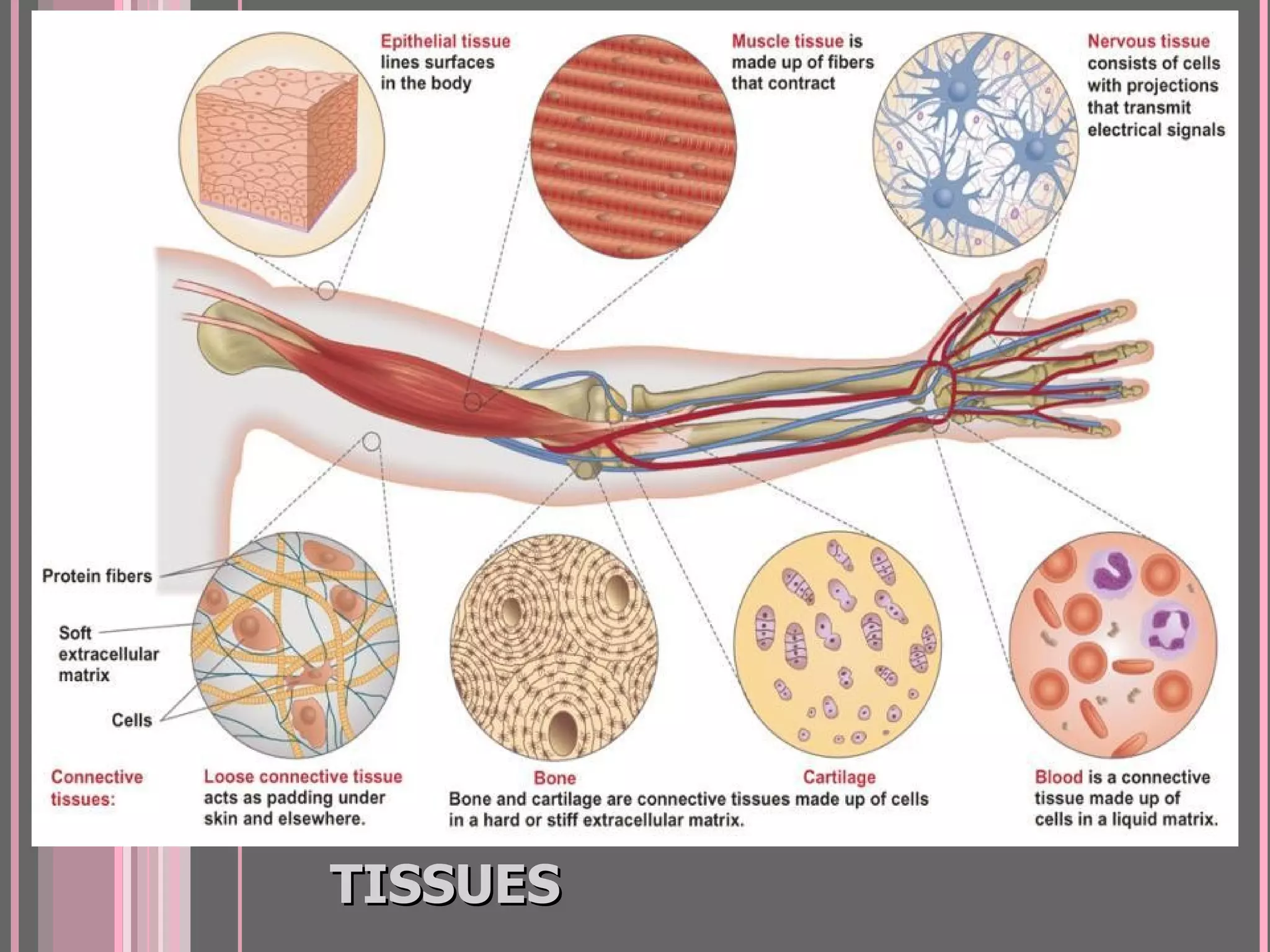
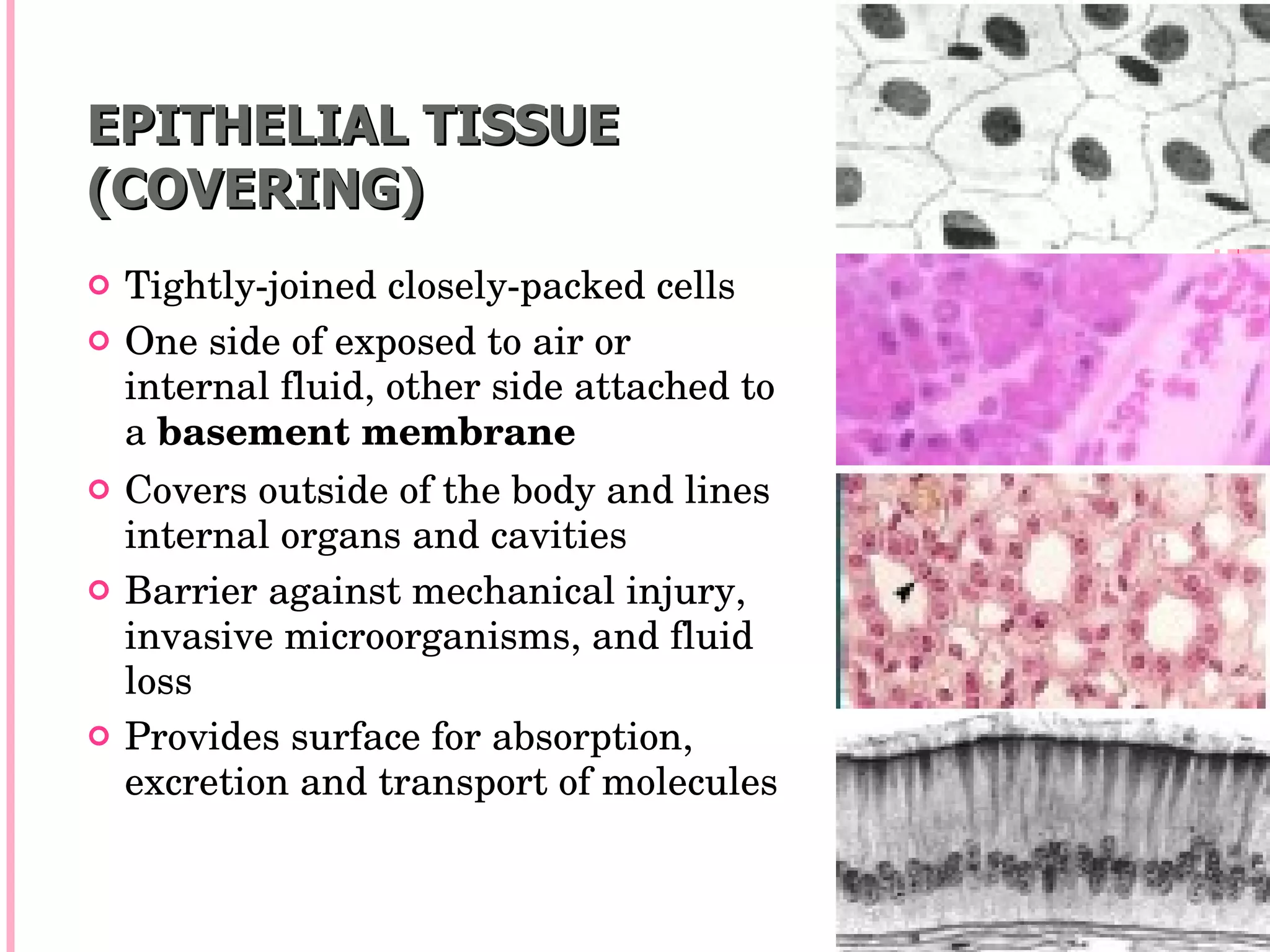
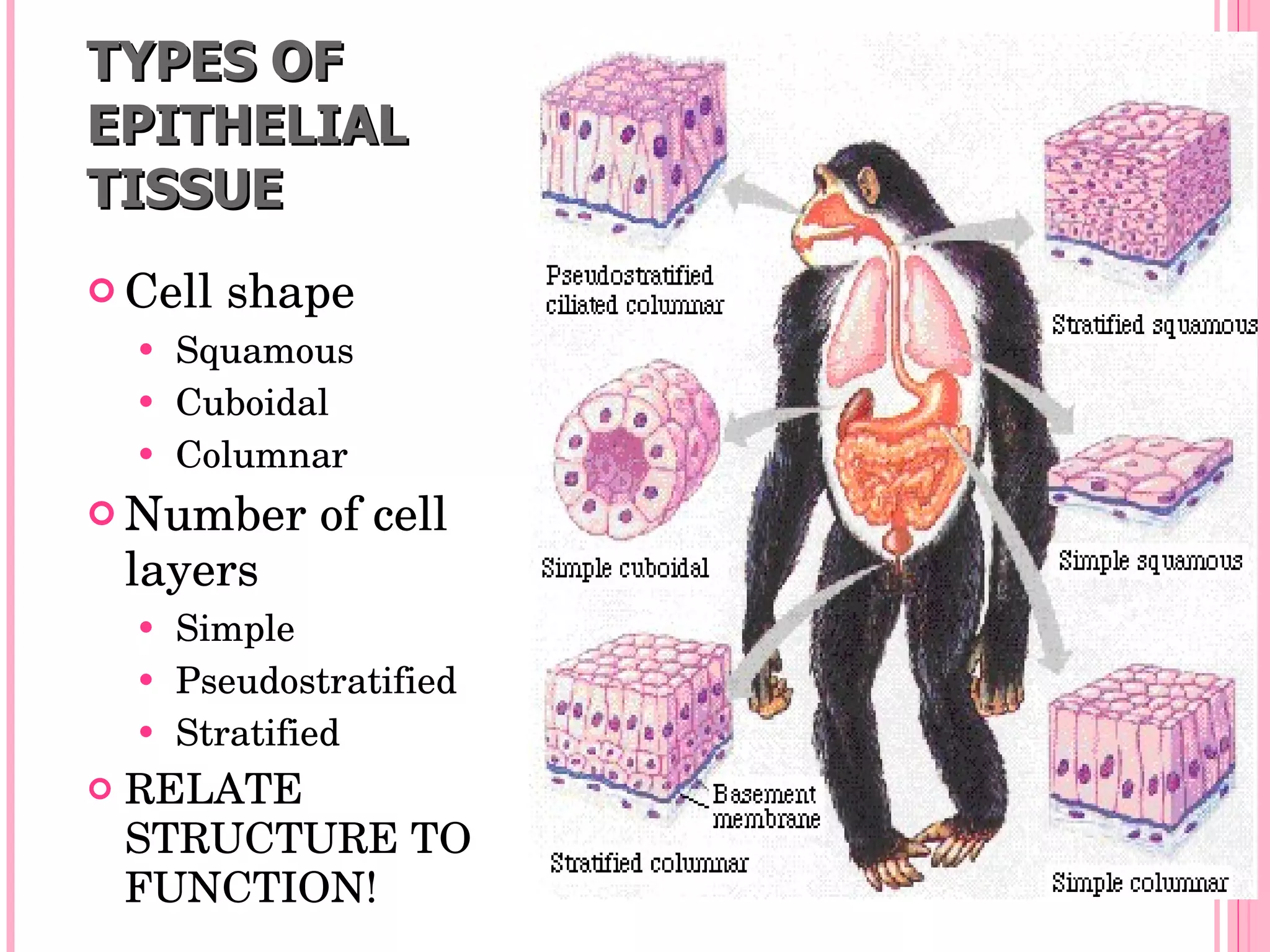
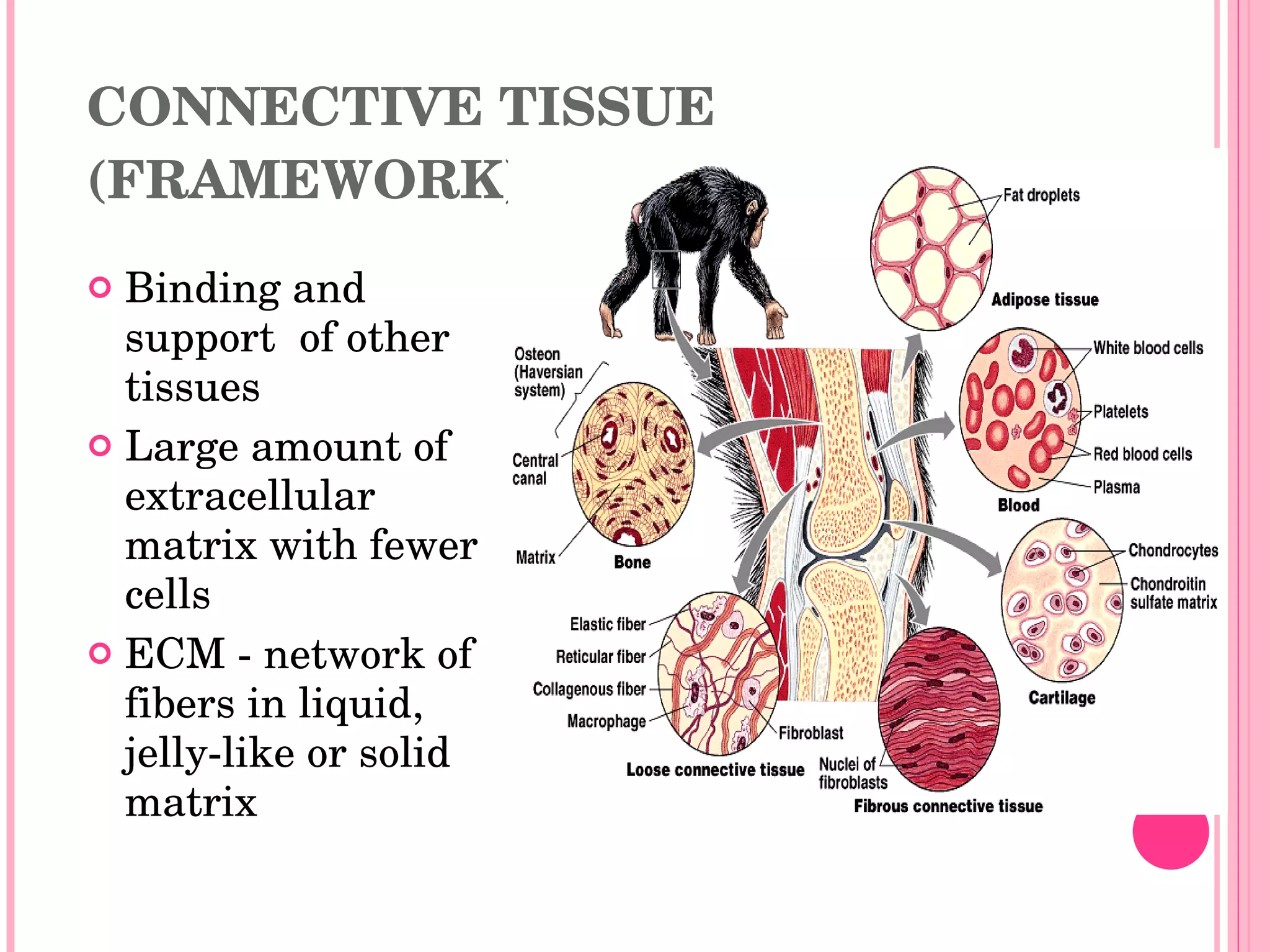
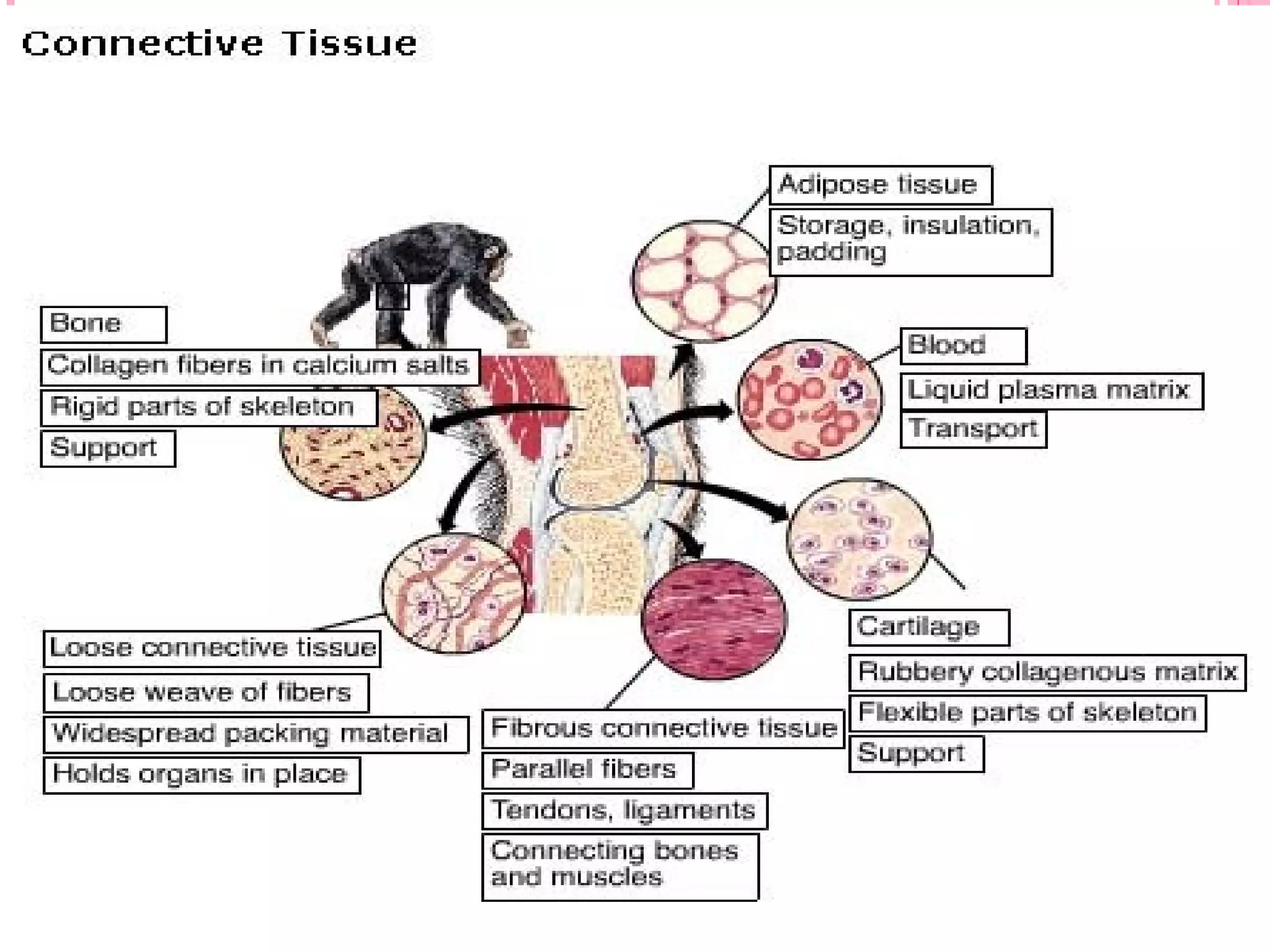
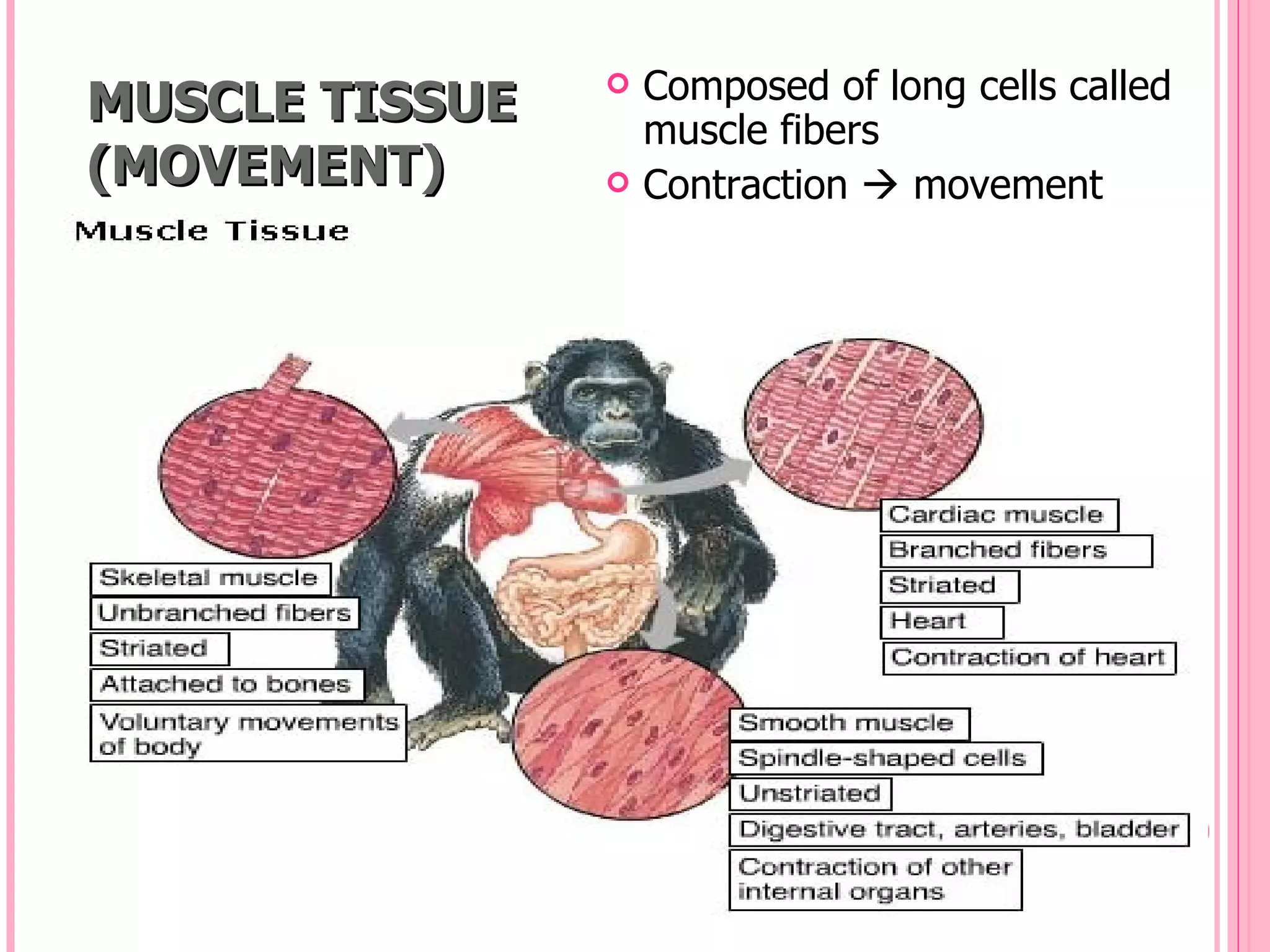
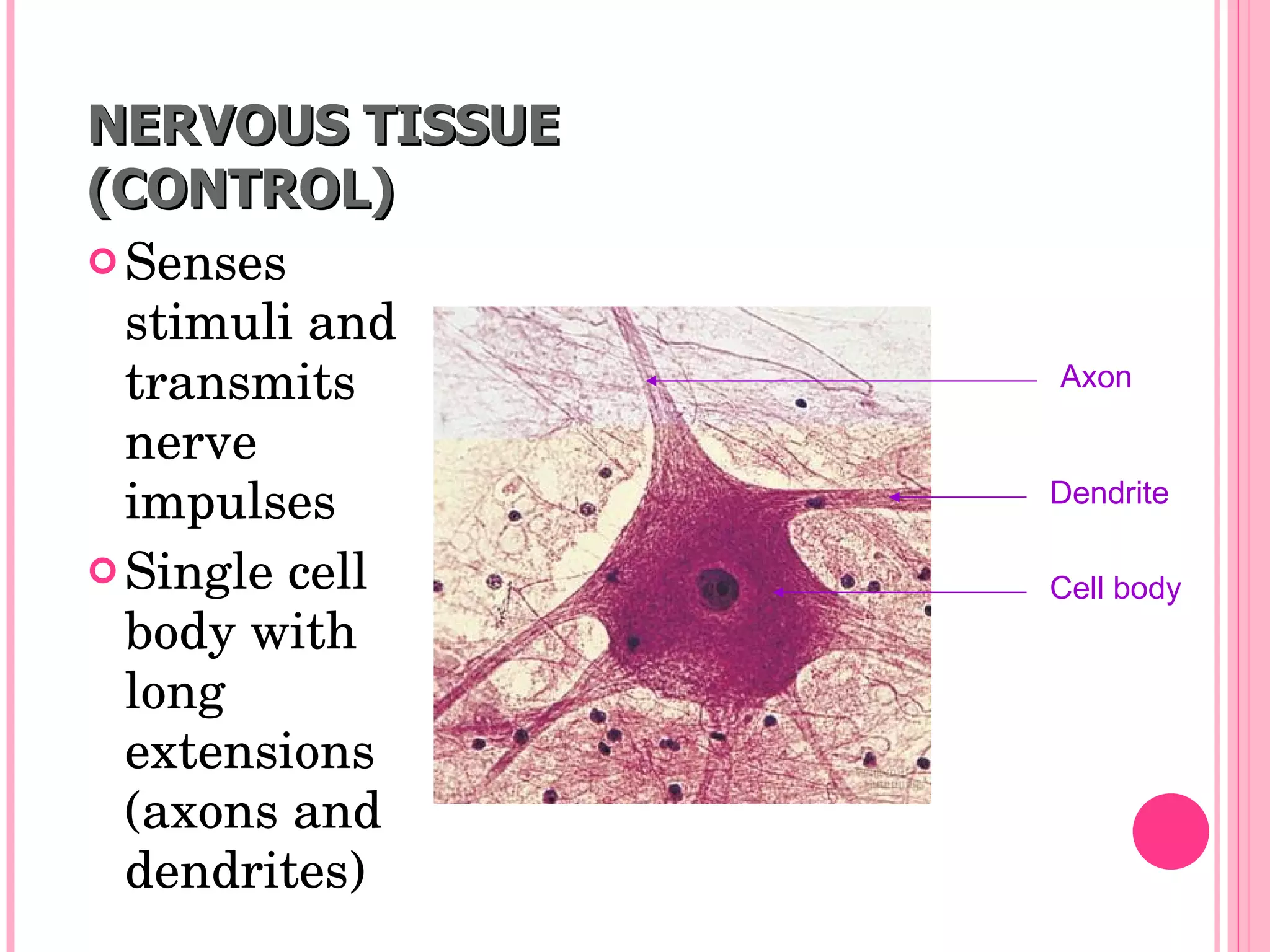
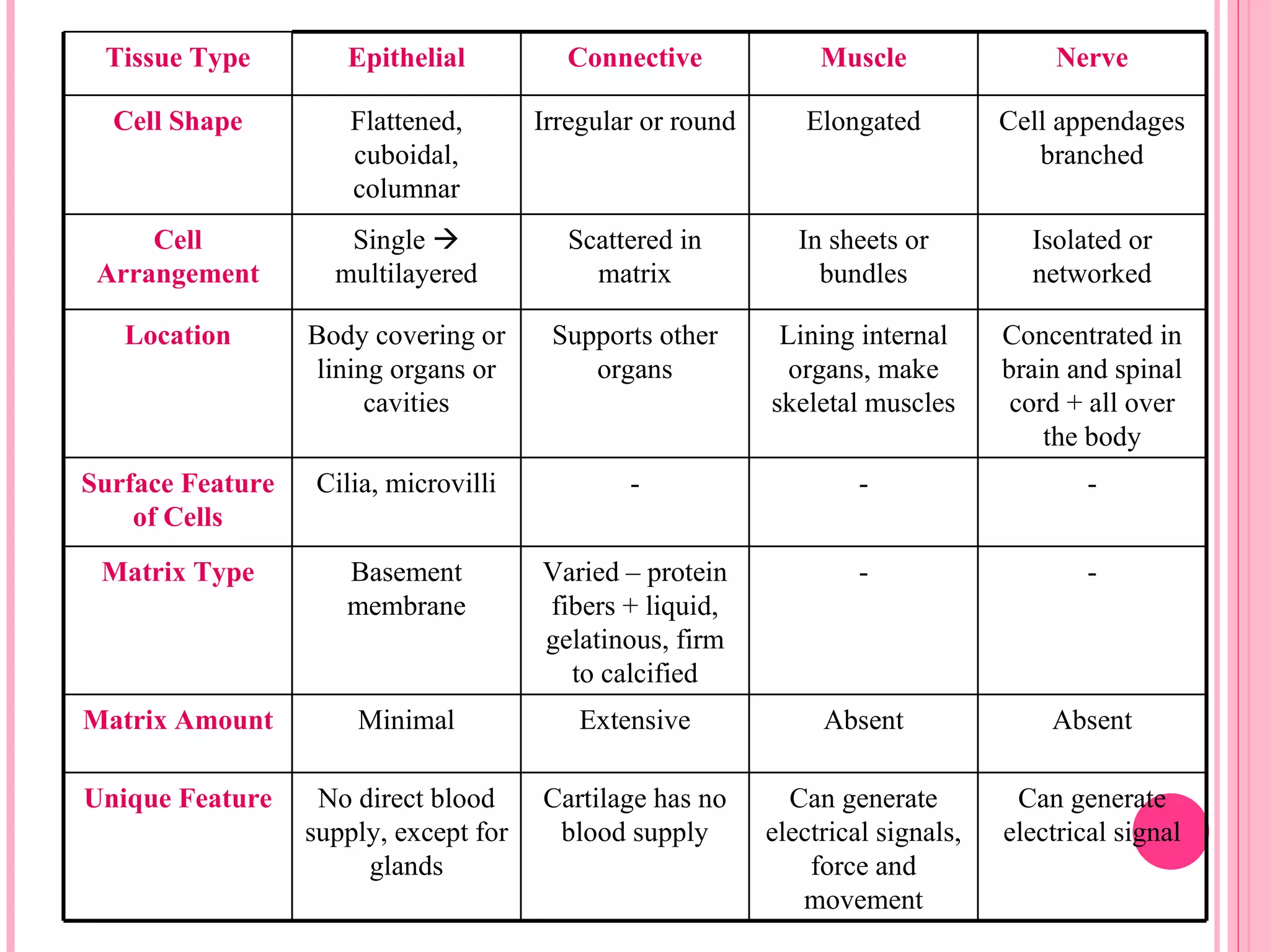
There are four main types of tissues in the body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissue forms protective barriers and lines body surfaces. Connective tissue provides structure and support. Muscle tissue allows for movement. Nervous tissue controls and coordinates the body through electrical signaling. Each tissue has distinct cell shapes, arrangements, locations in the body, and functions.