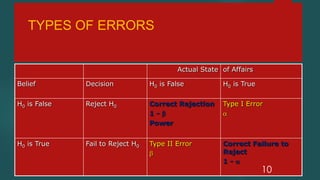
This document discusses hypothesis testing and p-values. It begins by defining a hypothesis as a proposition or prediction about the outcome of an experiment. Hypotheses are formulated and tested through science to evaluate their credibility. There are two main types of hypotheses: the null hypothesis, which corresponds to a default or general position, and the alternative hypothesis, which asserts a rival relationship. Hypothesis testing uses sample data to evaluate whether differences observed could be due to chance (the null hypothesis) or are real effects (the alternative hypothesis). Key concepts discussed include type 1 and type 2 errors, significance levels, one-sided and two-sided tests, and the relationship between p-values, confidence intervals, and the strength of evidence against