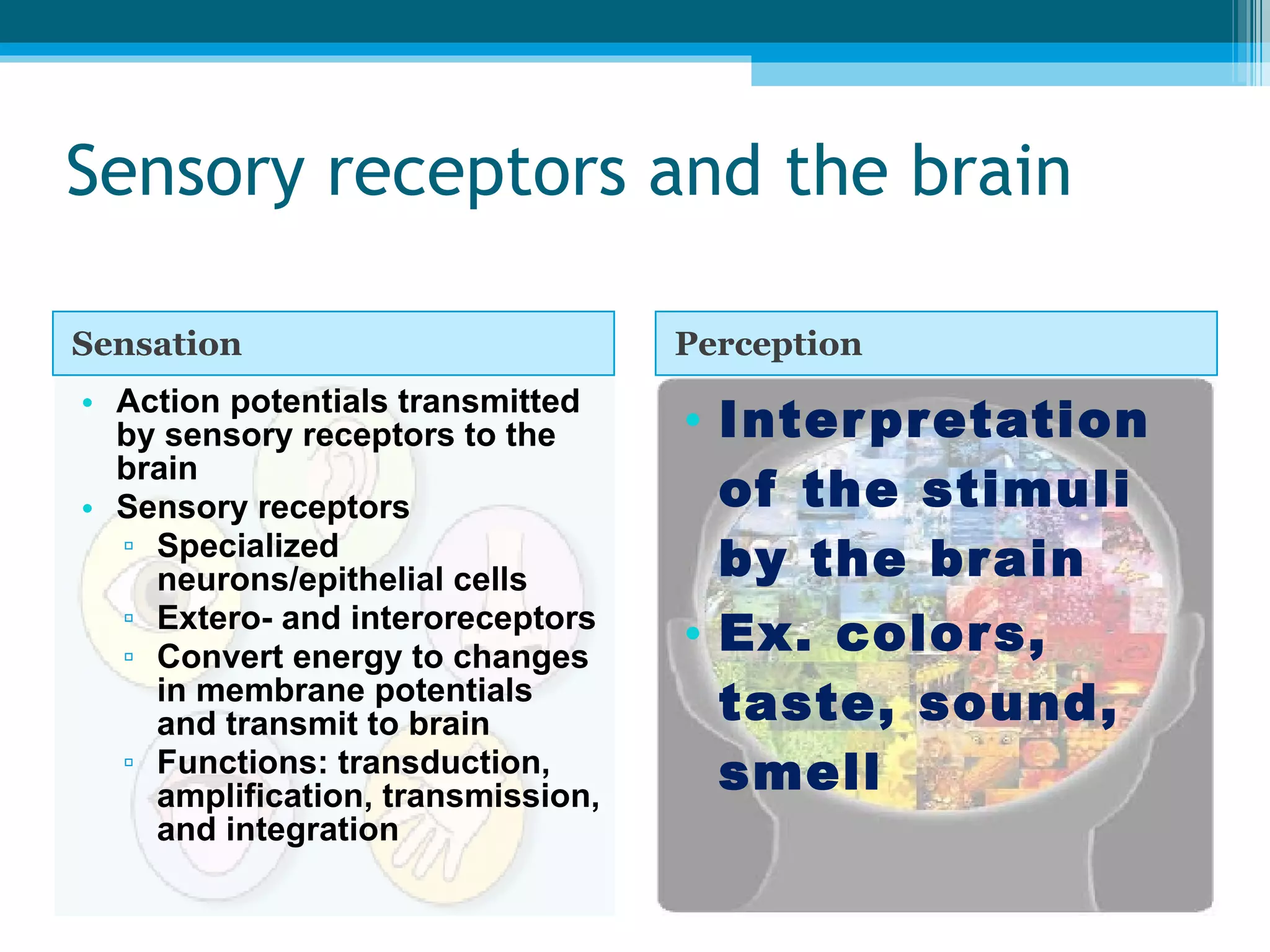
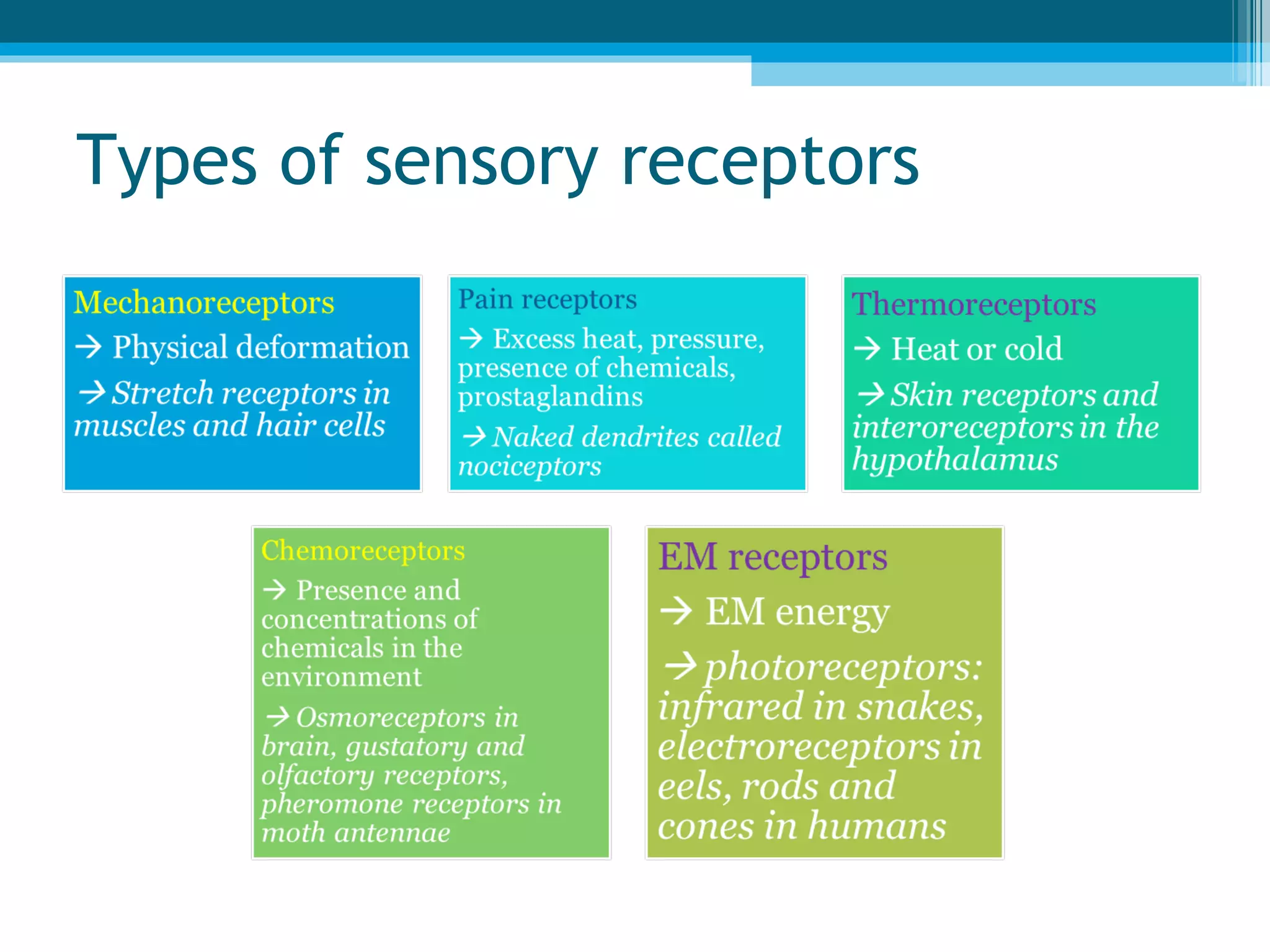
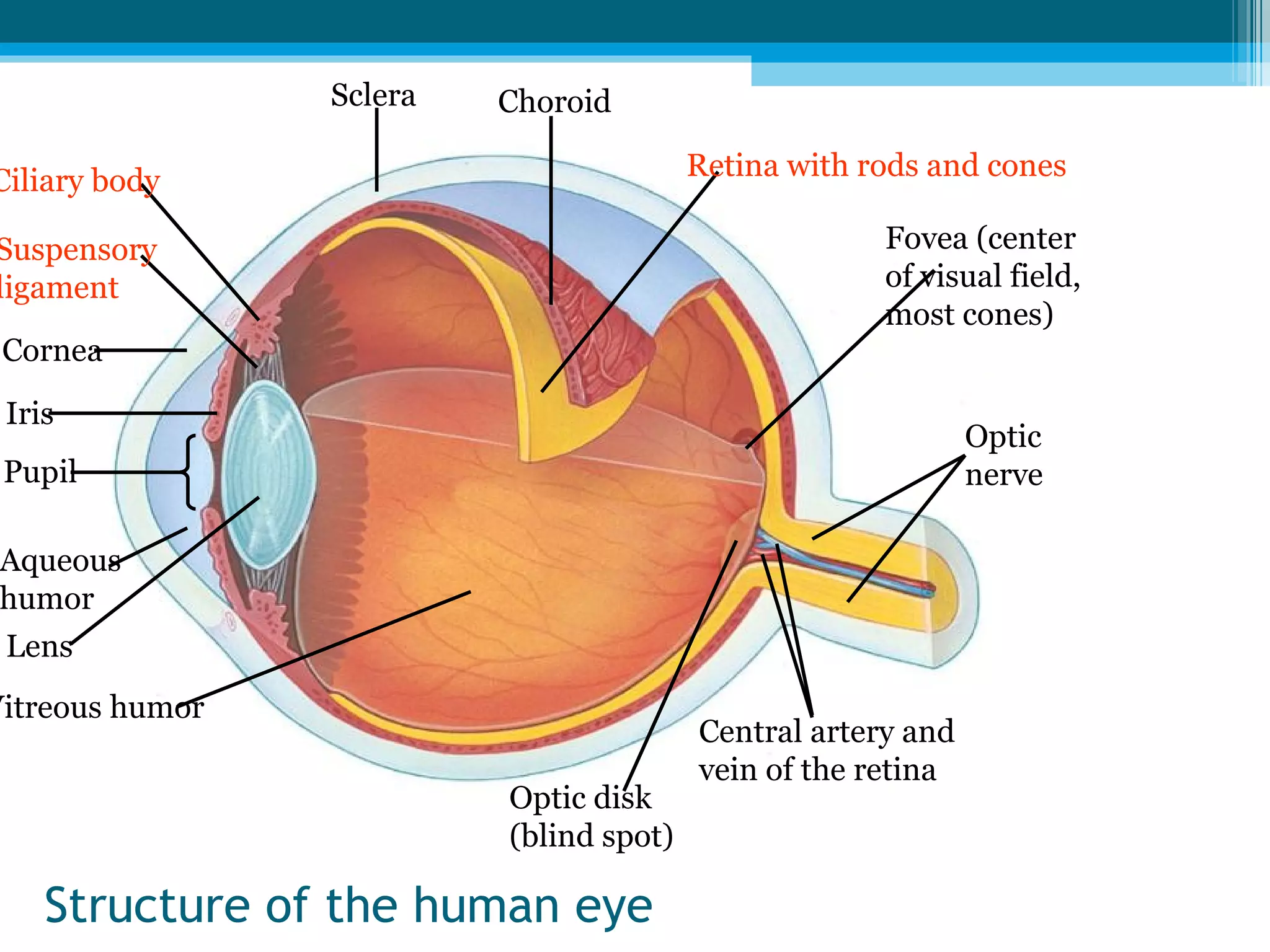
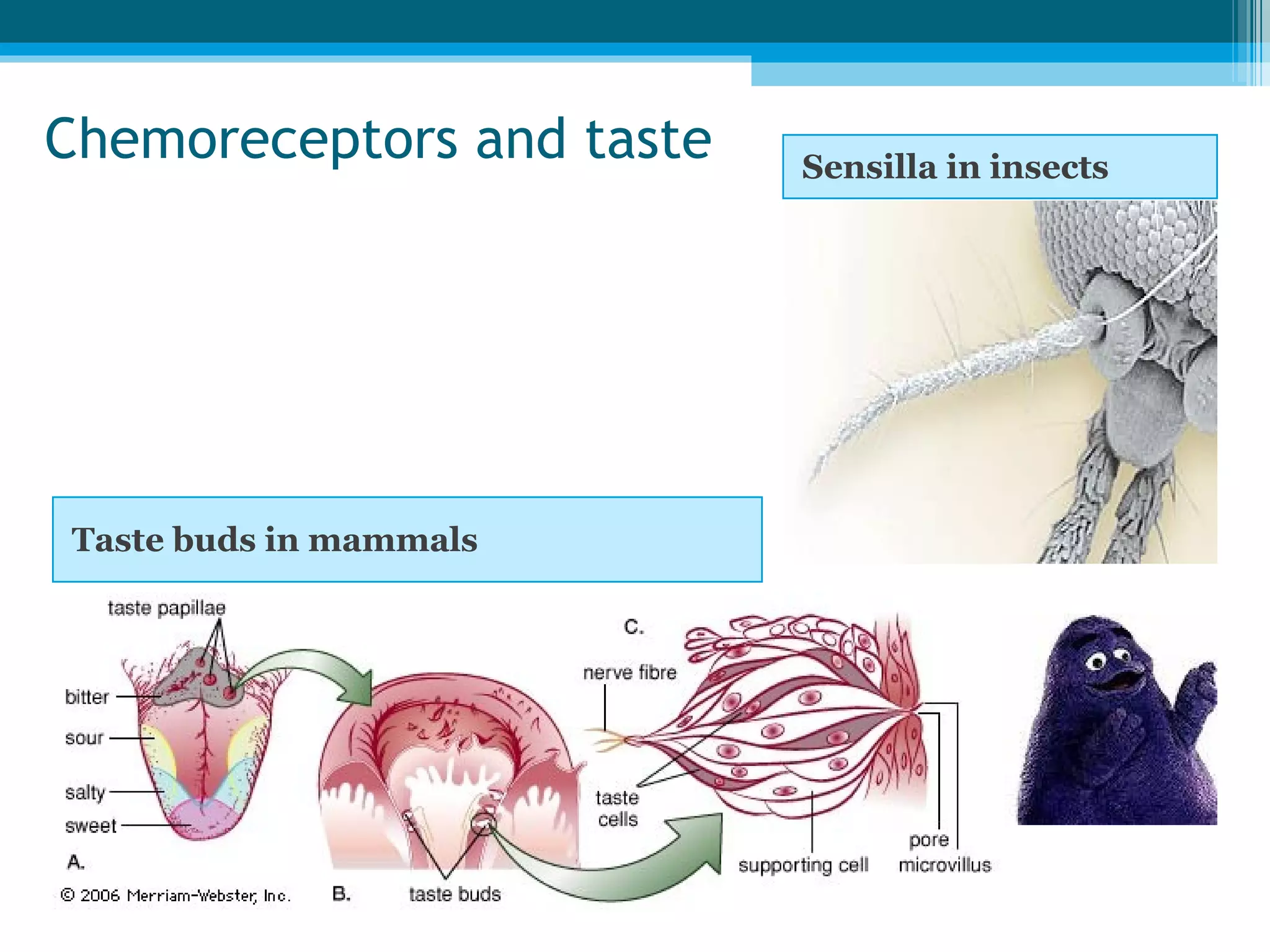
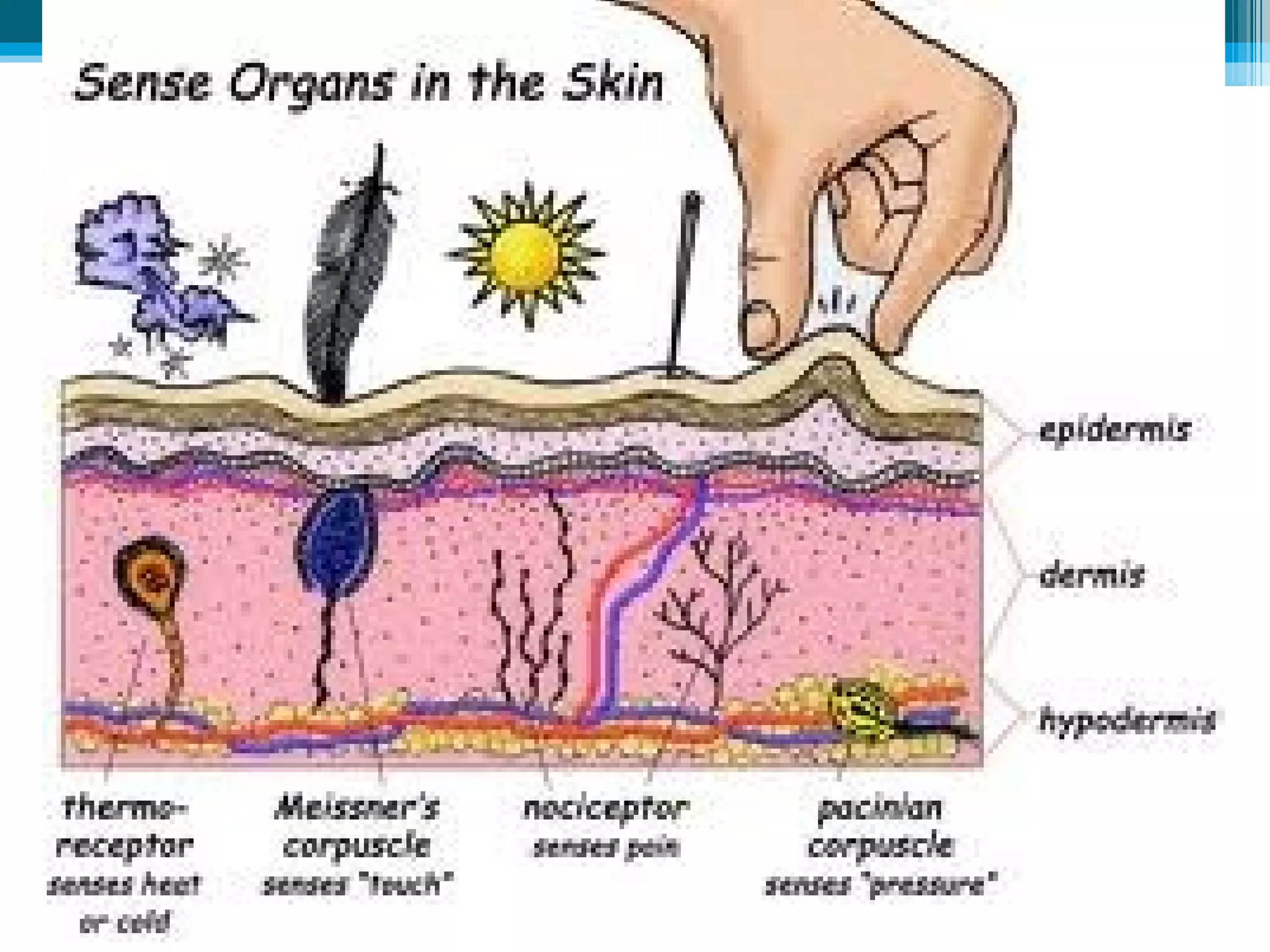
Sensory receptors in the skin, eyes, ears, tongue and nose detect various stimuli like light, sound, chemicals and pressure. These receptors convert the stimuli into electrical signals that are transmitted by sensory neurons to the brain. The brain then interprets these signals to form the perceptions of sight, hearing, smell, taste and touch. Sensory receptors include photoreceptors in the eyes, hair cells in the ears, taste buds in the tongue and olfactory receptors in the nose. The brain integrates information from sensory receptors to build an understanding of the external environment.