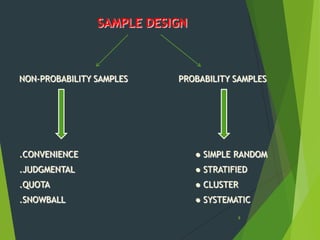
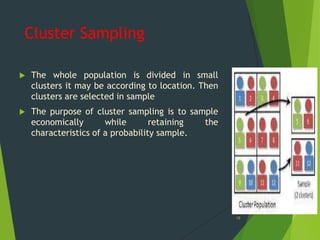
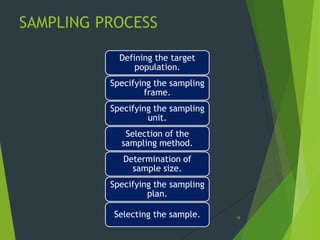
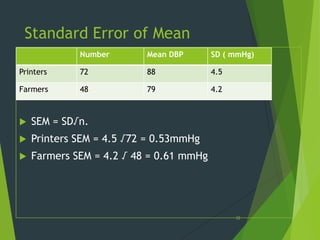
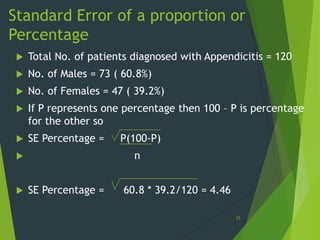
This document provides an overview of key concepts in sampling and statistics. It defines population as the entire set of items from which a sample can be drawn. It discusses different types of sampling methods including probability sampling (simple random, stratified, cluster, systematic) and non-probability sampling (convenience, judgmental, quota, snowball). It also defines key terms like bias, precision, randomization. The document discusses the sampling process and compares advantages and disadvantages of sampling. It provides examples of calculating standard error of mean and proportion. Finally, it distinguishes between standard deviation and standard error.