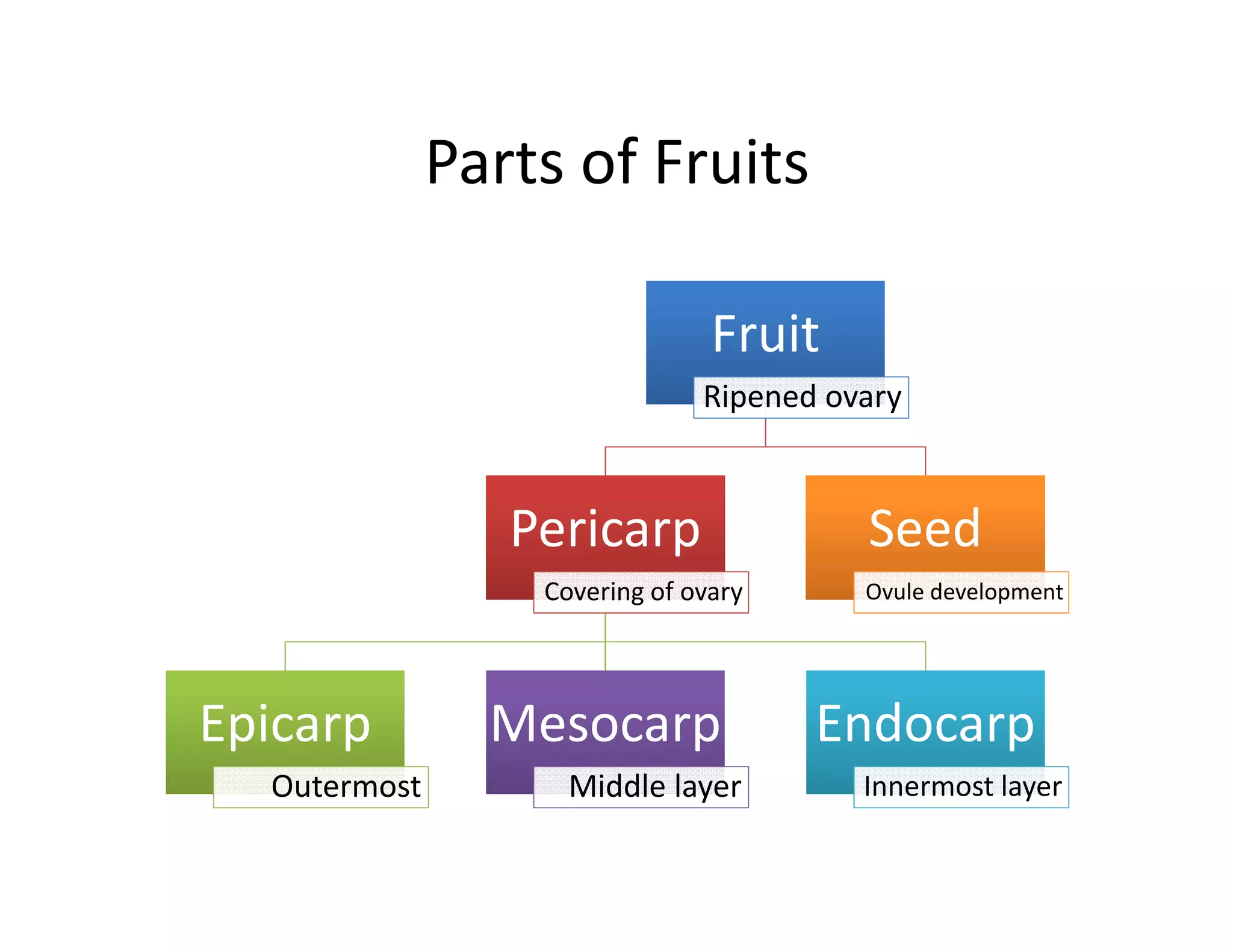
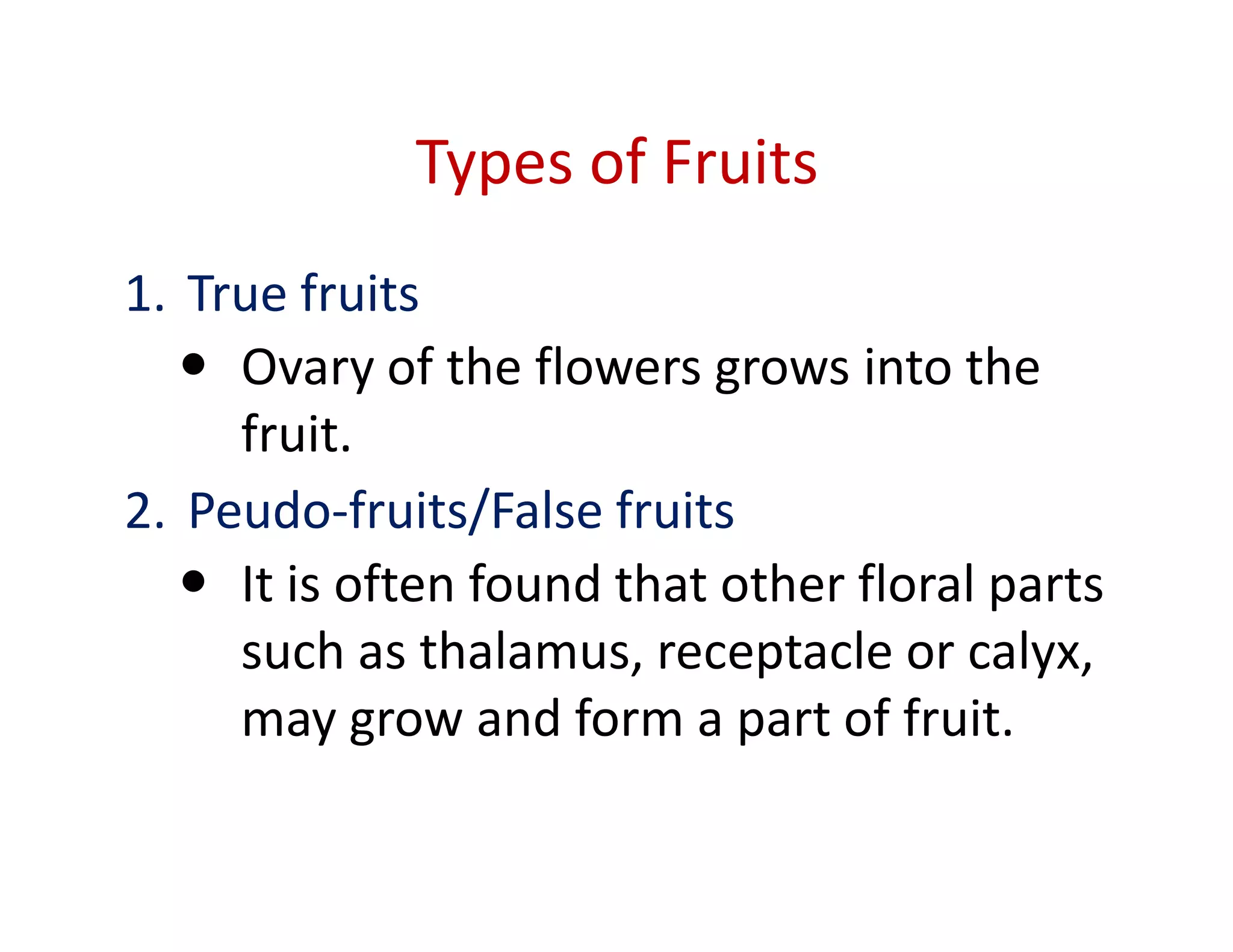
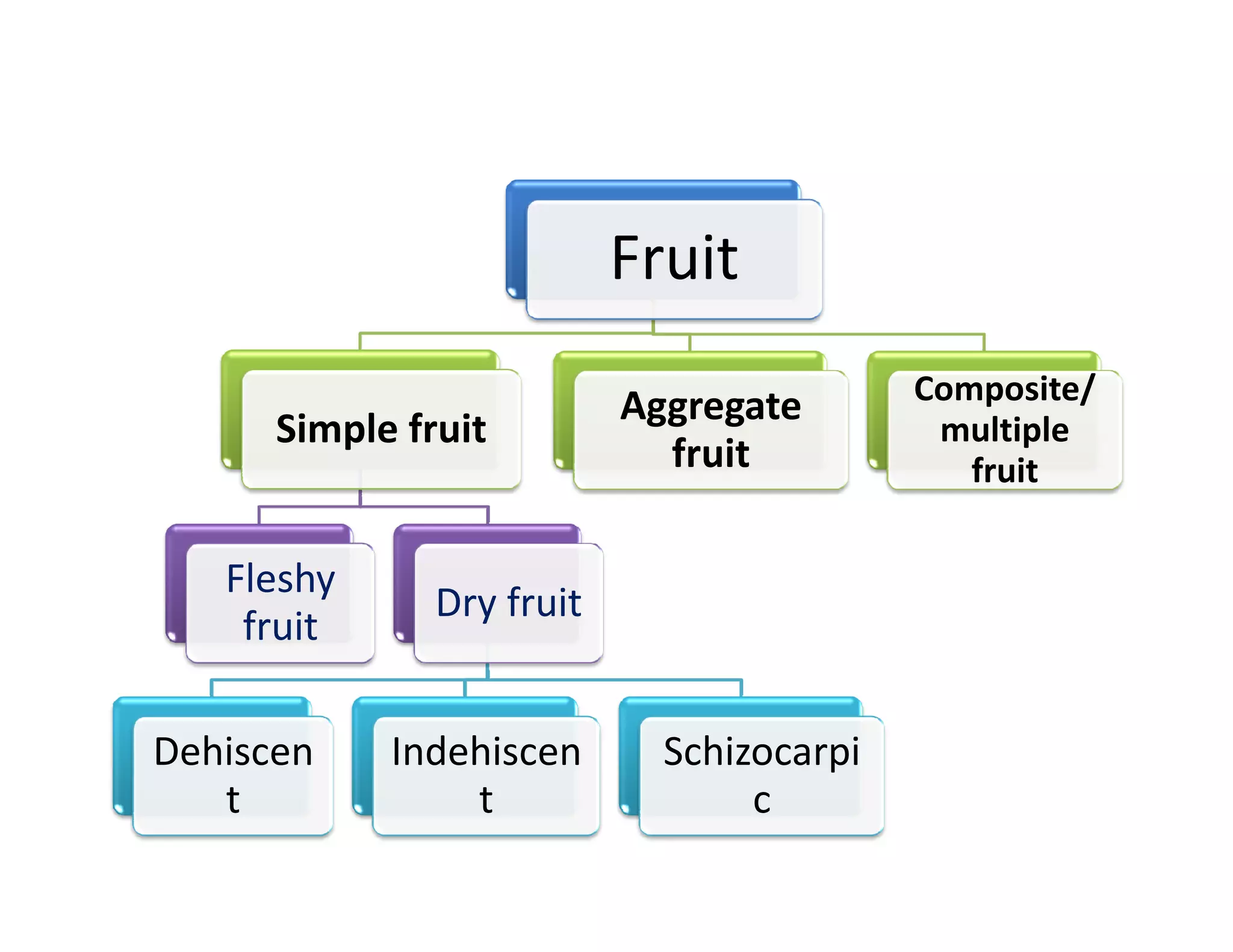
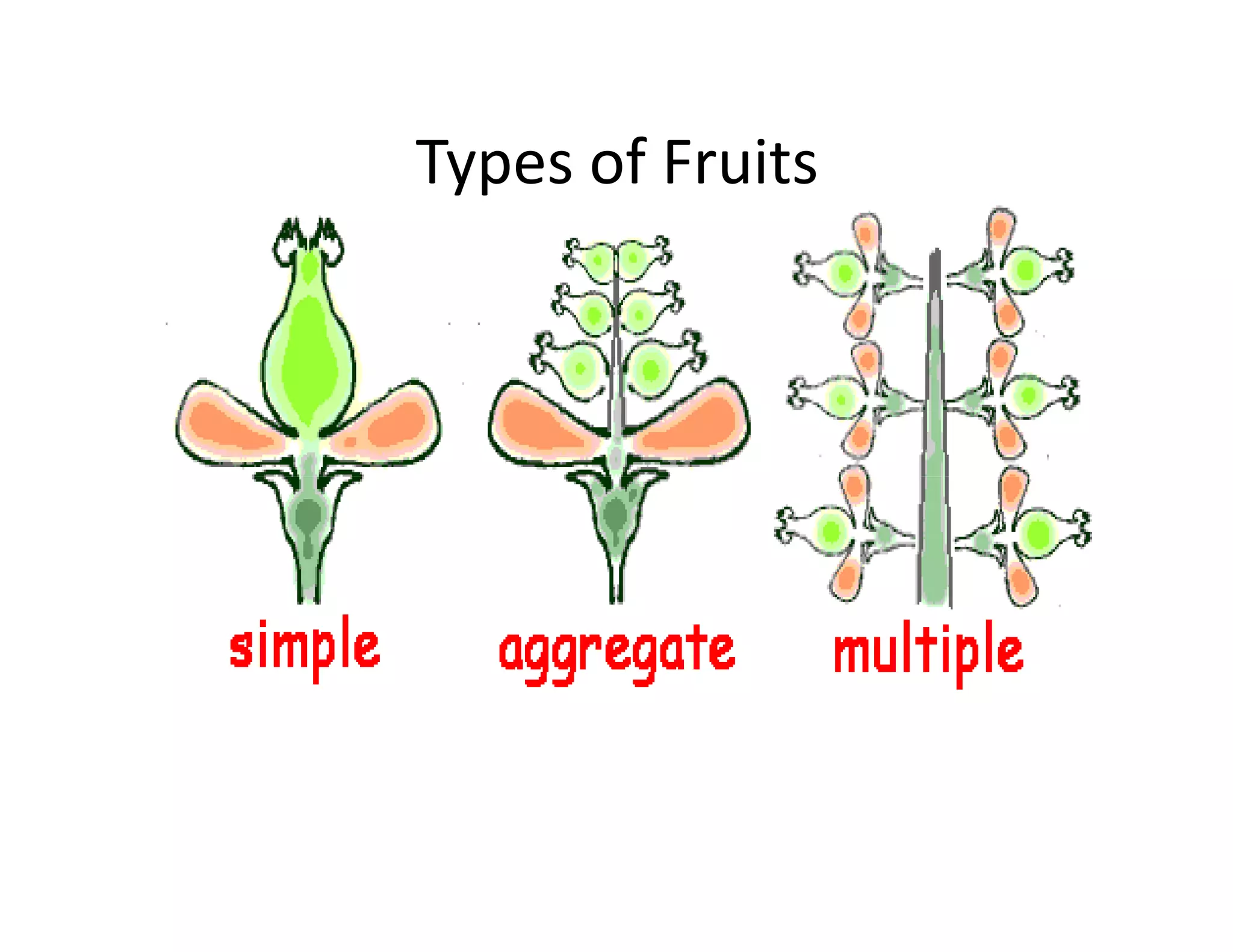
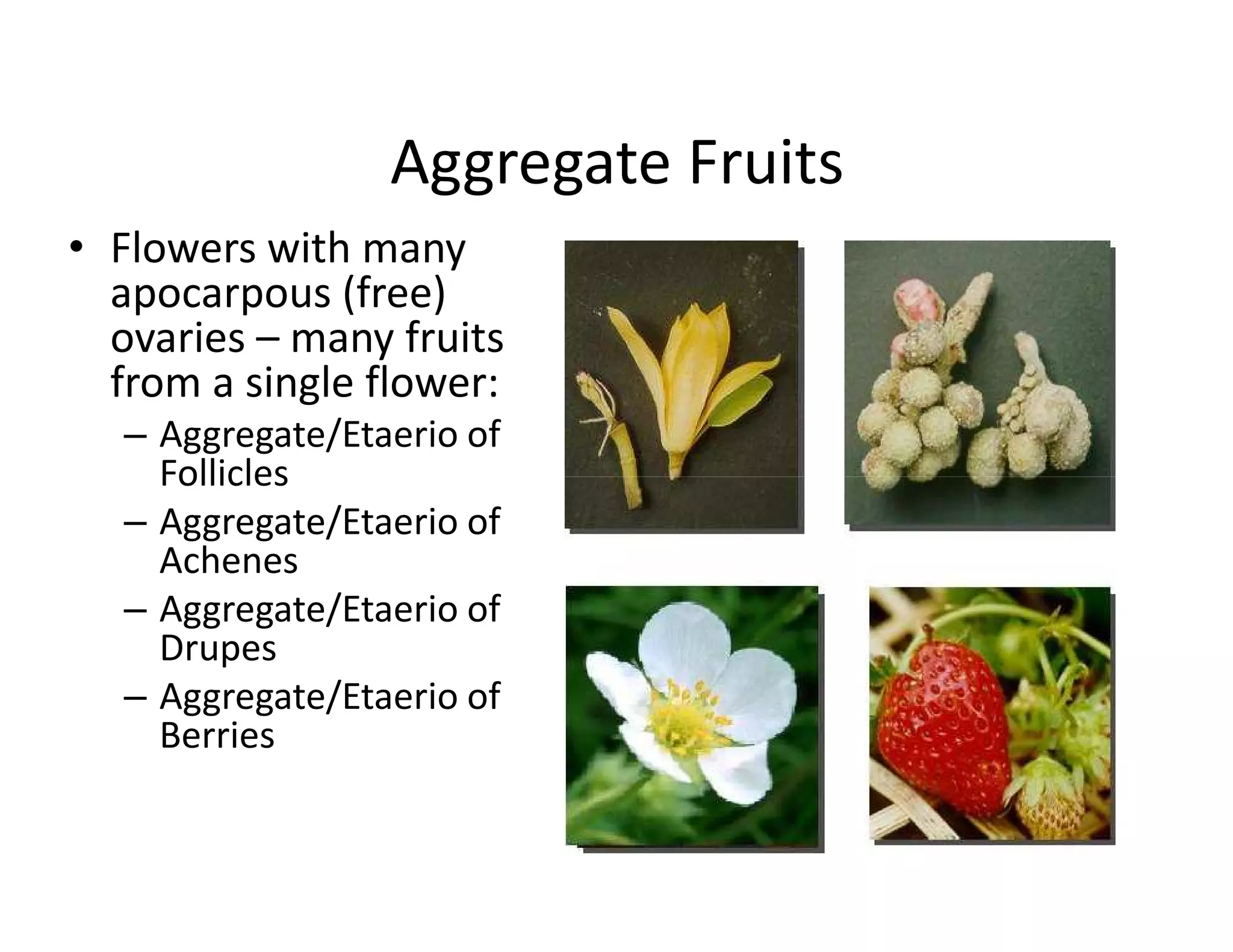
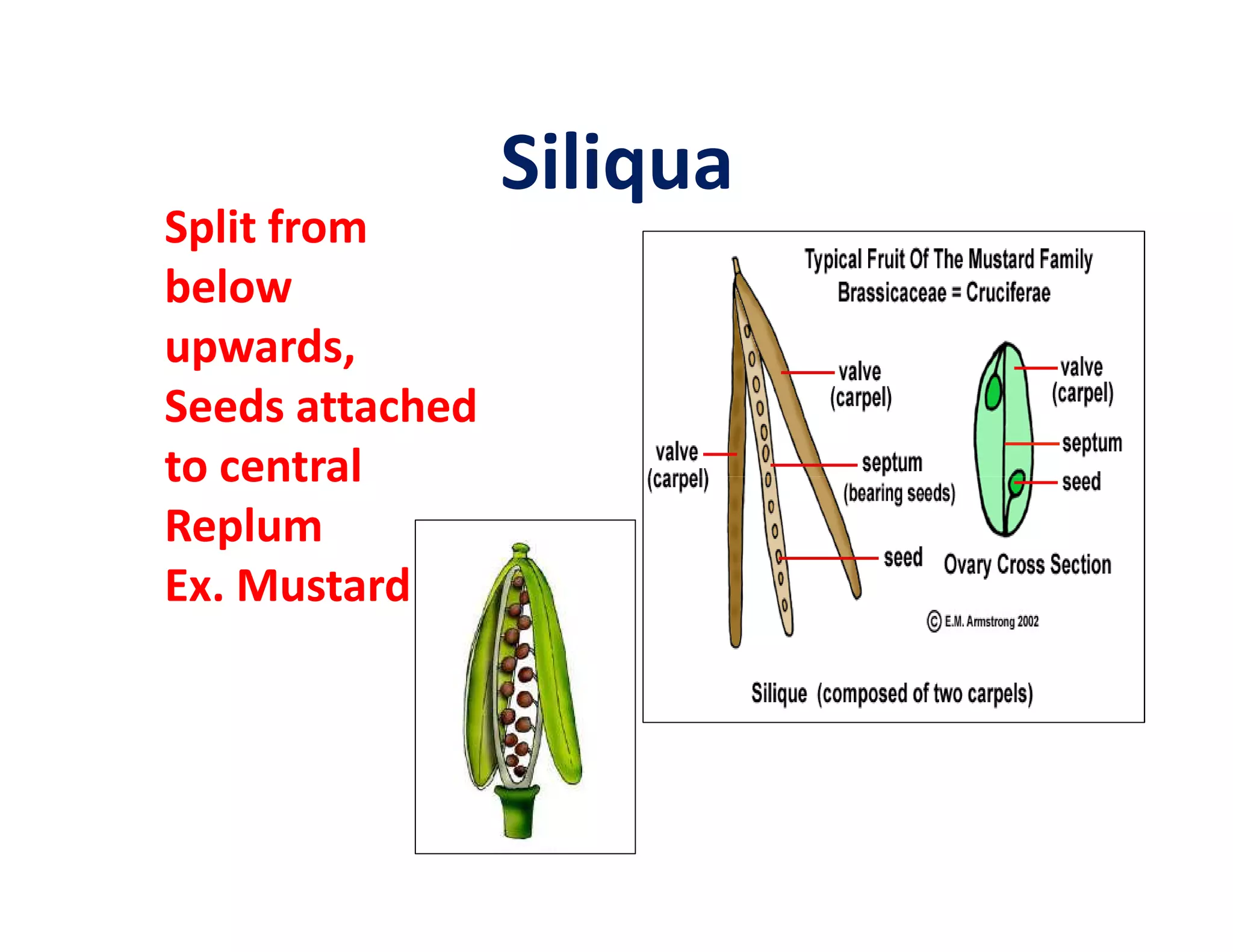
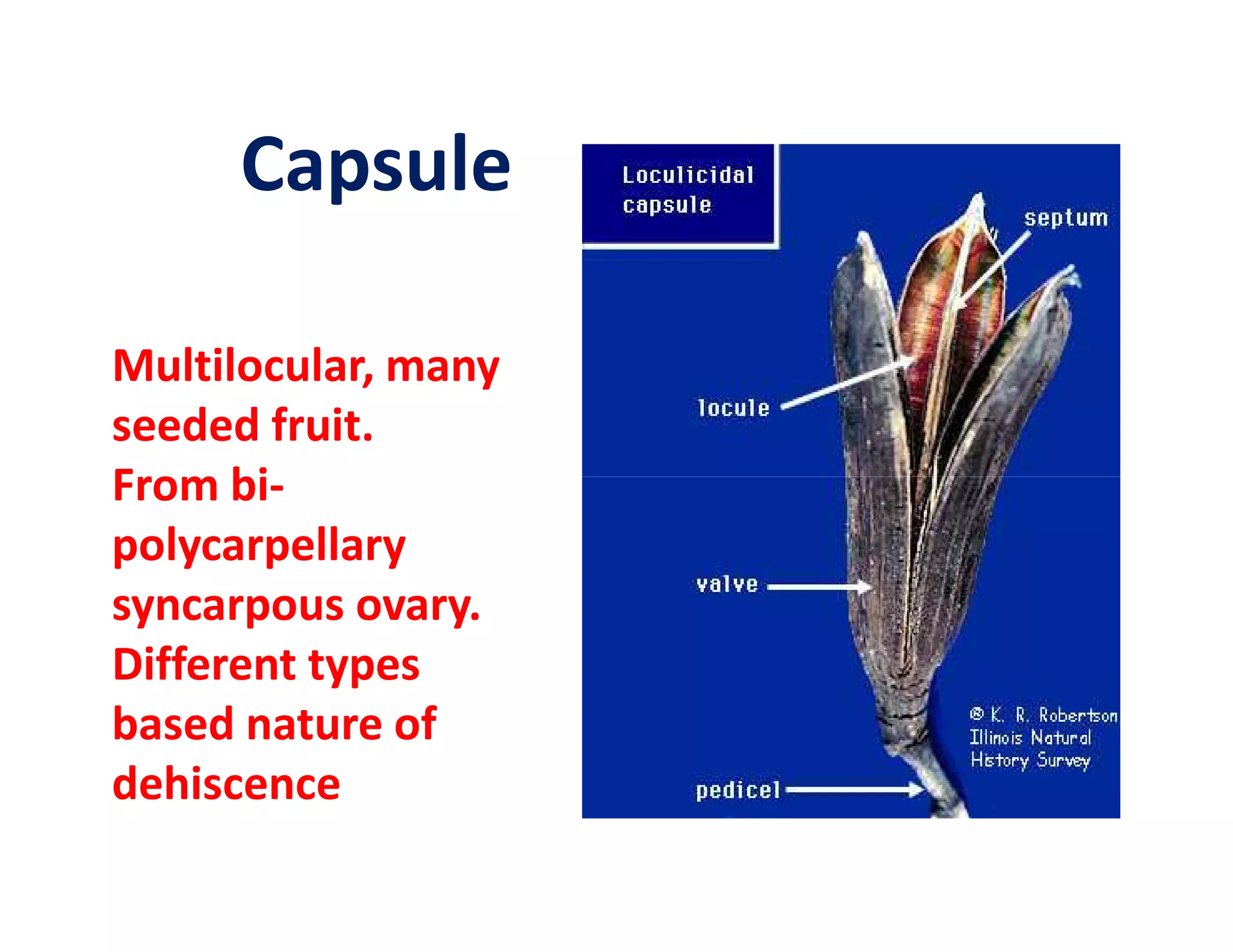
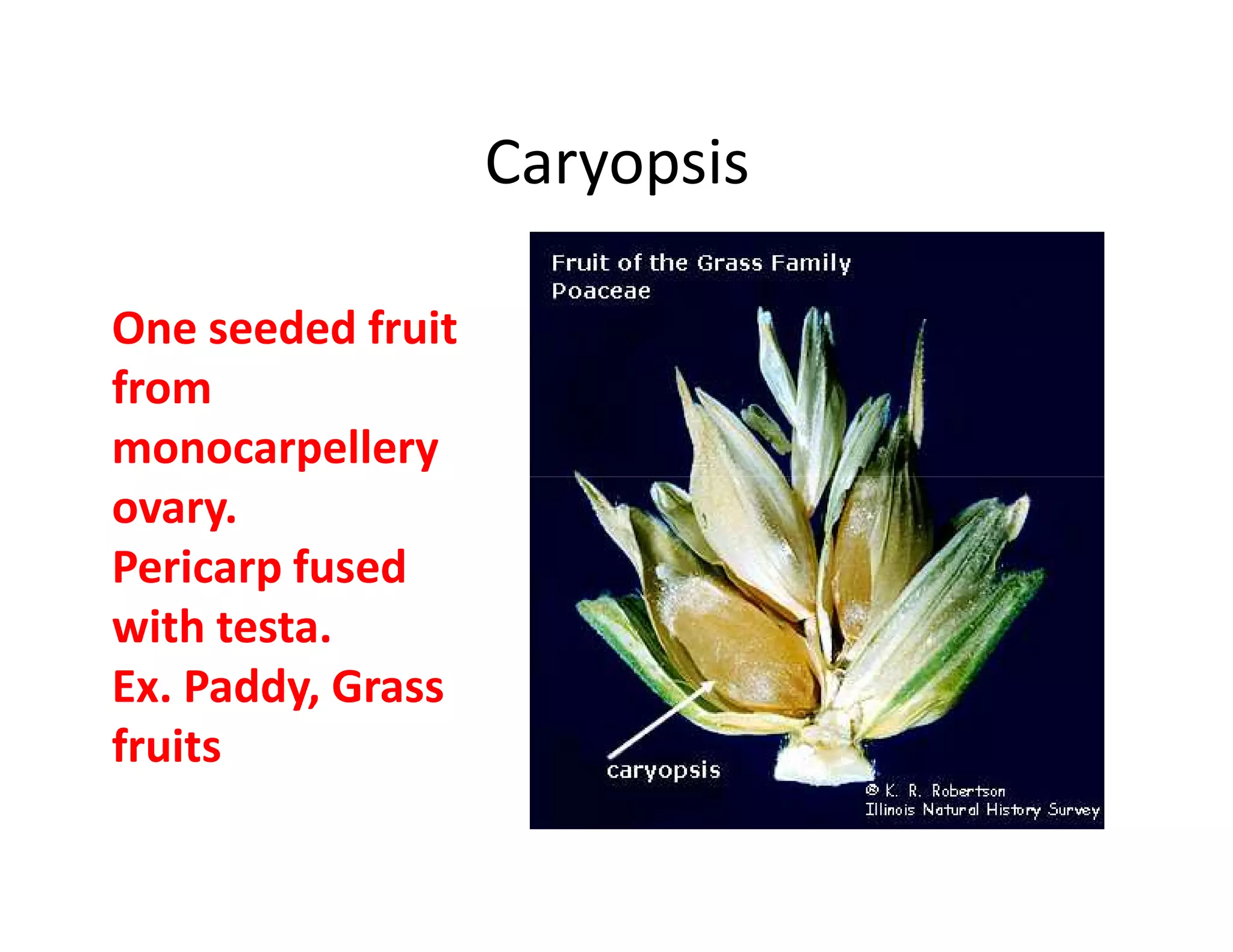
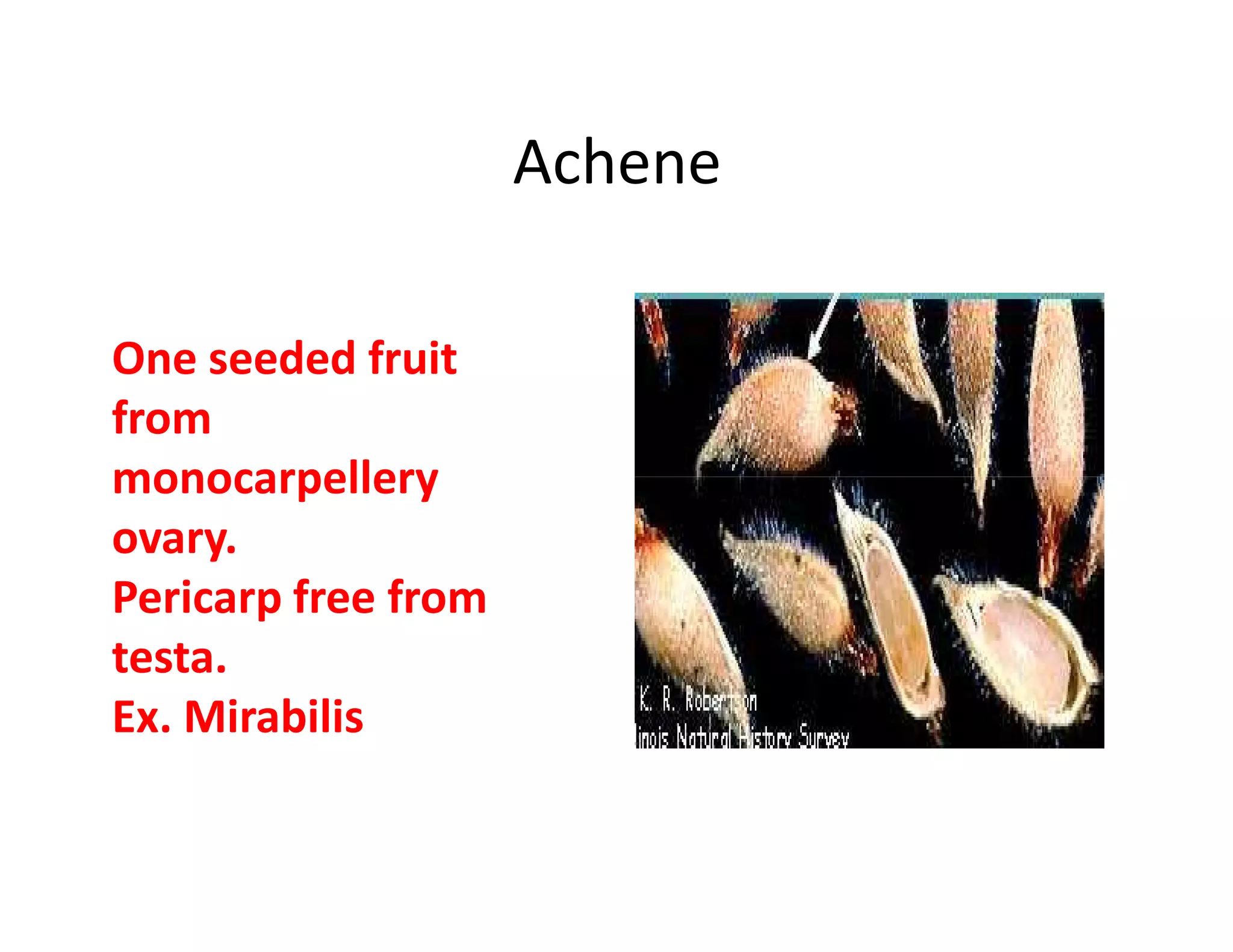
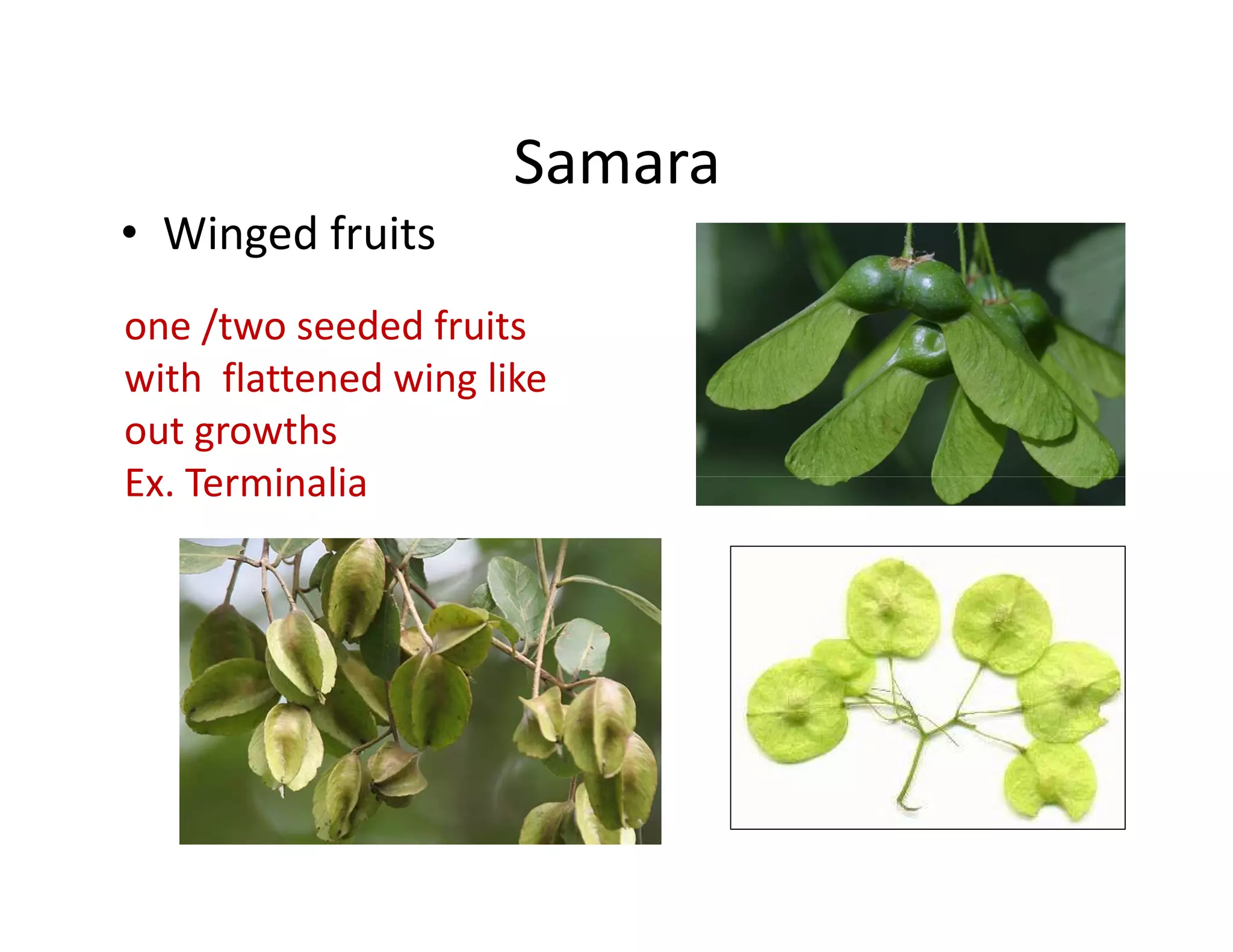
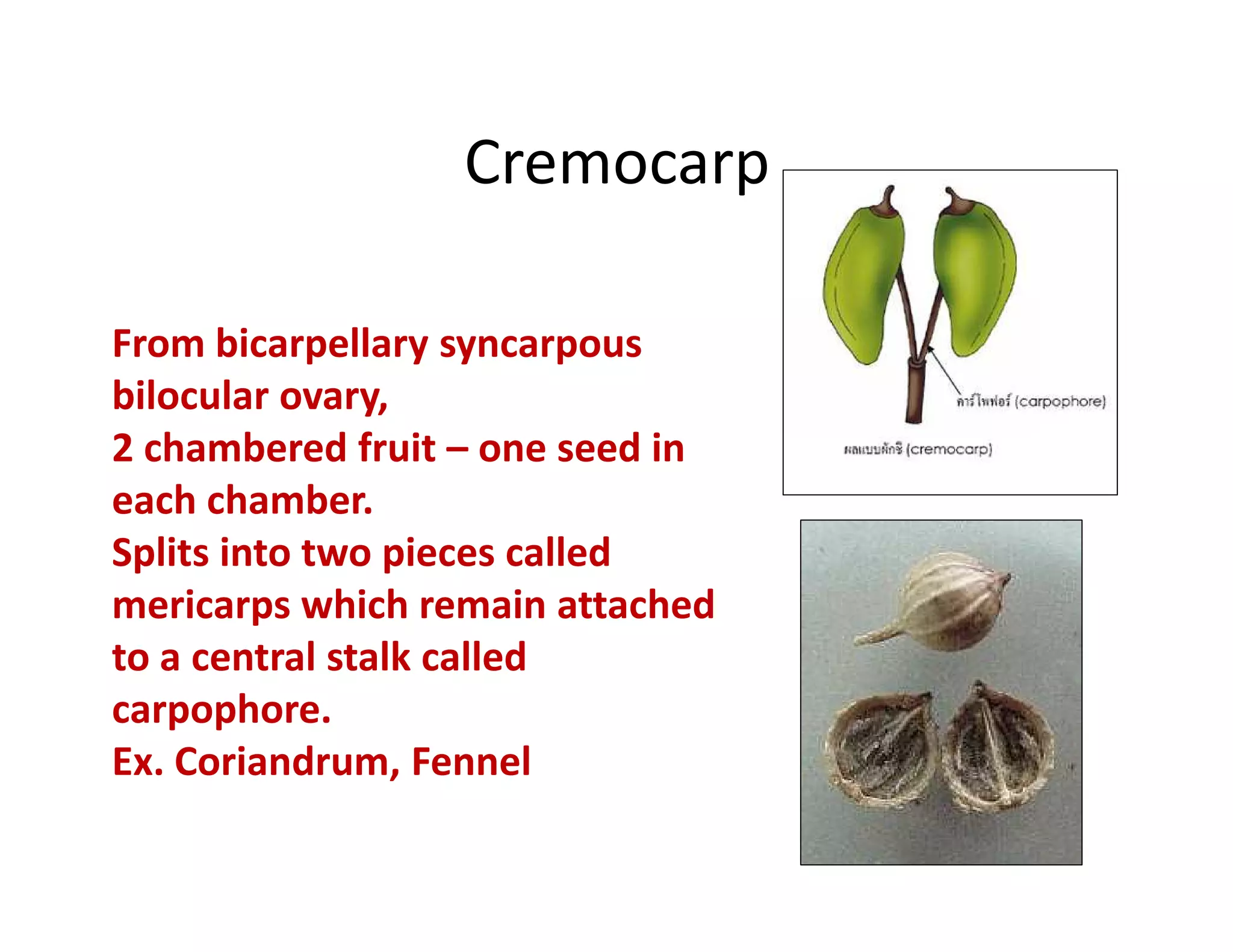
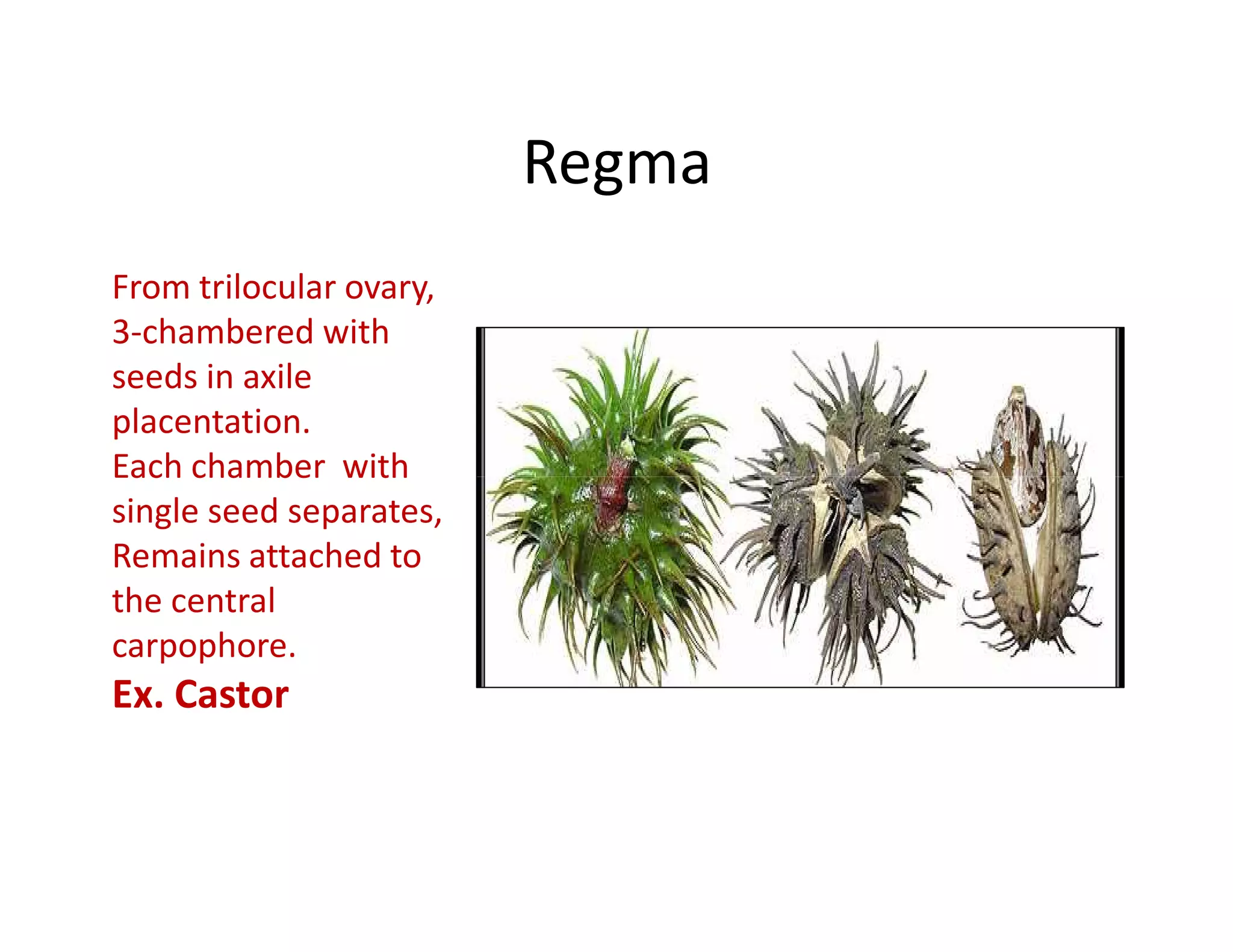
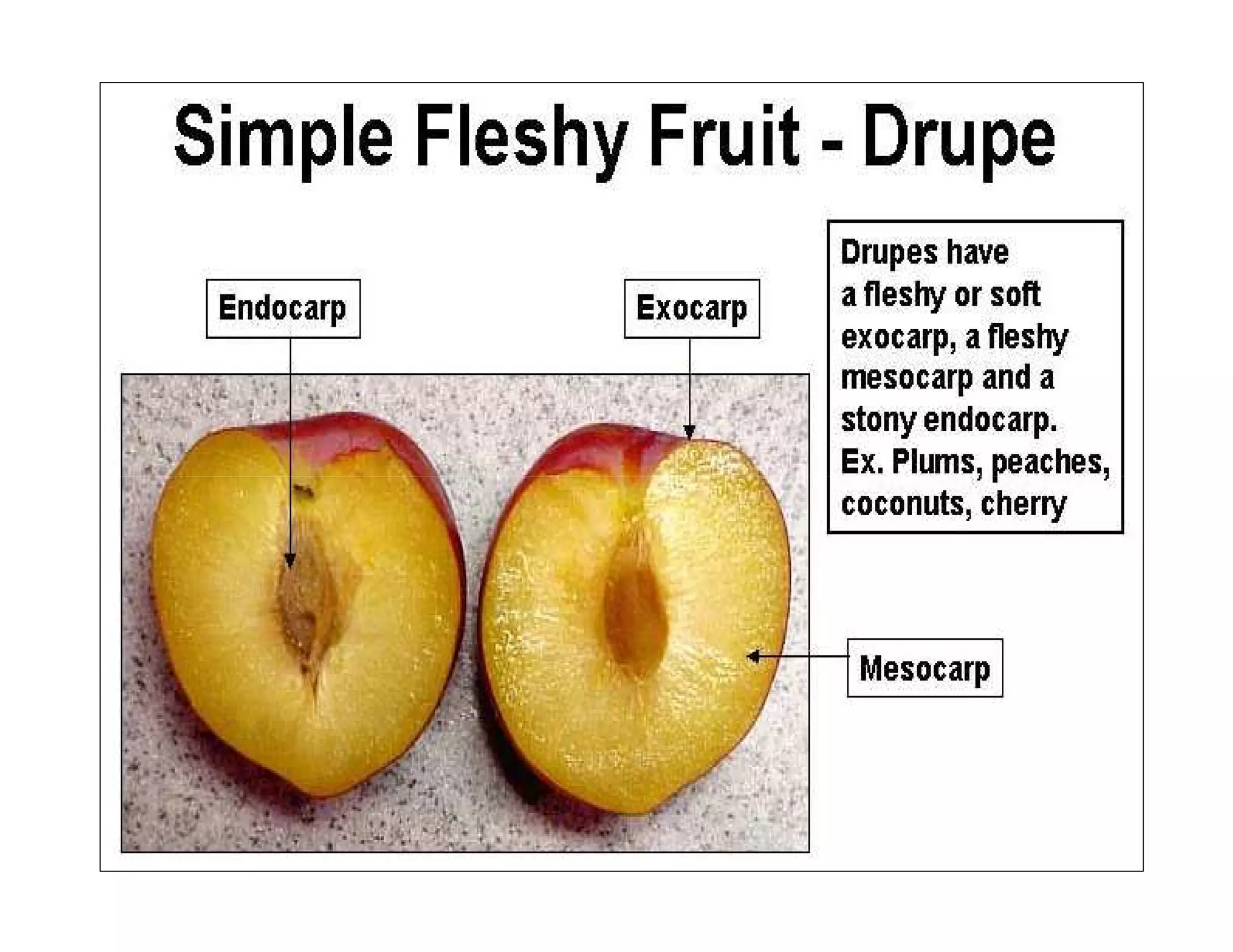
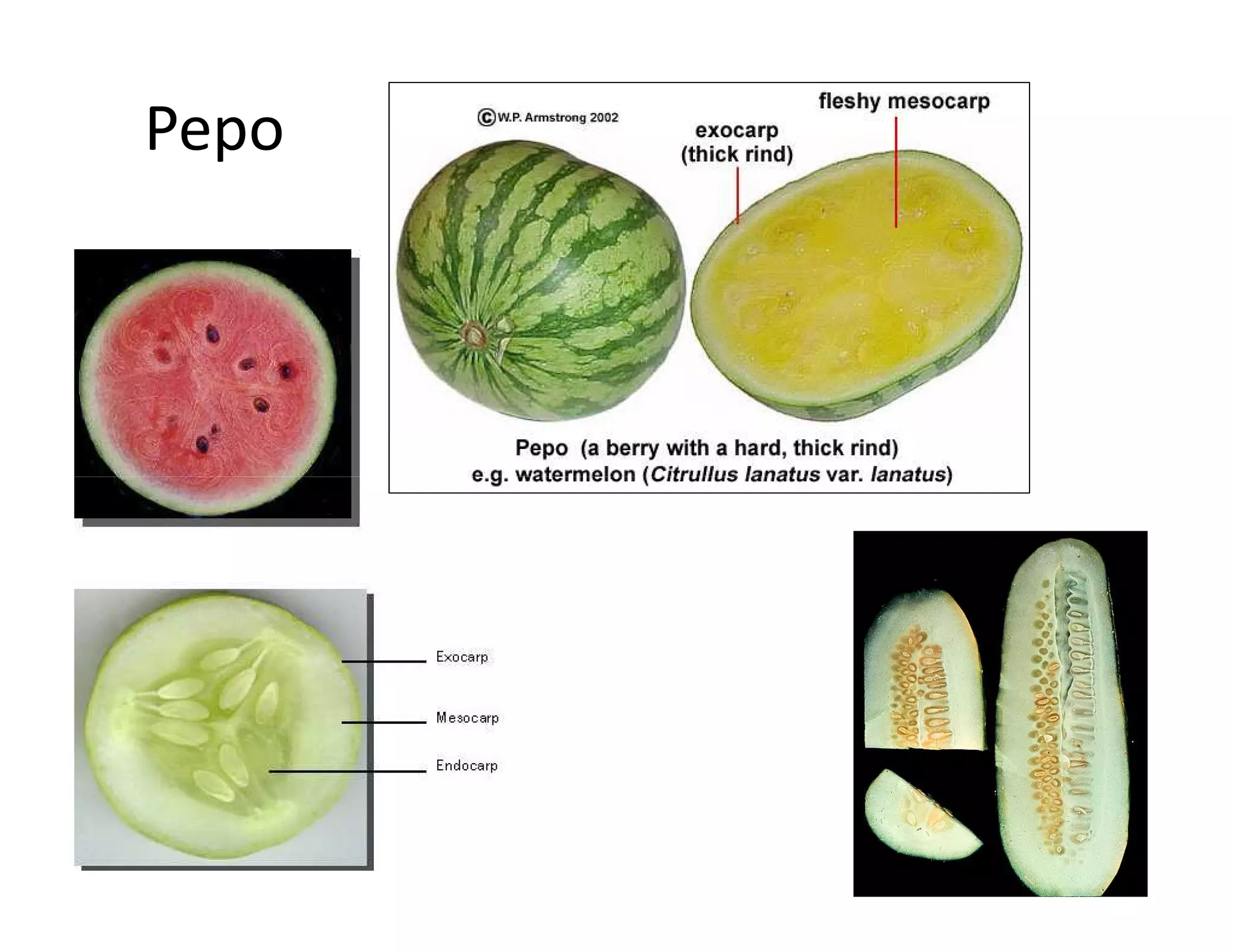
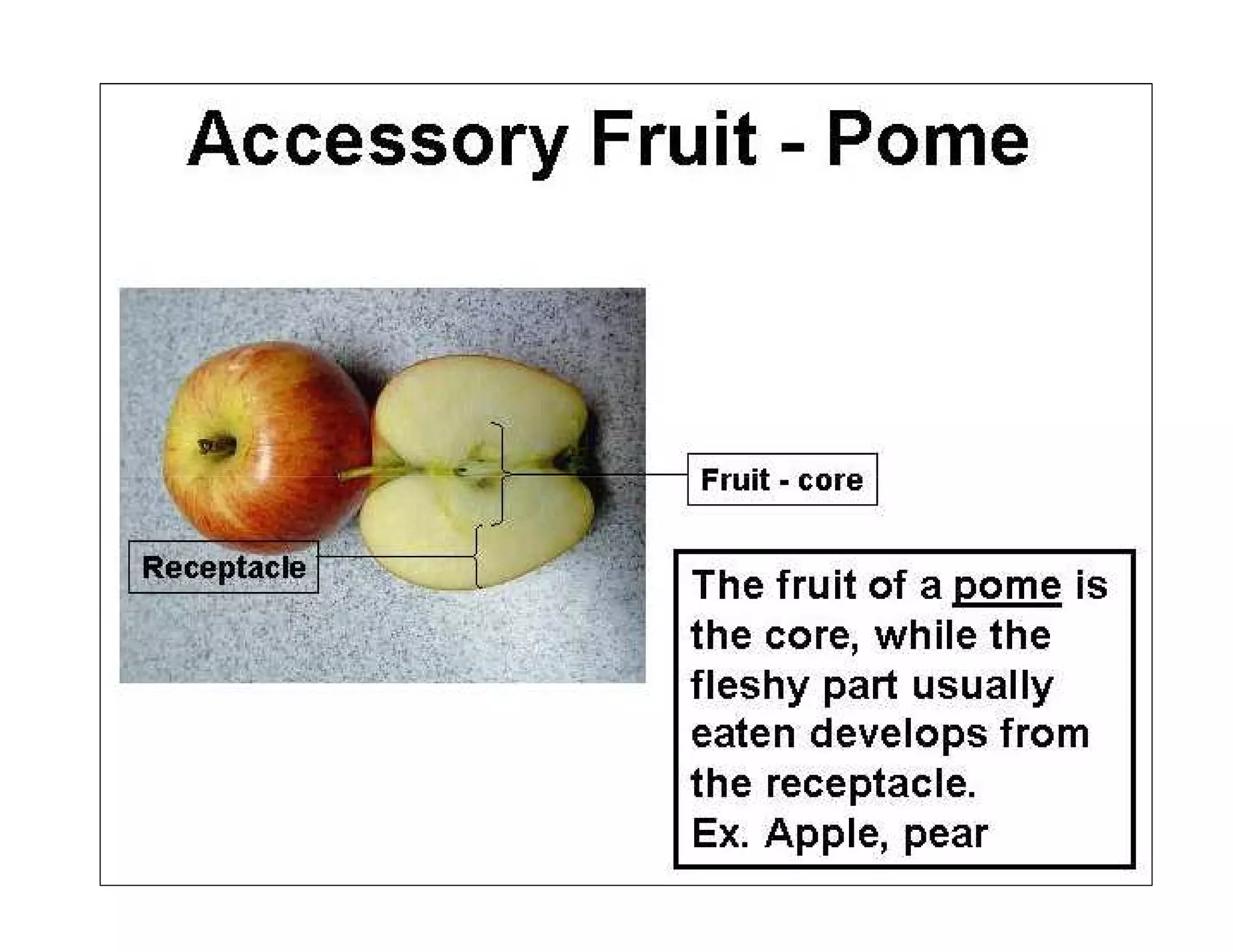
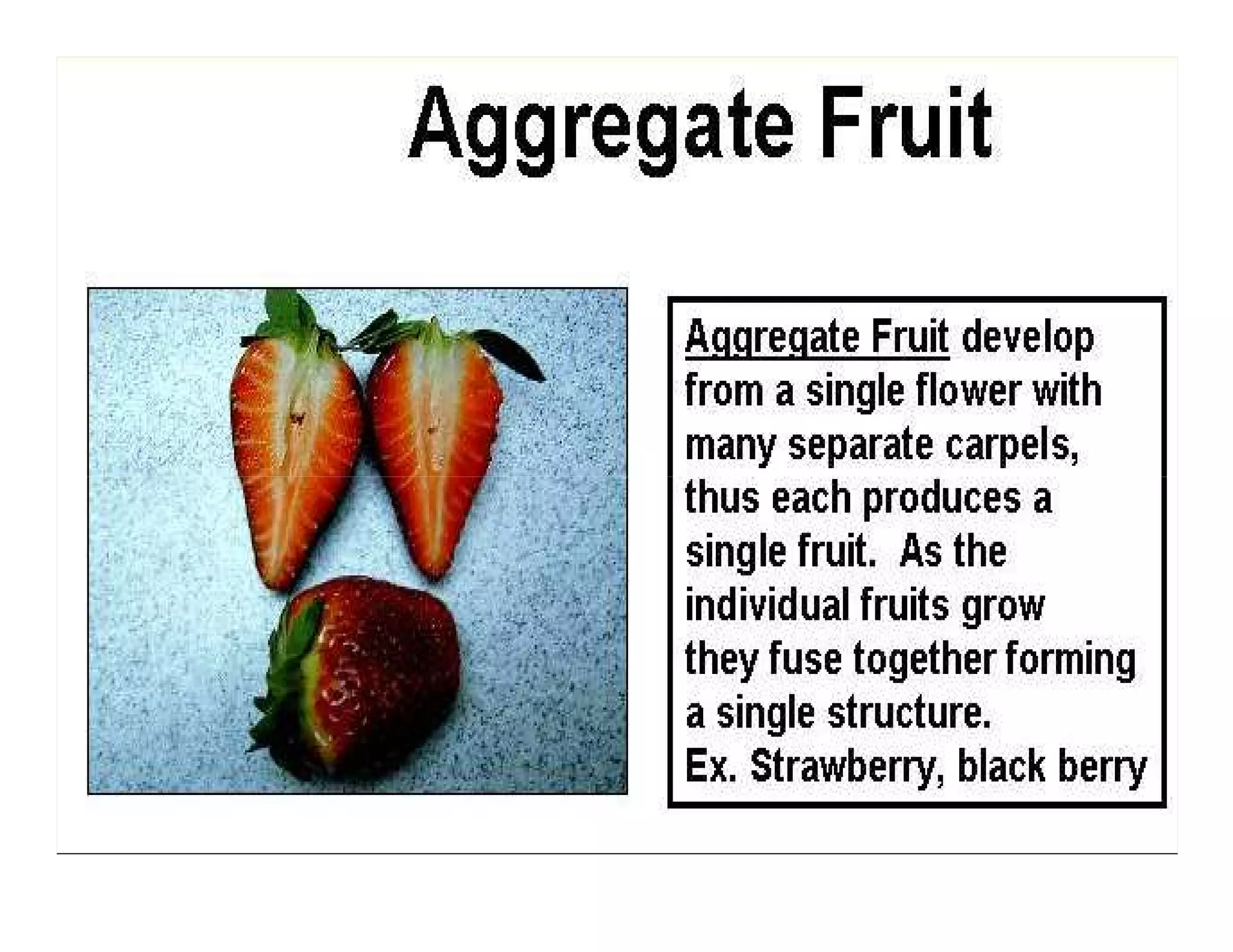
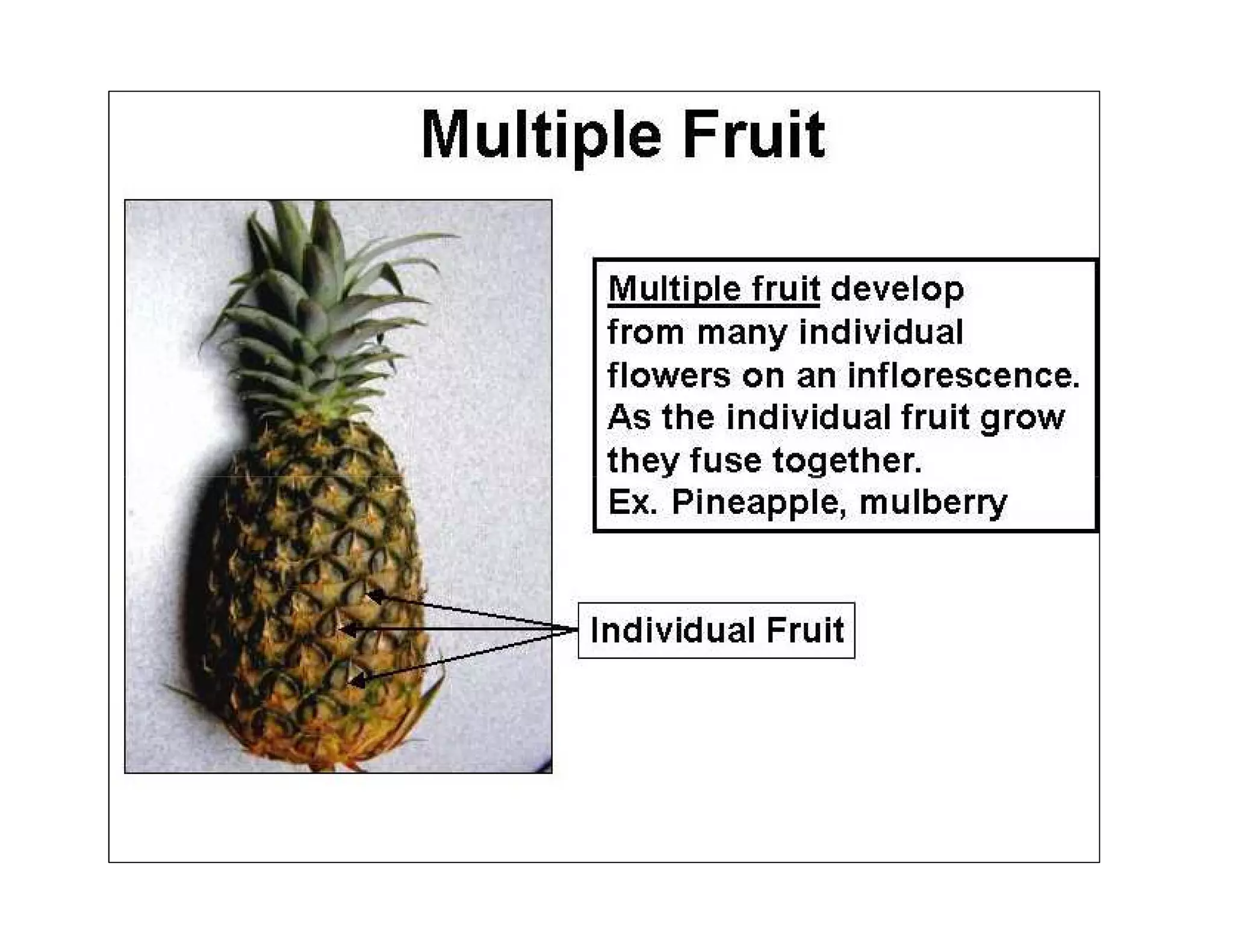
This document discusses the morphology of fruits. It defines a fruit as a ripened ovary formed after fertilization. Fruits have three layers - the epicarp, mesocarp, and endocarp. True fruits develop from the flower's ovary, while pseudo-fruits incorporate other floral parts. Fruits are classified by their structure, development, and dehiscence into simple, aggregate, and composite types. Examples of different fruit types like legumes, follicles, berries, and drupes are provided.