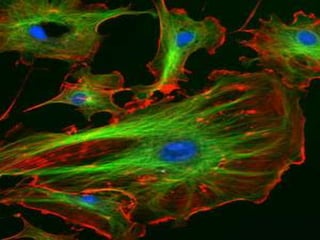
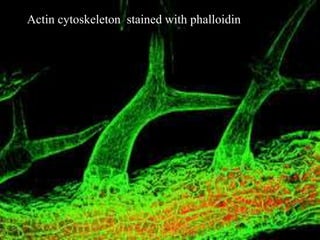
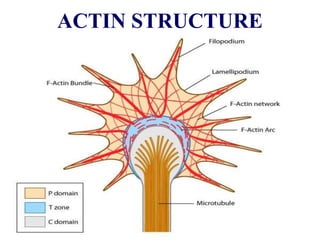
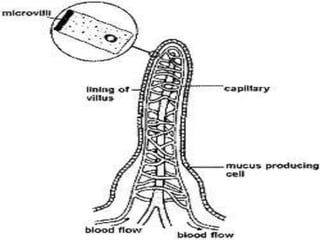
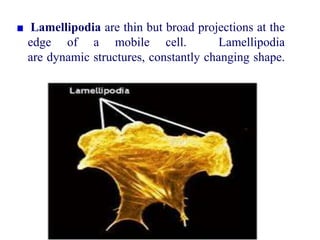
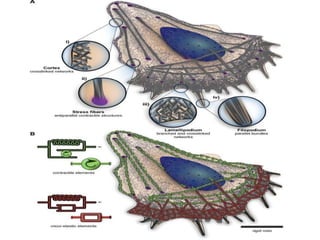
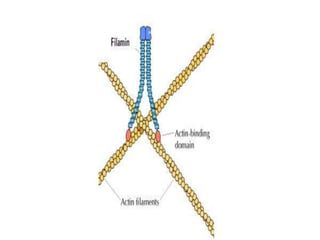
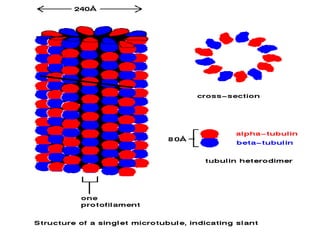
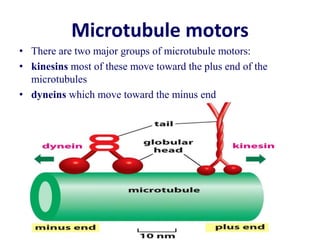
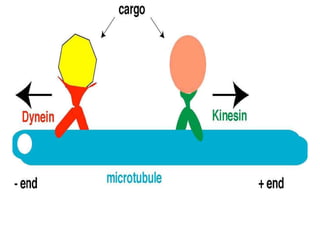
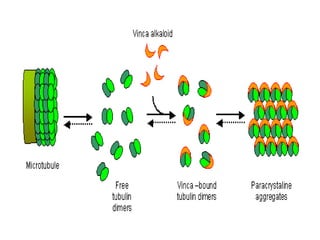
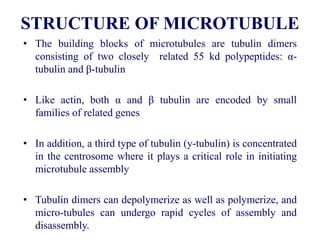
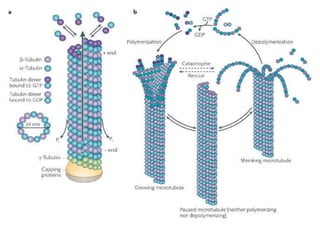
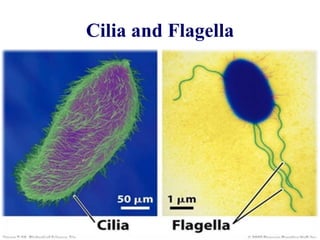
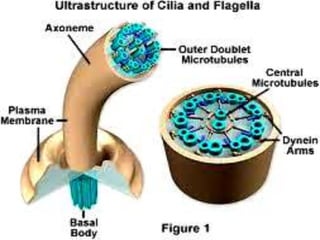
The cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments that extends throughout the cytoplasm. It provides structure and organization to the cell, determining shape and positioning organelles. The three main types of filaments are actin filaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Actin filaments are the thinnest filaments and form structures like filopodia, lamellipodia, and stress fibers. Microtubules are hollow cylinders composed of tubulin dimers and originate from the centrosome. They are involved in processes like cell division, organelle transport, and motility. Cilia and flagella project from the cell surface and use microtubule motors for movement.