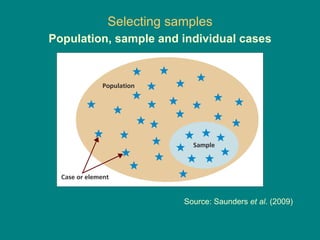
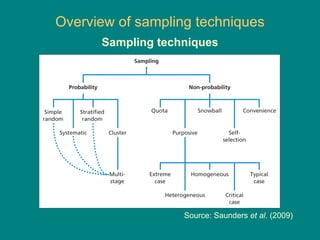
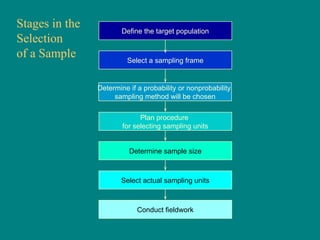
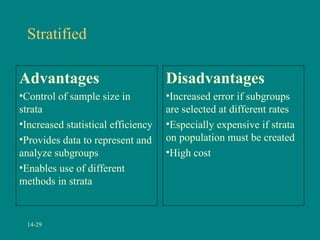
This document discusses research methodology and sampling techniques. It defines key terms like population, sample, census, and probability and non-probability sampling. It describes different sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and their advantages and disadvantages. Finally, it discusses issues around internet sampling and methods like using web site visitors, panels, and opt-in lists.