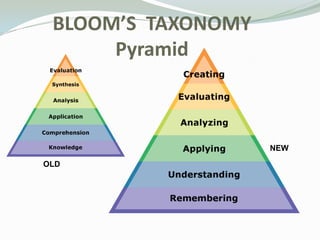
This document provides information about Bloom's Taxonomy and lesson planning. It discusses the original and revised versions of Bloom's Taxonomy, which structures thinking skills into six levels moving from basic recall to more complex levels of critical thinking. It then explains what a lesson plan is and its key elements: objectives, standards, materials, procedure, and assessment. Objectives should be written based on learning outcomes and be measurable. The materials, procedure, and assessment sections provide guidance on how to address each of these key lesson plan components. Standards refer to both state curriculum standards and technology standards. The document emphasizes that lesson plans provide structure and guidance for teaching.