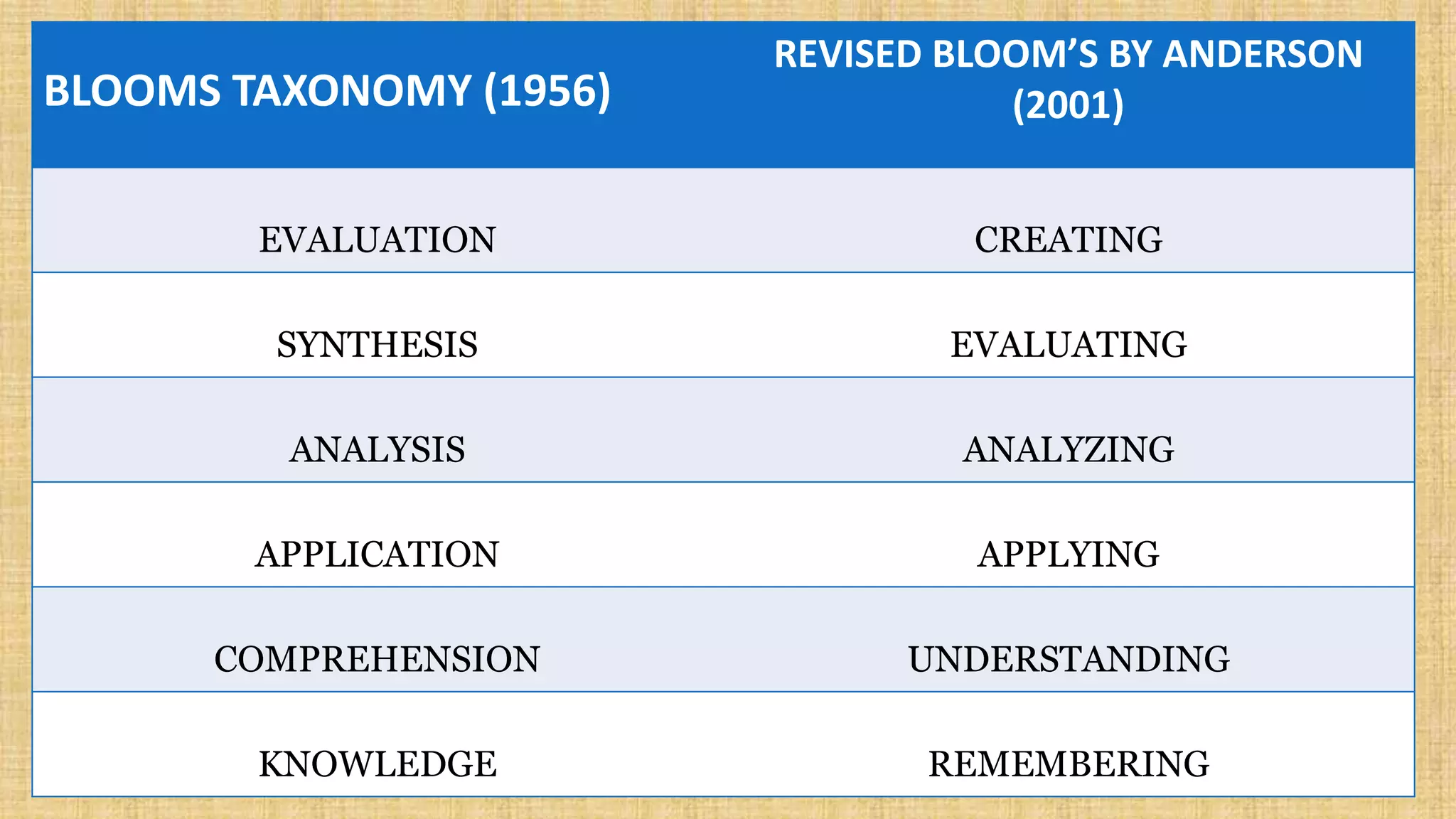
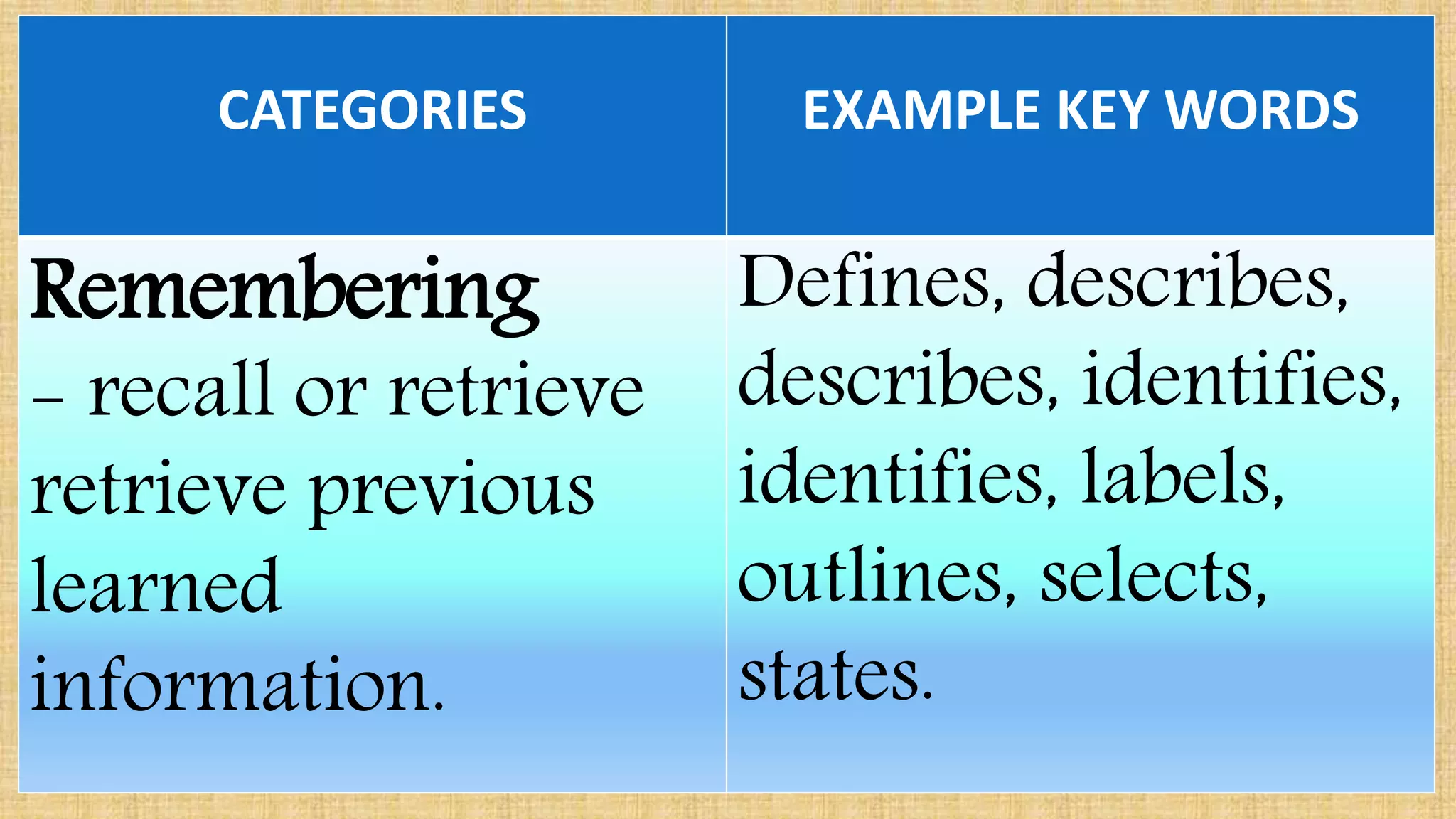
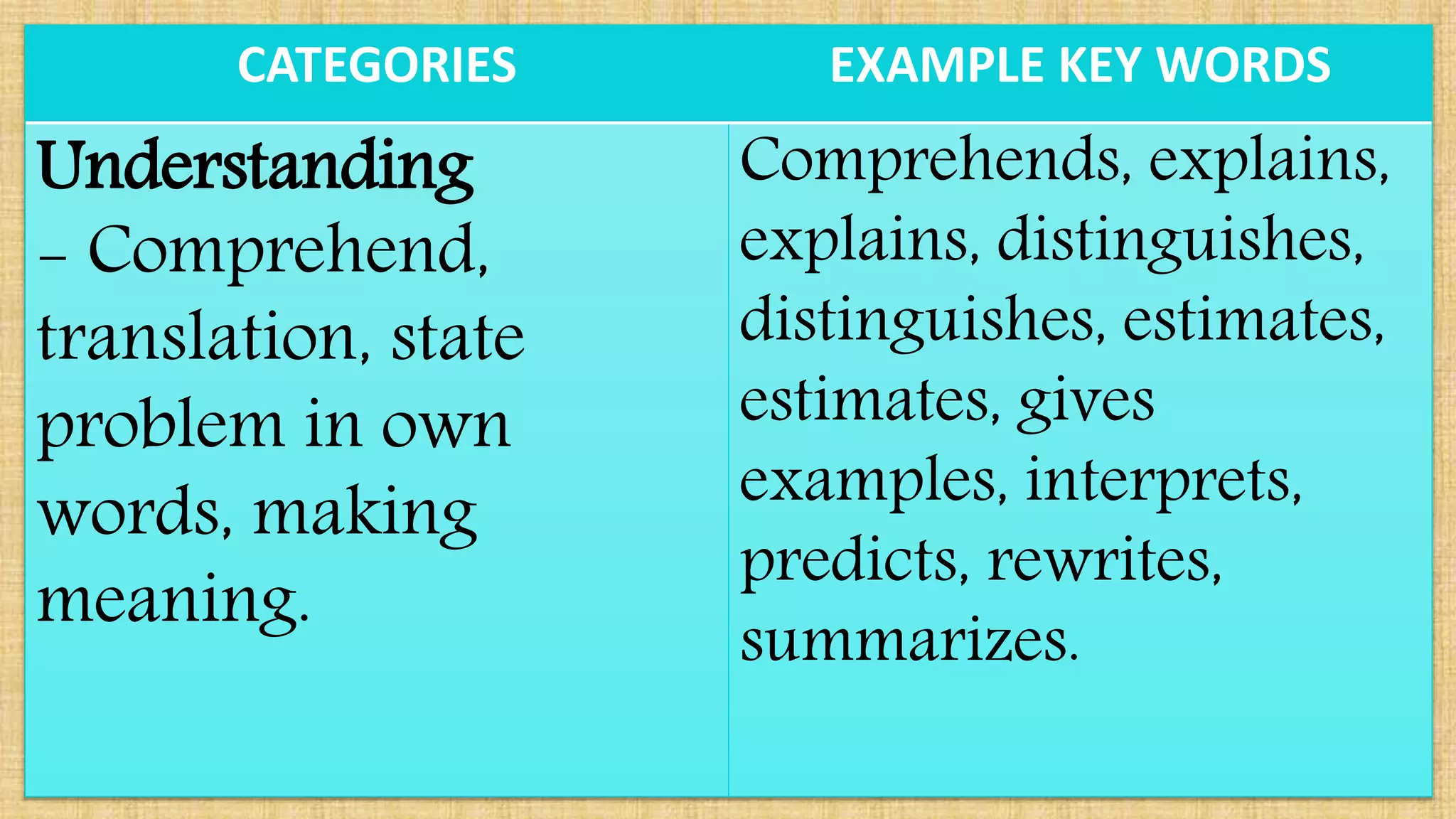
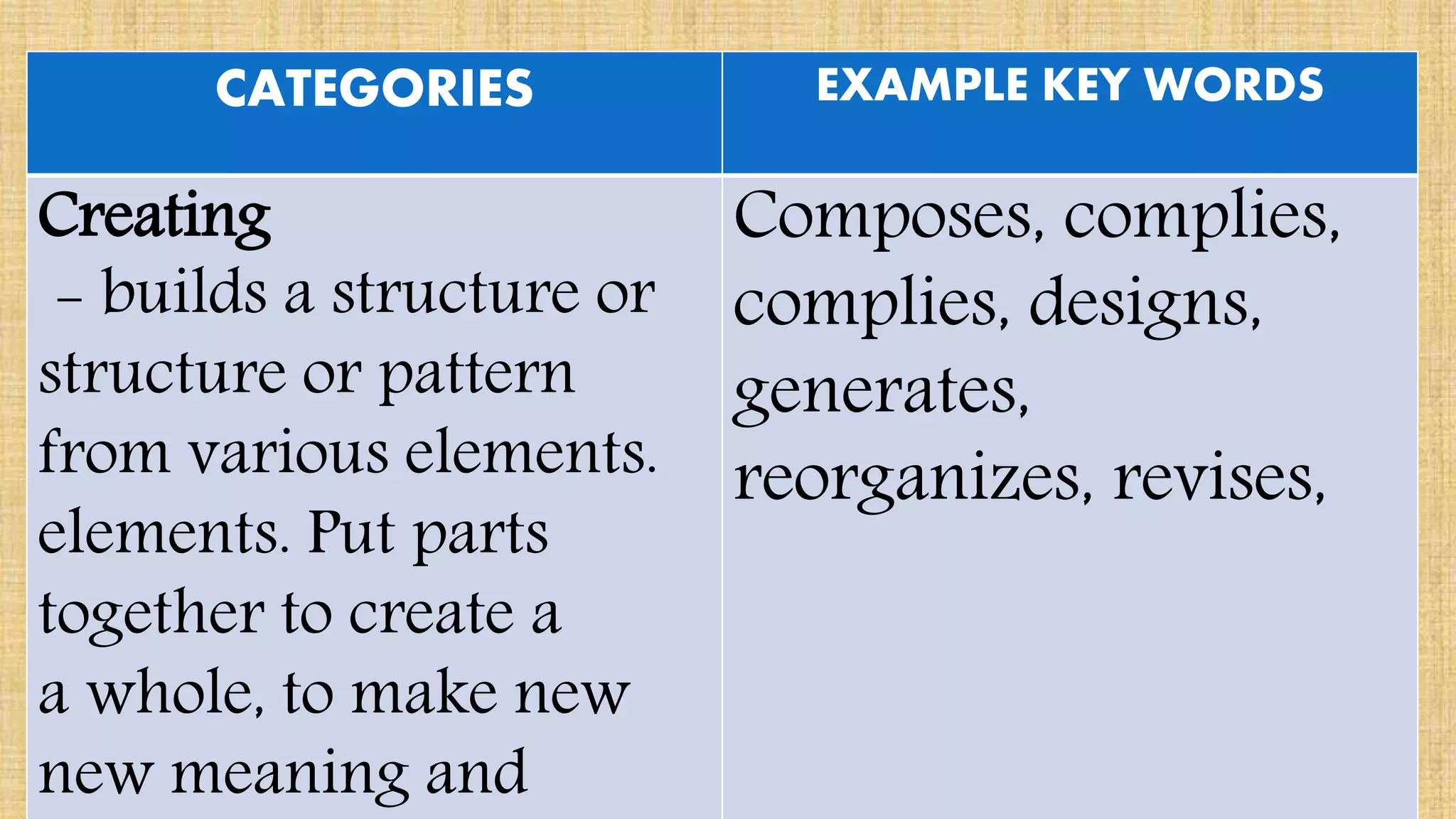
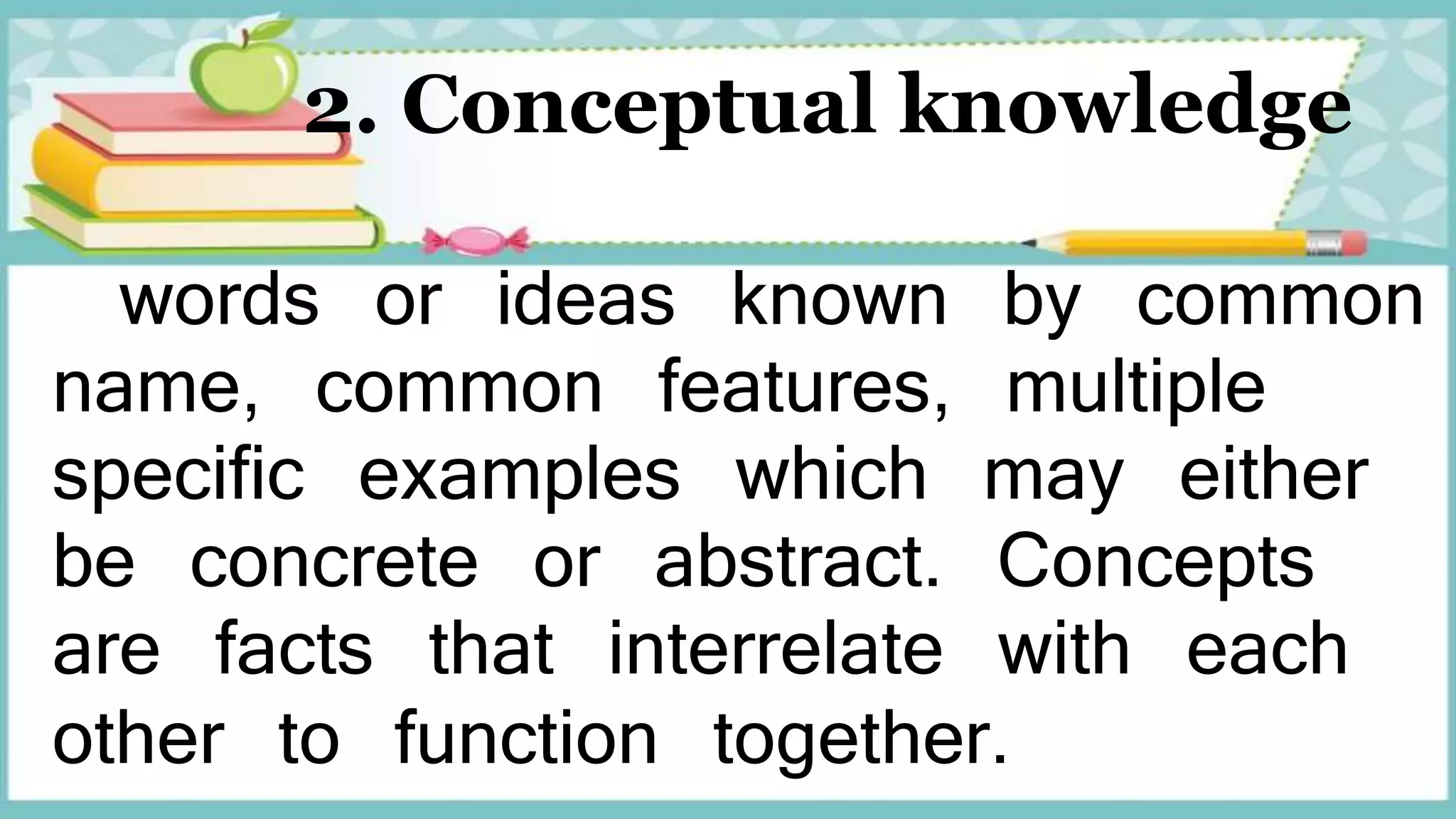
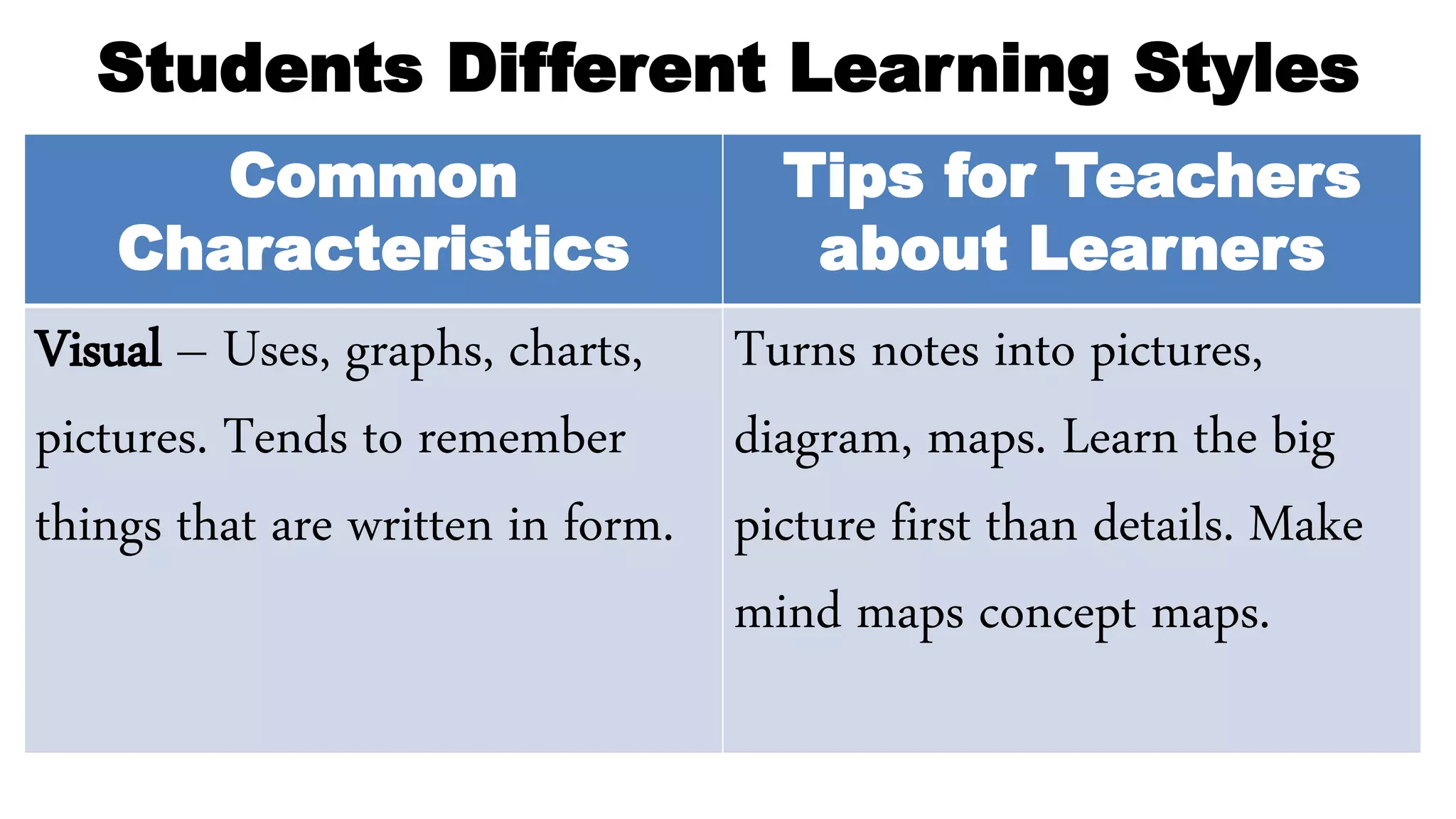
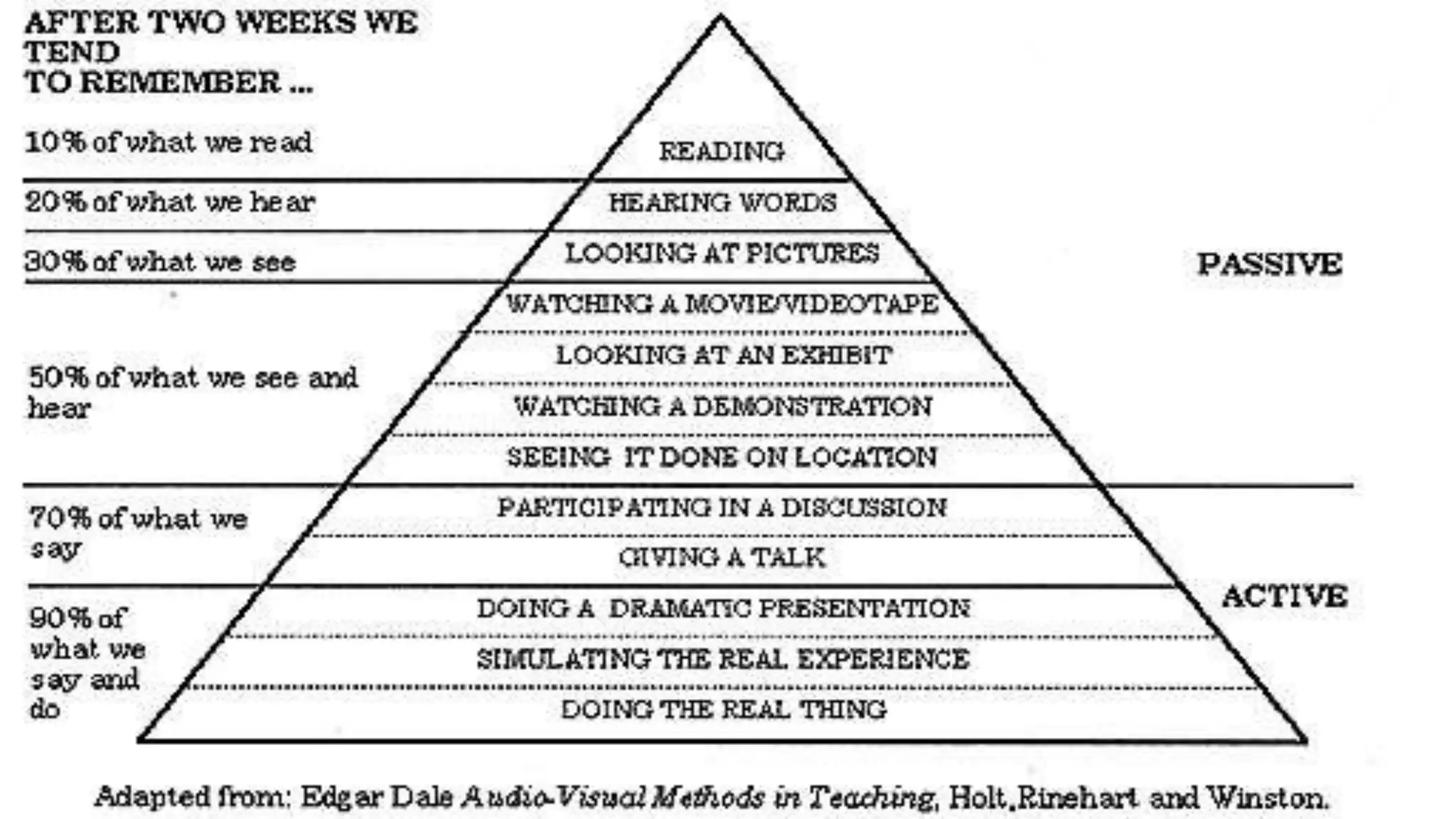
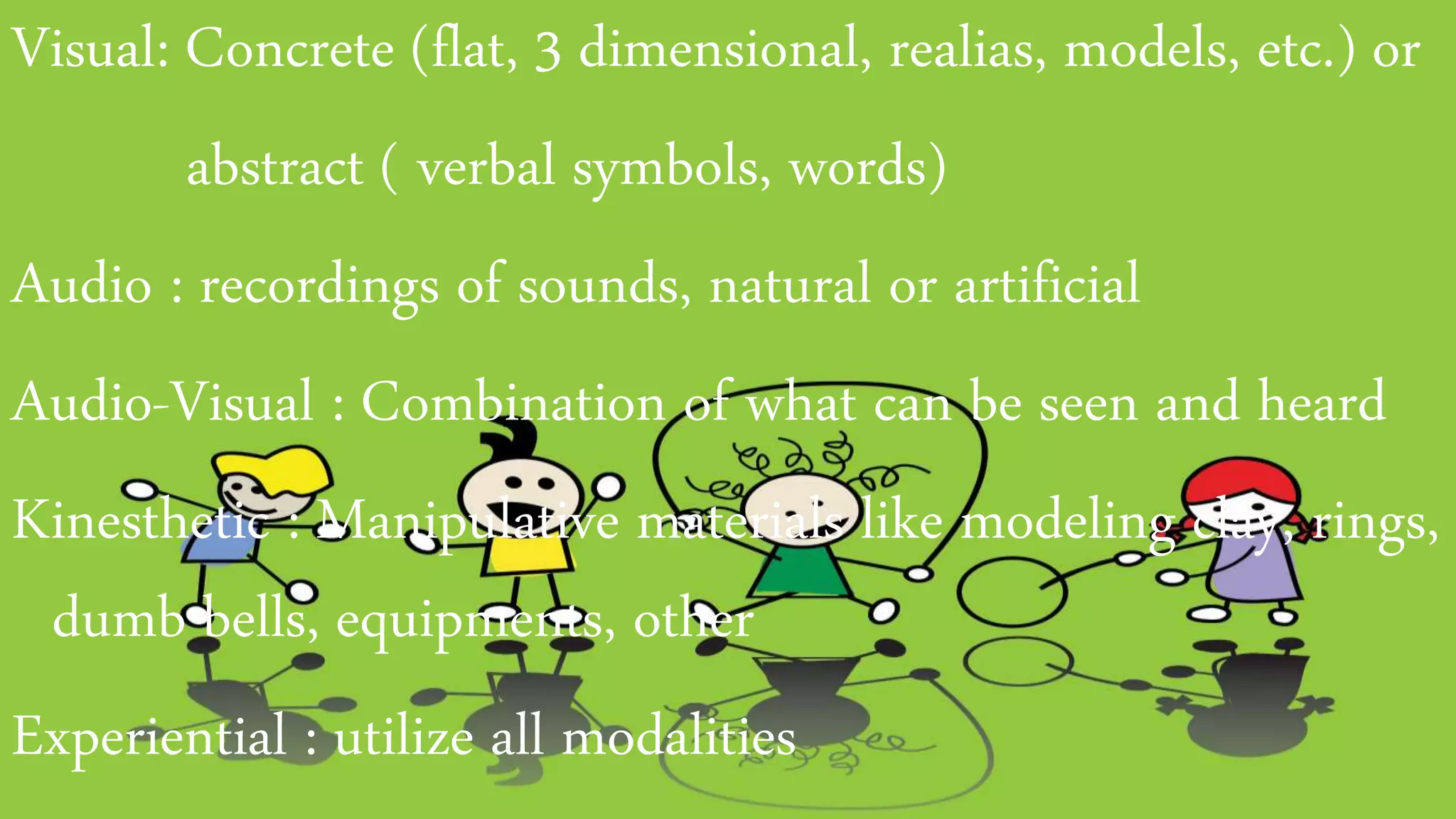
The document discusses guidelines for developing lesson plans for teachers. It states that teachers with less than 2 years of experience must prepare detailed daily lesson plans, while more experienced teachers can prepare less detailed daily lesson logs. It then outlines the main components that should be included in a lesson plan: objectives, subject matter, procedures, assessment, and assignment. The document also discusses Bloom's taxonomy and revised Bloom's taxonomy, providing examples of learning objectives for each level of thinking. It provides tips for teaching students with different learning styles like visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners. Finally, it discusses guidelines for selecting appropriate instructional materials based on the cone of learning theory.