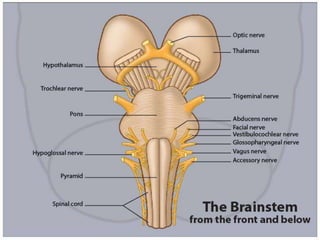
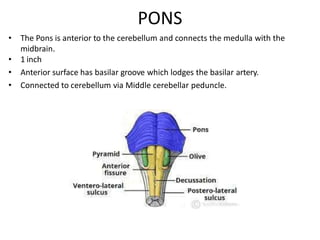
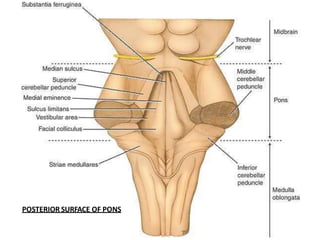
The brainstem consists of 3 parts - the midbrain, pons, and medulla. It connects the spinal cord to the forebrain and serves as a conduit for ascending and descending tracts. Important functions include control of consciousness, respiration, the cardiovascular system, and cranial nerve nuclei III-XII. The medulla contains the pyramids, olive, and inferior cerebellar peduncle. The pons connects to the cerebellum and contains the facial, vestibulocochlear, and glossopharyngeal nerves. The midbrain contains the cerebral aqueduct and corpora quadrigemina with superior and inferior colliculi.