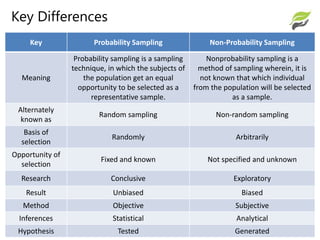
This document summarizes probability and non-probability sampling methods. Probability sampling assigns all population members an equal chance of selection, allowing for random selection techniques like simple random sampling. Non-probability sampling does not give all members an equal chance, relying instead on subjective judgment in techniques like convenience sampling. The key differences are that probability sampling is random, unbiased, and allows for statistical inferences, while non-probability sampling is non-random, potentially biased, and only permits analytical conclusions.