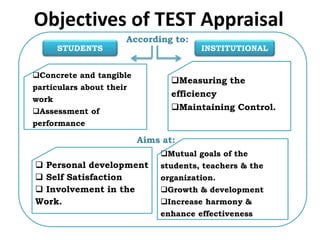
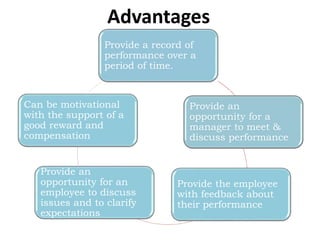
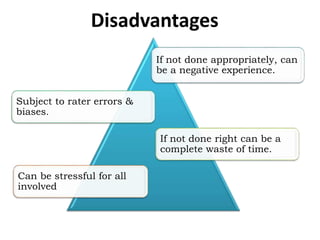
The document discusses test appraisal systems and item analysis. It defines test appraisal as the process used by educational institutions to evaluate how effectively they have conducted and evaluated students. Item analysis is a statistical technique used to select and reject test items based on their difficulty and ability to discriminate between stronger and weaker students. Item analysis provides benefits such as improving test construction, identifying weaknesses, and enhancing teaching methods.