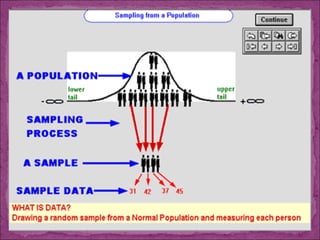
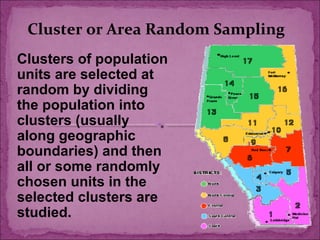
This document discusses sampling methods used in research. It defines sampling as obtaining information from a subset of a larger population. The key sections cover the sampling process, types of sampling including probability and non-probability methods, sources of sampling error, and factors to consider when determining sample size such as the nature of the population, number of variables, desired accuracy level, and available finances. Probability methods like simple random and stratified sampling aim to give all population members an equal chance of selection, while non-probability techniques like convenience and snowball sampling do not. Sample size is an important factor in controlling random error.