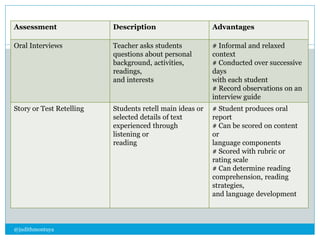
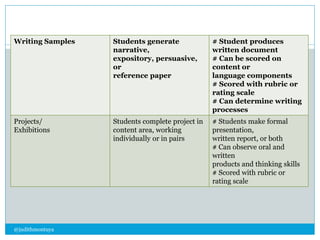
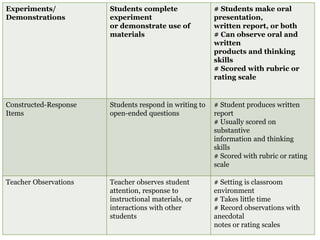
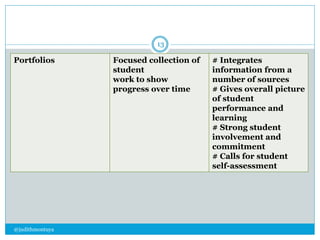
The document discusses different types of assessments including formative assessment, which is used to identify if students have achieved the lesson objective and determine gaps. Examples of formative assessments include questioning students and collecting assignments. Summative assessment provides grades based on performance over a period of time, such as final exams. Performance assessment evaluates what students can do in real-world scenarios through demonstrations and projects.